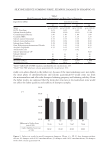
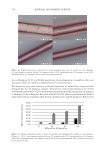
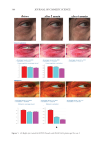
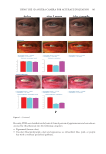
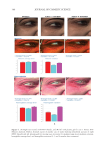
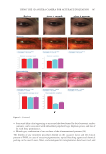
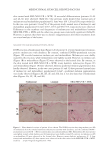
357 Silicone Reduce Combing Force, Flyaway, Damage in Shampoo The hair breakage and hair tensile test results indicated that treating the damaged hair with amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18 added to shampoos helped improve the strength of damaged hair, indicating damaged-hair repairing effects of the silicone. DIGITAL MICROSCOPE OBSERVATION AND SILICONE DEPOSTION TEST RESULTS Figure 10 shows the digital microscope observation image of Asian damaged hair samples after washing 28 times with each shampoo sample. We have hypothesized that the deposition of amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18 could improve the hair surface smoothness the microscopy image demonstrated this. From the image, we observed that in hair washed with the base shampoo sample (S1) the hair cuticles are not coated, some parts of the hair cuticles are removed, and the hair surface looks very rough, not shiny. For hair samples washed with S2 (0.21% amodimethicone), S3 (0.42% amodimethicone), and S4 (0.18% silicone quaternium-18), we can observe that the cuticle is uniformly coated, and the hair surface appears very smooth and has a natural shine. This confirmed that amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18 can form a thin film on the hair surface, and this thin silicone film on the hair surface improved the hydrophobicity of damaged hair and thus shows the damaged hair-repair effect of amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18. In addition, the thin film of silicone coated on the hair surface improved the smoothness of the hair surface, resulting in the wet and dry combing force reduction. This thin silicone film is also related to the improvement of hair tensile strength and hair breakage rate. Figure 11 shows the silicone deposition test results of Asian natural hair and damaged hair washed by each shampoo once. All the deposition data were extracted from the baseline that was deposition data of hair swatches cleansed by 10% SLES solution. We observed a small quantity of silicone deposition on damaged hair for S1, the base shampoo without silicone we assumed that it was error inherited from the difference of the hair swatch itself. 0.000 0.200 0.400 0.600 0.800 1.000 1.200 1.400 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Time (s) S1 S2 S4 Figure 9. Tensile strength test results on Asian damaged hair. S1: base shampoo without silicone S2: shampoo with 0.21% amodimethicone S4: shampoo with 0.18% silicone quaternium-18. Load (N)
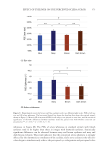
358 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE As our shampoos S2, S3, and S4 had much more silicone deposition, it would not affect our discussion. There was almost no deposition for S1 on natural hair. We observed a very small quantity of silicone deposition for natural hair compared with damaged hair for all shampoo samples. Natural hair treated with shampoos S2 (0.21% amodimethicone) and S3 (0.42% amodimethicone) showed more silicone deposition compared to shampoo S1 (base shampoo) hair treated with S4 (0.18% silicone quaternium-18) showed much more silicone deposition than S1 (base shampoo), S2, and S3 shampoos. Between S2 S1 S2 S3 S4 Figure 10. Digital microscope observation of Asian damaged hair after 28 washes by each shampoo. S1: base shampoo without silicone S2: shampoo with 0.21% amodimethicone S3: shampoo with 0.42% amodimethicone S4: shampoo with 0.18% silicone quaternium-18. 0.00 100.00 200.00 300.00 400.00 500.00 600.00 700.00 S1 S2 S3 S4 Natural hair Damaged hair Figure 11. Silicone deposition results on Asian natural hair and damaged hair washed by each shampoo. Means +/− SD. S1: base shampoo without silicone S2: shampoo with 0.21% amodimethicone S3: shampoo with 0.42% amodimethicone S4: shampoo with 0.18% silicone quaternium-18. The baseline was extracted for all deposition data. Silicone Deposition (μg/g ha)ir
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)