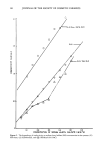
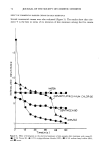
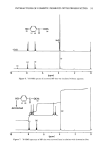
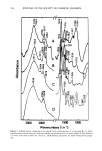
72 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS EFFECT OF COMMERCIAL BARRIER CREAMS ON SKIN RESISTANCE Several commercial creams were also evaluated (Figure 5). The results show that oint- ment V is the best in terms of its retention of skin resistance among the five creams WATE• Q5%C.r..'-TYLPYR• D• N IUM CHLORIDE 5 'l'irne(rni n ) EN80 0.5%S• Figure 6. Effect of detergents on the electrical resistance of skin samples after treatment with cream D. (,) 0.5% Tween 80, (&) 0.5% cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC), (O) 0.5% sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), and (I) water.
CONDUCTIVITY OF SKIN IN DETERGENT SOLUTIONS 73 evaluated. As can be seen from Figure 5, ointment V provides a very high initial value of normalized resistance, about 200 times greater than bare skin, and its rate of wash- off by a 0.5% sodium lauryl sulfate solution is almost zero. This result is consistent with that from white petrolatum ointment USP (Figure 4) since both formulations are prepared from the same type of ointment base. The data in Figure 5 also show that cream N, which is known to contain a (w/o)-type base, also has good protective effi- ciency. As expected from their hydrophilic properties, creams C, D, and P are more easily washed off the skin. 1 •00 0.5ø/oTWI•N 0 120 6C O.Bø/oSLS •/ --•k %CECH , Time(hr. ) Figure 7. Effect of various detergents on the resistance of skin samples after application of ointment V. (&) 0.5% Tween 80, (0) 0.5% cetylpyridinium chloride, and (O) 0.5% SLS. 0.05% NaC1 was added to the solution in the donor compartment.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)