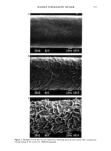
136 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS MATERIALS AND METHODS TEST ANIMALS Male New Zealand albino rabbits weighing approximately 2.0 to 3.5 kg were obtained from Clerco Research Farms. The animals were allowed to acclimate a minimum of four days prior to use. The animals were identified by the use of cage cards and colored head markings. No ear tags and/or ear tatoos were used. Animals were individually housed in suspended wire mesh cages. Room climate was controlled at approximately 22øC, rela- tive humidity at 50-70%, and light/dark cycles of 12 hours each were maintained throughout the course of the study. A diet of Purina Laboratory Chow and tap water was available ad libitum. CHEMICALS Quaternium-15 (Dow Chemical, Midland, MI Lot WP8611196658) and DMDM hy- dantoin (Glyco, Inc., Greenwich, CT Lot 730360) were both diluted to make 0.2% and 0.5% solutions using deionized water as a diluent. These concentrations represent the normal use levels for these preservatives in cosmetic formulations (9). Acetulan (Amerchol, Edison, NJ lot 836), used undiluted, served as a positive control. TEST PROTOCOL In this assay 0.2 ml of the appropriate solution was applied to each animal in a group of six rabbits. The material was administered evenly using a 1.0-cc syringe and inuncted with a gloved fingertip to the inner surface of the basal portion of the right ear of each test animal. Applications were made five days a week for two weeks in three of the six animals and five days a week for four weeks in the three remaining animals. As a positive control, the internal base of the left ear of one half of the animals was treated with 0.2 ml of Acetulan. The internal base of the left ear of the remaining animals served as an untreated control and was sham-treated. Both the test and control ears were evaluated grossly for evidence of comedone forma- tion on the fifth, tenth, fifteenth (if applicable), and twentieth (if applicable) day fol- lowing the initial dosing, and on the day of sacrifice. The scoring scale used was as follows: 0 = none 1 = trace (few comedones) 2 = mild (several comedones) 3 = moderate (extensive comedone formation) 4 = severe (confluent involvement of large comedones) At the conclusion of the treatment period, the animals were euthanized via cardiac puncture using T-61 euthanasia solution. Following termination, both ears were re- moved, appropriately labeled, and then refrigerated overnight. The next day a rectan- gular sample measuring 2.5 cm X 1.0 cm was removed at the base of the pinna just exterior to the ear canal from both the test and control ears. The tissue was immersed in water at 60øC for two minutes. The epidermis was then peeled off as an intact sheet and carefully mounted on a glass slide so that the inner surface faced upward. Each slide was
THE COMEDOGENIC POTENTIAL OF PRESERVATIVES 137 allowed to air dry thoroughly and was then examined microscopically using a stereomi- croscope. Both the test and control ears were examined for evidence of follicular hyper- keratinization using the above-described scale. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Observations of any changes which occurred during the "in-life" phase of these studies were compared using a statistical procedure referred to as the "sign test." The tested hypothesis in each case was that the treatment and the control were equally effective at eliciting a comedogenic response. Comparisons were made between each of the four treatments (preservatives) and each of the two (positive and negative) controls. Data describing comedo scores as determined by microscopic examination of processed tissue were compared using analysis of variance (ANOVA). RESULTS Data describing clinical (in-life) comedo scores after application of different treatment regimens are presented in Table I. Neither of the two dose levels of either quaternium- 15 nor DMDM hydantoin caused a significant increase in the number of comedones observed clinically during the 29-day observation period when compared with the sham treatment. Significantly elevated comedo counts were observed only in the ears of an- imals treated with Acetulan (positive control) Acetulan treatment yielded a positive comedogenic response at all observation points. Data describing comedo scores as determined by microscopic examination of processed tissue are presented in Table II. Neither of the two dose levels of either quaternium- 15 Table I In-Life Comedo Scores in Rabbits* Test Test Test Test Test Test Test material** day 5 day 12 day 15 day 19 day 26 day 29 Quaternium- 15, o. 2 % Quaternium- 15, o. 5 % DMDM hydantoin, 0.2% DMDM hydantoin, 0.5% Acetulan, 100%*** Sham treatment 0.8 0.8 1.0 0.7 0.7 1.0 ñ 0.2 + 0.2 + 0.0 + 0.3 ñ 0.3 + 0.0 0.8 1.0 0.3 0.3 0.0 0.0 ñ 0.2 + 0.0 ñ 0.3 + 0.3 ñ 0.0 + 0.0 0.7 0.5 0.7 1.0 1.0 1.0 ñ 0.2 + 0.2 --- 0.3 + 0.0 --- 0.0 --- 0.0 0.5 0.7 0.3 0.6 1.0 0.6 ñ 0.2 + 0.3 ñ 0.3 + 0.3 ñ 0.0 + 0.3 2.6 2.9 2.5 3.0 3.0 2.5 + 0.1 + 0.1 ñ 0.2 --+ 0.0 ñ 0.0 + 0.3 0.1 0.5 0.3 1.0 0.8 0.8 ñ 0.1 + 0.2 ñ 0.2 + 0.0 ñ 0.2 + 0.2 * Values represent the mean ñ standard error of the mean for sample sizes of 3 to 12 animals. ** Solutions prepared as w/v dilutions in distilled water. *** This treatment is significantly different from the sham treatment at p 0.01.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)