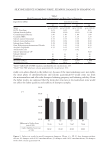
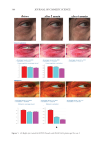
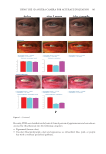
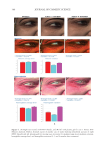
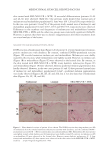
355 Silicone Reduce Combing Force, Flyaway, Damage in Shampoo after shampoo, while hair swatches washed by S2 shampoo (0.21% amodimethicone), S3 shampoo (0.42% amodimethicone), and S4 shampoo (0.18% silicone quaternium-18) showed a significant decrease of total volume area. In addition, hair swatches washed by S3 shampoo showed a trend of more effective total volume area decrease compared to hair swatches washed by S2 shampoo, which was very close to the hair swatches washed by S4. Therefore, both amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18 showed a beneficial effect on total volume control of damaged hair, and silicone quaternium-18 can control hair total volume at a relatively lower concentration in the formulation this was consistent with our deposition results. Figure 7 shows the representative images of damaged hair swatches before and after shampoo. We can see that compared with the hair swatch washed by S1, hair swatches washed with S2, S3, and S4 also show bulk volume reduction compared to hair swatches before washing with shampoo sample. HAIR BREAKAGE TEST AND HAIR TENSILE STRENGTH TEST RESULTS Figure 8 shows the hair breakage test results on Asian damaged hair. Our hypothesis was that the deposition of amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18 could improve the hair- surface smoothness and therefore could reduce the hair breakage. To test this, shampoos with 0.21%, 0.42% amodimethicone, and 0.18% silicone quaternium-18 were tested and shown to significantly reduced the number of broken hairs during combing on Asian damaged hair. The reduction rates were 83.3%, 87.3%, and 82.9% respectively (Table II). In combing S1 S2 S3 S4 Figure 7. Representative images of damaged hair swatches before and after shampoo. S1: base shampoo without silicone S2: shampoo with 0.21% amodimethicone S3: shampoo with 0.42% amodimethicone S4: shampoo with 0.18% silicone quaternium-18.
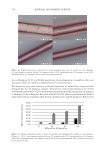
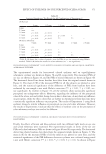
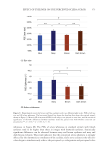
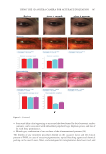
356 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE test results (Figure 5), it was shown that 0.21%, 0.42% additions of amodimethicone, and 0.18% addition of silicone quaternium-18 reduced the hair combing force and hair became smoother. During combing, the force needed for combing through hair swatches became smaller, therefore the damage caused by physical combing was reduced. Figure 9 shows the tensile strength test results on Asian damaged hair. Our hypothesis was that the deposition of amodimethicone and silicone quaternium-18 could repair hair damage and therefore increase tensile strength of damaged hair. Addition of 0.21% amodimethicone (S2) in shampoo slightly increased the maximum load of hair to be broken compared to base shampoo (S1) sample without silicone. A similar result was obtained for hair treated by shampoo S4, which added 0.18% silicone quaternium-18. The hair treated with shampoo S2 required a longer time to be broken compared to S4, although their maximum loads to be broken are similar (Table II). We are not certain of the reason. Enlarged View S1 Enlarged View S4 Enlarged View S3 Enlarged View S2 Figure 8. Hair breakage test results on Asian damaged hair. S1: base shampoo without silicone S2: shampoo with 0.21% amodimethicone S3: shampoo with 0.42% amodimethicone S4: shampoo with 0.18% silicone quaternium-18. Table II Number of Broken Hairs Counted, and the Reduction Rates Compared With Base Shampoo in Hair Breakage Test Hair Broken Time and Maximum Load When Broken in Tensile Strength Test Testing samples S1 S2 S3 S4 Hair breakage test No. of broken hairs counted 228 38 29 39 Reduction rate versus S1 -83.3% 87.3% 82.9% Tensile strength test Broken time(s) 47.1 52.4 -50 Maximum load (N) when broken 0.9937 1.0458 -1.0511 S1: base shampoo without silicone S2: shampoo with 0.21% amodimethicone S3: shampoo with 0.42% amodimethicone S4: shampoo with 0.18% silicone quaternium-18.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)