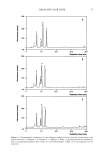
OXIDATIVE HAIR DYES 49 2OOO 1500 -- 1000 -- 500 -- -150 5 6 I I 0 7.5 15.0 I 22.5 30.0 Retention time (min) 2000 1500_ 1000 - 500 _ 1 3 5 -150 I I I 0 7.5 15.0 22.5 30.0 Retention time (min) Figure 1. Chromatographic separations of two synthetic formulations after matrix extraction. a: "light brown." b: "light blonde." Peaks: (1) NaAsc (intrinsic matrix, antioxidant), (2) matrix compound, (3) p-phenylenediamine, (4) m-phenylenediamine sulfate, (5) m-aminophenol, and (6) resorcinol. See text for experimental data and acronyms. compounds in pure standard solutions commonly found in oxidative hair dye formula- tions (9), the identification could then be performed by comparison between the ex- perimental data obtained and the recorded data. Table II and Figure 2 show the iden- tification obtained by combining the two criteria retention time and UV spectra. Peaks 3, 4, 5, and 6 are attributed to p-phenylenediamine, m-phenylenediamine sulfate, m- aminophenol, and resorcinol, respectively. Peaks 1 (attributed to sodium ascorbate) and 2, having retention times shorter than 5 min, are due to remaining matrix compounds not interfering with the dye separation, in accordance with previous observations (2,3).
50 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)