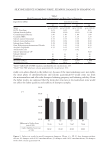
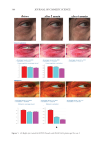
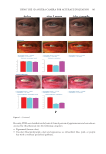
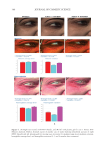
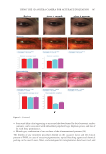
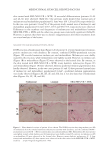
347 Silicone Reduce Combing Force, Flyaway, Damage in Shampoo METHODS ***Tests conducted by Beauty Hi-tech Innovation Co., Ltd. HAIR SOURCE All the hair swatches used in this paper are Asian hair swatches. The damaged flat hair swatches used in the experiments by Beauty Hi-tech Innovation Co., Ltd. were prepared as follows: 1) the Asian undamaged hair swatches (purchased from Beaulax Co., Ltd.) were soaked in 1% Sodium Laureth Sulfate (SLES) solution for one night, then washed and dried 2) the hair swatches were immersed in 1:1 mixture of 6% hydrogen peroxide solution and 2% ammonia solution for 30 minutes 3) after washing, the hair swatches were soaked in a buffer solution of pH 3.0 and then rinsed and 4) steps two and three were repeated three times, then dried. The hair swatch size was 21 cm in length, 5.5 cm in width, and 16.0 g in weight. The damaged ponytail hair swatches used for hair breakage test and hair tensile strength test were purchased from Beaulax Co., Ltd the hair swatch size was 30 cm in length and 10 g in weight. The damaged ponytail hair swatches used for flyaway control test were purchased from Staffs Co., Ltd the hair swatch size was 20 cm in length and 3.0 g in weight. Natural and damaged ponytail hair swatches used for deposition test and digital microscope observations were purchased from Shanghai Canyu Industrial Co., Ltd. The hair swatch size was 27 cm in length and 1.0 g in weight. SHAMPOO BASIC PROPERTY MEASUREMENT*** Viscosity was measured using a Brookfield RVDV-II+P viscometer (Brookfield Engineering Laboratories, Inc., Middleboro, MA, USA) at room temperature (spindle No. 6, 20 rpm, 30-second conditions). Shampoo transmittance was measured directly using an Optima SP-300 Spectrophotometer (Optima, Inc., Tokyo, Japan) at 600 nm. Shampoo lather test was done according to the blender foam volume drainage method (9) by adding 1.0 g of artificial sebum (lanolin) to the 5.0 g of shampoo while diluting to 50 g with water 7 g of this mixture was added to 143 g of water and mixed at high speed. Then the foam was added to a 1 L graduated cylinder. The instant foam volume was recorded. The foam was allowed to settle for 3.5 minutes, and the volume was again recorded. The test was repeated three times for each shampoo. The calculation was made as follows: Figure 1. Molecular structure of amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18 used in the study: a) amodimethicone b) silicone quaternium-18.
348 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Amount of Lather Score (out of 100)=instant foam volume (ml) /400 (ml) x 100 (400 ml is an internal foam volume with set lather score of 100 points) Lather Stability Score (out of 100)=100 (ml) height of liquid below foam (ml) x 100 (100 ml is an internal height of liquid below foam with set foam stability of 100 points). Sebum cleansing test was carried out by applying 1.0 g of artificial sebum**** to the dried, undamaged Asian flat hair swatches (16 g, purchased from Beaulax Co., Ltd.). The hair swatches were mounted to a Dynamic Combing Tester SK-7A (Techno Hashimoto, Nara City, Japan), 1.0 g of shampoo was applied evenly to the hair swatches, and the swatches were combed by wet brush five times. Then the hair swatches were rinsed and combed five times under a warm-water shower. The shower was stopped, and the hair swatches were combed three times. Finally, the hair swatches were allowed to dry naturally overnight and placed in an 80°C incubator for 1 hour for further drying. Three hair swatches were tested for each shampoo sample. The cleaning rate was calculated by the following formulas: sebum cleansing rate percent=(weight of sebum rinsed off (g) /weight of sebum applied [g]) x 100 weight of sebum applied (g)=weight of hair swatch after sebum applied (g)− weight of hair swatch before applying sebum (g) weight of sebum rinsed off (g)=weight of sebum applied (g)−(weight of hair bundle after drying [g]−weight of hair bundle before applying sebum [g]). ****artificial sebum composition (10): wild soybean oil 48%, oleic acid 13%, myristic acid 12%, squalene 12%, paraffin 10%, glyceryl oleate 3%, cholesteryl stearate 2% HAIR DYNAMIC COMBING TEST AND HAIR FLYAWAY CONTROL TEST*** Dynamic combing test was performed using the dynamic combing tester SK-7A (Techno Hashimoto) on Asian damaged flat hair swatches. It was conducted as follows (11): The hair swatches were wet by warm-water shower, and 1.5 g of shampoo was applied evenly on both sides of hair swatches. The hair swatches were combed five times without shower, and the combing force during lathering was recorded. The hair swatches were combed 10 times while rinsing in the shower the first 5 combing-force data were recorded during Rinse 1, and the second 5 combing-force data were recorded during Rinse 2. Then the hair swatches were combed five times and the combing-force data were recorded as After Rinse. The hair swatches were dried overnight, and the dry hair swatches were combed without shower four times the combing-force data were recorded as Dried. We separated the rinse stage to Rinse 1 and Rinse 2 to observe the different combing-force data during different rinsing stages and to probe the performance of shampoos with amodimethicone and silicone polyquaternium-18, as compared to nonsilicone. Three hair swatches were tested for each shampoo sample. Hair flyaway control test was conducted as follows: 1) 3 g, 20 cm ponytail damaged hair swatches were rinsed with 40°C water for 10 seconds, towel dried and combed through, then dried at 25°C and 30% relative humidity (RH) for 18 hours 2) photos were taken in a photographing box 3) hair swatches were wetted with 40°C water, then a 0.2 g testing sample was applied, washed, and rinsed with 40°C water, towel dried and combed through, then dried under 25°C at 30% RH for 18 hours 4) photos were taken in a photographing box and 5) the flyaway and total volume were calculated by the area
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)