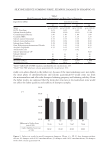
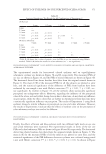
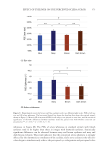
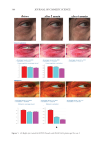
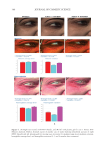
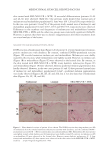
397 MESENCHYMAL STEM CELL-DERIVED FACTORS skin treated with MEL/NB-UVB +MTK, 10 successful differentiations (patients 41–44 and 46–51) were observed (Table IC). Our previous study showed that normal sizes of melanocyte and melanoblast populations/0.1 mm2 were 100–120 and 100, respectively (11). In the two cases (patients 44 and 51) of the present study, normal sizes of melanocyte and melanoblast populations/0.1 mm2 (105.7, 107.6 and 98.9, 97.5, respectively) were observed. Differences in the numbers and frequencies of melanocytes and melanoblasts between MEL/NB-UVB +MTK and the other two groups were statistically significant (Table II). However, it appears that there was no distinct repigmentation after these treatments from our visual analysis of the lesions. MELANOCYTE AND MELANOBLAST POPULATIONS DOPA reaction of nonlesional skin (Figure 1A) of patient 41 revealed numerous tyrosinase- positive melanocytes with dendrites. By contrast, combined DOPA–premelanin reaction (Figure 1D) revealed numerous melanocytes and melanoblasts. Melanocytes were darkly stained by this reaction, while melanoblasts were lightly stained. However, no melanocytes (Figure 1B) or melanoblasts (Figure 1E) were observed in the lesional skin. By contrast, in the skin treated with MEL/NB-UVB +MTK, many dendritic melanocytes (Figure 1C) and melanoblasts (Figure 1F) were observed, whereas epidermal melanin pigmentation was hardly observed. However, in the two cases (patients 44 and 51) that possessed normal sizes of melanocyte and melanoblast populations/0.1 mm2, epidermal melanin pigmentation was clearly observed (Figures 2B, 2D, 2F, and 2H), but it was less than that of nonlesional skin (Figures 2A, 2C, 2E, and 2G). Figure 1. Histochemical sections of patient 41 are shown. The DOPA reaction detecting melanocytes (M) of nonlesional skin (A) revealed numerous melanocytes (arrows) with dendrites, and the combined DOPA– premelanin reaction (D, M +Mb) revealed melanocytes and melanoblasts (Mb). Melanoblasts (D, short arrows) were lightly stained, while melanocytes (D, long arrows) were darkly stained. By contrast, no melanocytes (B) or melanoblasts (E) were observed in the lesional skin. However, many dendritic melanocytes (C, F, long arrows) and melanoblasts (F, short arrows) were observed in the skin treated with MEL/NB-UVB +MTK. Scale bar =25 µm. Original magnification ×400.
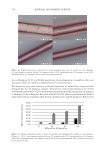
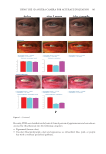
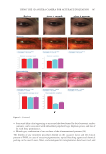
398 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Gender and age differences in the numbers and frequencies of melanocytes and melanoblasts in the skin treated with MEL/NB-UVB alone and MEL/NB-UVB +MTK are shown in Table III. No significant differences were observed between them. COLLAGEN AND ELASTIN FIBERS In the skin of patient 41, collagen fibers were well developed in nonlesional (Figure 3A), lesional (Figure 3B), MEL/NB-UVB-treated (Figure 3C), and (MEL/NB-UVB +MTK)-treated (Figure 3D) skin. No marked differences were observed in the distribution and density of collagen fibers. Figure 2. Histochemical sections of patients 44 (A, B, C, D) and 51 (E, F, G, H) are shown. The DOPA reaction detecting melanocytes (M) of nonlesional skin (A, E) revealed many melanocytes with dendrites (arrows). Although melanocytes were also present in (MEL/NB-UVB +MTK)–treated skin (B, F), epidermal melanin pigmentation was much less than that of nonlesional skin (A, E). The combined DOPA–premelanin reaction (C, D, G, H, M +Mb) revealed dark-stained melanocytes and lightly-stained melanoblasts (Mb). Melanoblasts (short arrows) were lightly stained, while melanocytes (long arrows) were darkly stained. Scale bar =25 µm. Original magnification ×400.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)