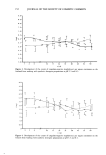
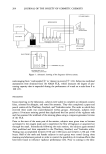
142 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS syndet, soap, •. 0.5 mM Zn % syndet, 0.1 mM Zn soap, 0.1 mM Zn 0.00 0.05 0.10 % soap or syndet Figure 7. Reduced binding of Zn-GLY to hair from soap and syndet compositions. 0.15 Ohio. The study assessed the deodorant efficacy of Zn-GLY. A test solution 1.5 % in Zn (4.5% Zn-GLY) was employed this level represents the maximum solubility of Zn-GLY in aqueous solution. The positive control was 5.0% aluminum chlorhydrate. At this level the aluminum compound effects deodorancy via antimicrobial action but does not inhibit perspiration. The negative control was distilled deionized water. A summary of the results of the deodorancy study is given in Table II. Mean odor scores represent the four-judge average odor scores, post-treatment. The control values are the average baseline odor scores for the various cells. The differences among these evalua- tions were analyzed using the distribution free signed-rank test described in reference 8. Zn-GLY (4.5%) was significantly more effective than H20 in controlling malodor at each post-treatment evaluation. Aluminum chlorhydrate (5.0%) was significantly more effective than H20 in controlling malodor at each post-treatment evaluation. The Hill Top report does not include a comparison between the deodorant efficacies of Zn-GLY and aluminum chlorhydrate. We therefore performed Student's t-test of the data (Cricket Statworks). The results are given in Table III. The group receiving Zn-GLY treatment exhibited lower mean odor scores than did the group receiving aluminum chlorhydrate treatment at all six evaluations. Of these six differences, four
ODOR INHIBITION 143 Table II Summary of Results of Deodorancy Study Application #2 5 hr 24 hr Zn-GLY H20 Zn-GLY Mean odor score 3.12 4.03 3.34 % Difference 22.6% 28.1% H20 4.65 ACH H20 ACH H20 Mean odor score 3.13 4.75 3.91 % Difference 34.0% 27.8% 5.41 Application #3 5 hr 24 hr Zn-GLY H20 Zn-GLY Mean odor score 2.33 3.47 3.27 % Difference 32.7% 30.5% H20 4.70 ACH H20 ACH H20 Mean odor score 2.95 4.15 3.88 % Difference 28.8% 26.1% 5.24 Application #4 5 hr 24 hr Zn-GLY H20 Zn-GLY Mean odor score 2.60 3.94 3.11 % Difference 34.0% 34.5 % H20 4.74 ACH H20 ACH H20 Mean odor score 2.90 4.45 3.64 % Difference 34.9% 29.5% 5.16 Baseline odor scores: Zn-GLY, 6.41 H20 , 6.42 ACH, 6.64 H•O, 6.73 Zn-GLY concentration: 4.5%. ACH (aluminum chlorhydrate) concentration: 5.0%. were significant: all three 24-hr evaluations gave significant differences. Only one of the 5-hr evaluations gave significant differences. Zn-GLY appears to provide a stronger and more long-lasting deodorant effect than does aluminum chlorhydrate at these levels. ANTIMICROBIAL PROPERTIES OF ZINC GLYCINATE Simple salts of zinc are well known to be bacteriostatic. One possible outcome of our work was discovering a way to reduce axillary odor without destroying the natural flora of the axilla. Therefore MIC values of several zinc complexes and the antiseptic Irgasan DP 300 (positive control) were measured against several organisms that occur naturally in the underarm, including S. epiderrnid)s, S. aureus, and a lipophilic diphtheroid. Results are shown in Table IV. The "" signs indicate that bacterial growth occurred
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)