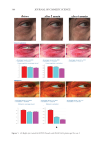
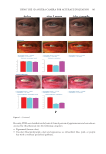
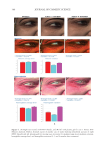
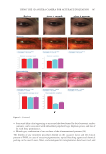
416 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE for main skin-delivery approaches. The development of nanocarriers for effective skin delivery of curcumin is an emerging field with a huge potential. Hence, future research in curcumin cosmetics should be more focused on advanced extraction methods with higher yields investigating more effective delivery methods by integrating with fields such as nanotechnology improving the chemical stability of curcumin under real-time process conditions and developing cosmetic formulations with enhanced delivery efficiency for skin antiaging while understanding the biochemistry of curcumin-based skin antiaging effects at a molecular level. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors state no conflicts of interest. REFERENCES (1) D. J. Tobin, Introduction to skin aging, J. Tissue Viability 26(1), 37–46 (2017). (2) A. R. Young, Acute effects of UVR on human eyes and skin, Prog. Biophys. Mol. 92(1), 80–85 (2006). (3) M. Yaar and B. A. Gilchrest, Photoageing: mechanism, prevention and therapy, Br. J. Dermatol. 157(5), 874–887 (2007). (4) D. A. Gunn, H. Rexbye, C. E. M. Griffiths, P. G. Murray, A. Fereday, S. D. Catt, Why wome women look Yyoung for their age, PLoS One. 4(12), e8021 (2009). (5) D. J. Tobin, Biochemistry of human skin—our brain on the outside, Chem. Soc. Rev. 35(1), 52–67 (2006). (6) R. Ghadially, B. E. Brown, S. M. Sequeira-Martin, K. R. Feingold, and P. M. Elias, The aged epidermal permeability barrier: Structural, functional, and lipid biochemical abnormalities in humans and a senescent murine model, J. Clin. Investig. 95(5), 2281–2290 (1995). (7) J. J. Nordlund, The lves of pigment cells, Dermatol. Clin. 4(3), 407–418 (1986). (8) G. L. Grove, Physiologic changes in older skin, Clin. Geriatr. Med. 5(1), 115–125 (1989). (9) G. J. Fisher, S. Kang, J. Varani, Z. Bata-Csorgo, Y. Wan, S. Datta, Mechanisms of photoaging and ahronological skin aging, Arch. Dermatol. 138(11), 1462–1470 (2002). (10) M. A. Farage, K. W. Miller, P. Elsner, and H. I. Maibach, Structural characteristics of the aging skin: A review, Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 26(4), 343–357 (2007). (11) J. L. Contet-Audonneau, C. Jeanmaire, and G. Pauly, A histological study of human wrinkle structures: Comparison between sun-exposed areas of the face, with or without wrinkles, and sun-protected areas, Br. J. Dermatol. 140(6), 1038–1047 (1999). (12) J. Uitto, Connective tissue biochemistry of the aging dermis: Age-related alterations in collagen and elastin, Dermatol. Clin. 4(3), 433–446 (1986). (13) R. Tundis, M. R. Loizzo, M. Bonesi, and F. Menichini, Potential role of natural compounds against skin aging, Curr. Med. Chem. 22(12), 1515–1538 (2015). (14) A. C. Weihermann, M. Lorencini, C. A. Brohem, and C. M. de Carvalho, Elastin structure and its involvement in skin photoageing, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 39(3), 241–247 (2017). (15) R. Stern and M. J. Jedrzejas, Hyaluronidases: Their genomics, structures, and mechanisms of action, Chem. Rev. 106(3), 818–839 (2006). (16) S. M. Pilkington, S. Bulfone-Paus, C. E. M. Griffiths, and R. E. B. Watson, Inflammaging and the skin, J. Invest. Dermatol. 141(4s), 1087–1095 (2021). (17) K. Obayashi, K. Kurihara, Y. Okano, H. Masaki, and D. B. Yarosh, L-Ergothioneine scavenges superoxide and singlet oxygen and suppresses TNF-α and MMP-1 expression in UV-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 27(3), 191–192 (2005).
417 Curcumin Against Skin Aging (18) S. Silva, M. Ferreira, A. S. Oliveira, C. Magalhães, M. E. Sousa, M. Pinto, Evolution of the use of antioxidants in anti-ageing cosmetics, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 41(4), 378–386 (2019). (19) D. Rossetti, M. G. Kielmanowicz, S. Vigodman, Y. P. Hu, N. Chen, A. Nkengne, A novel anti-ageing mechanism for retinol: Induction of dermal elastin synthesis and elastin fibre formation, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 33(1), 62–9 (2011). (20) K. K. Lee, J. J. Cho, E. J. Park, and J. D. Choi, Anti-elastase and anti-hyaluronidase of phenolic substance from Areca catechu as a new anti-ageing agent, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 23(6), 341–346 (2001). (21) D. Min, S. Park, H. Kim, S. H. Lee, Y. Ahn, W. Jung, Potential anti-ageing effect of chondroitin sulphate through skin regeneration, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 42(5), 520–527 (2020). (22) K. Indira Priyadarsini, Chemical and structural features influencing the biological activity of curcumin, Curr. Pharm. Des. 19(11), 2093–2100 (2013). (23) K. I. Priyadarsini, Free radical reactions of curcumin in membrane models, Free Radic. Biol. Med. 23(6), 838–843 (1997). (24) A. Jitoe-Masuda, A. Fujimoto, and T. Masuda, Curcumin: From chemistry to chemistry-based functions, Curr. Pharm. Des. 19(11), 2084–2092 (2013). (25) A. Naseema, L. Kovooru, A. K. Behera, K. P. P. Kumar, and P. Srivastava, A critical review of synthesis procedures, applications and future potential of nanoemulsions, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 287, 102318 (2021). (26) K. I. Priyadarsini, The chemistry of curcumin: From extraction to therapeutic agent, Molecules. 19(12), 20091–20112 (2014). (27) S. C. Gupta, G. Kismali, and B. B. Aggarwal, Curcumin, a component of turmeric: From farm to pharmacy, BioFactors. 39(1), 2–13 (2013). (28) T. Jiang, R. Ghosh, and C. Charcosset, Extraction, purification and applications of curcumin from plant materials—A comprehensive review, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 112, 419–430 (2021). (29) Z. Rafiee, M. Nejatian, M. Daeihamed, and S. M. Jafari, Application of different nanocarriers for encapsulation of curcumin, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 59(21), 3468–3497 (2019). (30) Z. Rafiee, M. Nejatian, M. Daeihamed, and S. M. Jafari, Application of curcumin-loaded nanocarriers for food, drug and cosmetic purposes, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 88, 445–458 (2019). (31) A. Bokov, A. Chaudhuri, and A. Richardson, The role of oxidative damage and stress in aging, Mech. Ageing Dev. 125(10–11), 811–826 (2004). (32)Y .Panahi, O. Fazlolahzadeh, S. L. Atkin, M. Majeed, A. E. Butler, T. P. Johnston, Evidence of curcumin and curcumin analogue effects in skin diseases: A narrative review, J. Cell. Physiol. 234(2), 1165–1178 (2019). (33) F. Shahidi and P. Ambigaipalan, Phenolics and polyphenolics in foods, beverages and spices: Antioxidant activity and health effects—A review, J. Funct. Foods. 18, 820–897 (2015). (34) K. Bala, B. C. Tripathy, and D. Sharma, Neuroprotective and anti-ageing effects of curcumin in aged rat brain regions, Biogerontology 7(2), 81–89 (2006). (35) A. Zia, T. Farkhondeh, A. M. Pourbagher-Shahri, and S. Samarghandian, The role of curcumin in aging and senescence: Molecular mechanisms, Biomed. Pharmacother. 134, 111119 (2021). (36) B. Kocaadam and N. Sanlier, Curcumin, an active component of turmeric (curcuma longa), and its effects on health, Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 57(13), 2889–2895 (2017). (37) R. L. Thangapazham, S. Sharad, and R. K. Maheshwari, Skin regenerative potentials of curcumin, Biofactors 39(1), 141–149 (2013). (38) K. Jakubczyk, A. Druzga, J. Katarzyna, and K. Skonieczna-Zydecka, Antioxidant potential of curcumin—A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials, Antioxidants 9(11) (2020). (39) A. R. Vaughn, A. Branum, and R. K. Sivamani, Effects of turmeric (curcuma longa) on skin health: A systematic review of the clinical evidence, Phytother. Res. 30(8), 1243–1264 (2016). (40) T. Ak and I. Gulcin, Antioxidant and radical scavenging properties of curcumin, Chem. Biol. Interact. 174(1), 27–37 (2008).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)