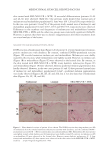
395 MESENCHYMAL STEM CELL-DERIVED FACTORS 1.5 mm in depth) were taken from each skin area using an electric micro drill (SIRIUS NT Micro at 90 g Gerlach SIRIUS NT Micro, Eduard Gerlach GmbH, Lübbecke, Germany) as reported previously (10). Three punch biopsies of nonlesional (area one) and lesional (area two) skin were fixed at the time of initiation, and those of the treated skin (areas three, four, and five) were fixed at the time of cessation. HISTOCHEMISTRY Skin samples were fixed with 16% neutral formalin in phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) for 16–24 hours at 2°C. The samples were then washed with distilled water and incubated with a 0.1% L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine solution in phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) for 16–24 hours at 37°C (1). The DOPA reaction reveals only tyrosinase-containing differentiated melanocytes. Serial sections 10 µm thick were deparaffinized and counterstained with eosin. For the combined DOPA–premelanin reaction (combined DOPA–ammoniacal silver nitrate staining), deparaffinized sections after the DOPA reaction were incubated in a 10% ammoniacal silver nitrate solution for 5 minutes at 58°C (1,10). Ammoniacal silver nitrate staining after the DOPA reaction was used for the light microscopic detection of melanoblasts with unmelanized stage I and II melanosomes in addition to differentiated melanocytes, since metallic silver particles were deposited on stages I, II, III, and IV melanosomes with a high degree of selectivity (1). The specimens were also counterstained with eosin. The number of melanocytes (cells positive to the DOPA reaction) and the number of melanoblasts plus melanocytes (cells positive to the combined DOPA–premelanin reaction) in the epidermis were counted through 10 consecutive sections (each individual datum was an average of 3 skin samples) and expressed per 0.1 mm2 of the interfollicular epidermis. The number of melanoblasts was calculated by subtracting the number of melanocytes from the combined number of melanoblasts and melanocytes. A “melanoblast” is defined here as an unpigmented cell that possesses no tyrosinase activity. For Azan staining (collagen staining), deparaffinized sections were first treated with Mallory’s azocarmine G for 7 minutes at room temperature. Then the specimens were treated with 5% phosphotungstic acid for 30 minutes at room temperature for the differentiation of azocarmine G. Next, they were stained with Mallory’s aniline blue orange G for 3 minutes at room temperature. They were dehydrated with a graded series of alcohols and made transparent by xylene and finally embedded with Canada balsam. For elastin staining, deparaffinized sections were first treated with HBs antigen oxidizing solution for 10 minutes at room temperature. Then the specimens were treated with 2% oxalic acid solution for 30 seconds. After treating the specimens with 95% ethanol for 2 minutes, they were treated with Victoria blue for 18–24 hours at room temperature. After treating with 70% ethanol to differentiate Victoria blue for 25 minutes, they were treated with nuclear fast red for 20 minutes at room temperature. They were dehydrated with graded series of alcohols and made transparent by xylene and finally embedded with Canada balsam (5). STATISTICS The statistical significance of the differences in the number of melanocytes and melanoblasts, in the number of sessions of MEL/NB-UVB, and in the total doses of MEL/NB-UVB
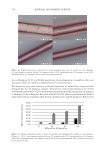
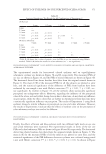
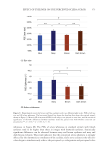
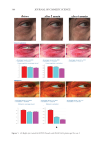
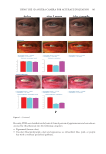
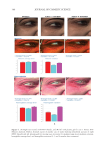
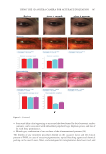
396 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE between each group was determined by Student’s t-test (two-tailed). Also, the statistical significance of differences in the percentages of restored skin with melanocytes/melanoblasts and of restored elastin fibers between each group was determined by the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. RESULTS INDUCTION OF MELANOCYTE/MELANOBLAST DIFFERENTIATION Total sessions of MEL/NB-UVB exposures reached 1 to 83 times, and their total doses ranged from 0.2 to 204.9 J/cm2 (Table I). Although the difference in the average number of sessions between MEL alone and MEL +MTK was statistically significant (Table II), those between MEL alone and MEL +MT as well as between NB-UVB alone and NB-UVB +MT/MTK were not statistically significant (Table II). The total doses of phototherapy among the three groups were also not statistically significant (Table II). In the lesional skin treated with MEL +NB-UVB, only one (patient 14) successful melanocyte/melanoblast differentiation was observed, but the numbers were very low (Table IA). In the skin treated with MEL/NB-UVB +MT, three successful differentiations (patients 22, 27, and 28) were observed (Table IB). However, their numbers and frequencies were not significant compared with MEL/NB-UVB alone (Table II). By contrast, in the Table II Effects of Treatment With MEL/NB-UVB Alone, MEL/NB-UVB +MT, and MEL/NB-UVB +MTK on Epidermal Melanocytes/Melanoblasts and Elastin Fibers in the Vitiliginous Skin MEL/NB-UVB alone MEL/ NB-UVB +MT MEL/ NB-UVB +MTK Patient (F:M) 17 (F6:M11) 17 (F8:M9) 17 (F9:M8) Age (Ave) 38.3 ± 5.6 38.3 ± 5.6 36.9 ± 5.5 MEL (No. of sess) 15.7 ± 3.3a (N =17) 8.5 ± 2.0 (N =13) 7.2 ± 2.3b (N =13) NB (No. of sess) 18.1 ± 6.1 (N =13) 11.3 ± 2.8 (N =12) 7.1 ± 1.1 (N =11) Dose (J/cm2) 28.3 ± 9.1 9.4 ± 3.0 16.5 ± 11.5 MT, MTK (Treated days) 0 48.3 ± 10.2 39.9 ± 10.1 M (Nonlesional) 102.3 ± 7.8 112.2 ± 8.1 109.9 ± 6.3 M (Lesional) 0 0 0 M (Treated) 0.1 ± 0.1c 1.8 ± 1.1d 25.9 ± 8.4e Mb (Nonlesional) 104.6 ± 2.5 100.8 ± 1.9 108.0 ± 2.5 Mb (Lesional) 0 0 0 Mb (Treated) 0.3 ± 0.3f 3.7 ± 2.5g 27.5 ± 8.2h M (Frequency) 5.9% (1/17)i 17.6% (3/17)j 58.8% (10/17)k Mb (Freqency) 5.9% (1/17)l 17.6% (3/17)m 58.8%(10/17)n Elastin (Treated) 0% (0/17)o 82.4% (14/17)p 100% (17/17)q The melanocyte and melanoblast populations/0.1 mm2 in the interfollicular epidermis in addition to the recovery of elastin fibers after the treatment with MEL/NB-UVB alone, MEL/NB-UVB +MT, and MEL/ NB-UVB +MTK are shown. MT, treatment with FFC, collagen peptide, and elastin peptide MTK, MT +UCB-MSCCS MEL NB, NB-UVB sess, sessions of MEL/NB-UVB M, melanocyte Mb, melanoblast F, female M, male Dose, total dose of UVB Ave, average. Statistically significant differences, j-k, m-n (P 0.05) a-b, c-e, d-e, f-h, g-h, i-k, l-n (P 0.01) o-p, o-q (P 0.001).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)