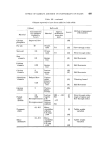
JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Stability in the presence of electrolytes In general, SCMCs with very high D.S. values show better fluoride or monofluorophosphate tolerance than those with D.S. 0.7-0.8. In the case of toothpaste containing calcium ions, all SCMC toothpastes which are alkaline tend to harden due to the formation of the calcium carboxymethyl cellulose which is insoluble. The calcium salt does not form so readily in neutral pastes and in practice only chalk pastes of pH above 8.5 give any difficulty. Glycerine compatibility The well-known dehydrating effect of glycerine on SCMC and other mucilages results in a large change in viscosity which is reflected in the consistency of the finished toothpaste. Fig. 2 shows the effect of replacing water with glycerine in 1% SCMC slurries. Quality control is easier, and •00.. 0 6000, •ooo, Glycerinel Water IOO 90 lb 2'0 30 '40 50 6i0" 70 80 90 I00 BO 70 60 50 40 30 20 IO O Figure paste consistency/dry-out characteristics are improved if ratios on the steep parts of the curve are avoided.
SYNTHETIC HYDROCOLLOIDS AND DENTIFRICES 4(37 Hydroxy ethyl cellulose The behaviour of hydroxy ethyl cellulose in toothpaste is somewhat of an extrapolation of the behaviour of SCMCs with very high D.S. values except, of course, that being non-ionic in character it has good com- patibility with electrolytes. Products are usually smooth, relatively non-thixotropic and disperse less rapidly in the mouth. Dispersion is important in terms of speed of foam and flavour production in the mouth and the sensation communicated to the user. Hydroxy ethyl cellulose toothpastes do not thin when treated with cellulase. This is due to the uniformity of distribution of the substituted groups. Hydroxy ethyl cellulose is used mainly in fluoride toothpastes, and its general use is probably somewhat restricted by its relatively slow dispersibility. Carboxymethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose (CMHEC) A possible application for this material in dentifrices, is as a more dispersible replacement for hydroxyethyl cellulose in toothpastes with high electrolyte content. The stannous fluoride product was initially promising, but severe hardening on storage occurred at 37øC. The CMHEC is presumably sufficiently anionic in character to be liable to ionic interactions. Hydroxy pro•pyl cellulose ttydroxy propyl methyl cellulose The introduction of the more hydrophobic propyl group, is sufficient to prevent the hydrocolloid from retaining water in the presence of the glycerine. These hydrocolloids are unsuitable for use in most dentifrices. Colloidal microcrystalline cellulose The gels formed by this material are very thin and have little thickening power. It is doubtful whether it has any particular value in the kind of formulations being considered.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)