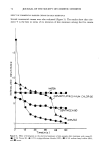
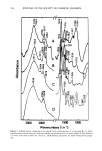
INTERACTIONS OF COSMETIC PIGMENTS WITH PRESERVATIVES 95 Table VIII Effect of the Replacement of Phenolic Hydrogen of MP, With Na and K Ions on Its Bactericidal Activity Phenolic Viable cell count hydrogen after 5-hr incubation MP Exist Below 10 3 MP, treated with Amberlyst-XN Na form Disappear 1.02 X 108 K form Disappear 1.49 X 108 Solutions of MP, untreated or treated with Amberlyst-XN, were inoculated with S. aureus, shaken, and incubated at 37øC for 5 hr. Aliquots were then decimally diluted with a 1% sterile solution of polysorbate 80. The number of surviving bacteria was determined by the viable cell count method. left column shows the metal ion concentrations found in the test tube where only MP was added. The central column shows data for the test tube in which only ultramarine blue was added. The right column shows data for the test tube where MP and ultra- marine blue were incubated together. It was found that the concentration of Na, Mg, and Fe ions increased unexpectedly when ultramarine blue was added to MP solution. It is possible that the MP might help dissolve these metal ions from ultramarine blue. REPLACEMENT OF PHENOLIC HYDROGEN OF MP AND BP WITH SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IONS When MP was eluted through Amberlyst XN-1004, the phenolic hydrogen of MP was replaced easily by Na or K ions, and its bactericidal activity drastically reduced (Table VIII). In the case of BP, however, exchange of its phenolic hydrogen did not occur, even though it was treated in the same way with the Amberlyste resin (Table IX). EFFECT OF EDTA ON THE BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF MP Figure 11 shows the effect of EDTA on the bactericidal activity of MP in the presence of ultramarine blue. When 0.01% EDTA 3Na was added to the incubation mixture, it reduced the ID. These results suggest that the mechanism of preservative inactivation Table IX Effect of the Replacement of Phenolic Hydrogen of BP With Na and K Ions on Its Bactericidal Activity Phenolic Viable cell count hydrogen after 5-hr incubation BP Exist Below 10 3 BP, treated with Amberlyst-XN Na form Exist Below 10 3 K form Exist Below 10 3 Inoculum size: 2.54 X 108. Solutions of BP, treated or untreated with Amberlyst-XN, were inoculated with S. aureus, shaken, and incubated at 37øC for 5 hr. Aliquots were then decimally diluted with a 1% sterile solution ofpolysorbate 80. The number of surviving bacteria was determined by the viable cell count method.
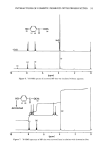
96 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 10 0 - o o i i I 10 '• 10 -1 1 EDTA.3Na (%) Figure 11. Effect of EDTA ß 3Na on the bactericidal activity of MP in the presence of ultramarine blue. EDTA ß 3Na was added to the incubation mixture, and this mixture was incubated at 37øC for 5 hr. Number of surviving bacteria was determined by the plate count method. by pigment involves replacement of phenolic hydrogen of MP by some metals from the coexistent pigment. THE MECHANISM OF PRESERVATIVE INACTIVATION BY PIGMENT The proposed mechanism of paraben inactivation by pigment follows. When ultra- marine blue is added to MP solution, the pH becomes alkaline, reaching pH 7.3. In the case of a powdered dispersion, it is assumed that there is the possibility of a difference between the pH of the solution and that of the powder surface. If this assumption is
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)