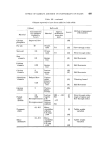
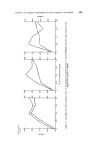
488 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS flow conditions. Fig. 2 illustrates the effect of orifice diameter on flow rate in ternary mixtures and it can be seen that as the orifice size increases, the percentage fines required to produce optimum flow decreases. In compression processes, gravity discharge through orifices studies are of limited value since it is the die filling capacity of the formulation which is the important parameter. It has been shown that these particle Table III Glidants reported to have been added to bulk solids. Bulk solid Approx. Method of assessmenl Material arithmetic Source of flowability mean size (gm) Lactose 950 - -149 (7) Flow through orifice Lactose 805 (8) Flow through orifice S.D. -177 (5) Angle of repose and Lactose- flow through orifice Aspirin 541 Calcium sulphate 541 (1) (39) Sulpha- thiazole 213 (35) Angle of repose Lactose 950 -- -149 (7) Flow through orifice S.D. Lactose -177 (5) Angle of repose and Aspirin 541 flow through orifice Calcium sulphate 541 Various tablet (40) Vibrating funnel diluents Lactose 950 -- -149 (7) Flow through orifice S.D. Lactose -177 (5) Angle of repose and Aspirin 541 flow through orifice Calcium sulphate 541 Sulpha- 335 thiazole 163 (35) Angle of repose (1) Various tablet (40) Vibrating funnel diluents Glidant Concentration for optimum Material flowability % w/w 0.5 up to 3 Talc 1 No improvement No improvement up to 4 0.5 up to 1 No improvement No improvement Starch No improvement 5 delayed flow No improvement 0.5 0.25 0.25 Magnesium 0.25-1 stearate No improvement No improvement Delayed flow Polyethylene glycol 4000 Delayed flow Improved flow tablet ' (40) Vibrating funnel diluents (1)
EFFECT OF GLIDANT ADDITION ON FLOWABILITY OF SOLIDS 489 Table III--continued Glidants reported to have been added to bulk solids. Material Calcium phosphate Fly ash Microcell Zinc stearate Lithium stearate Calcium stearate Aluminium stearate Calcium silicate Fumed silica dioxide Pyrogenie silica Silico- aluminate Glidant Concentration for optimum flowability % Improved flow 20 3.6 0.5 0.25 2 0.25 Delayed flow 0.25 0.5 0.25 No improvement No improvement 0.1-0.5 0•1-0.5 Bulk solid Material Ottawa sand Ottawa sand Sponge Iron Sponge Iron Lactose sponge iron Various tablet diluents Sponge iron Thermo- plastic Powder Lactose Aspirin S.D. Lactose Calcium sulphate Micro- crystalline cellulose S.D. Egg yolk Micro- crystalline cellulose S.D. egg yolk Approx. arithmetic mean size (•m) 711 711 950 -+ -149 541 -177 541 Method of assessment of flowability Flow through orifice Flow through orifice Hall flowmeter Hall flowmeter Hall flowmeter Vibrating funnel Hall flowmeter Flow through orifice Angle of repose and flow through orifice Tablet weight variation Tablet weight variation
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)