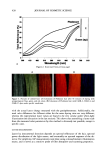
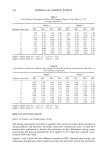
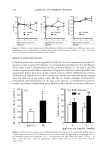
476 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 0.4 I (a) 0'2 f 0.1 0 • 0 ** -0- V ehJele -•- BE 40 0.6 30 -O- Vehicle ß •- BE ' ' '6 0 ' ' ' 0 ' ' ' 2 4 0 2 4 6 0 2 4 6 Application period [Application period [Application period (weeks) (weeks) (weeks) Figure 3. Effbcts of topical application of Bifidobacteri•-fermented soy milk extract (BE) on elasticity (a), viscoelasticity (b), and thickness (c) of hairless mouse skin. Values are mean _+ SD (n = 5). **(p 0.01) and *(p 0.05) show a significant diffbrence from vehicle. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In hairless mouse skin, topical application of BE for six weeks significantly restored the decrease in skin elasticity (Ur) (Figure 3a), increased skin viscoelasticity (Uv/Ue) (Figure 3b) at weeks 4 and 6, and thickened the skin at week 6 (Figure 3c). At week 6, the HA content (Figure 4a) and surface conductance (Figure 4b) of the skin treated with BE were significantly higher than those of skin treated with the vehicle. Inflammatory reaction (infiltration of lymphocytes in skin sections and edema) and abnormal weight change were not observed in any mouse. Also, BE did not induce irritation, phototoxicity, sensitization, photosensitization of the skin, acute toxicity, or mutagenicity in several animal experiments (unpublished data). Moreover, BE induced an increase in HA pro- 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 (a) o 6O 50 4O 3O 2O 10 Vehicle BE Vehicle BE 0 6 Application period (weeks) Figure 4. Effbcts of topical application of Bifidobacteri•-fermented soy milk extract (BE) on HA content (a) and surface conductance (b) of hairless mouse skin. HA content was expressed as a percentage of con- trol (vehicle-treated skin), containing 1.03 _+ 0.04 mg HA/g dry skin. Values are mean _+ SD (n = 5). ##(p 0.01) and *(p 0.05) are significantly diffbrent from vehicle at week 6 and BE at week 0, respectively.
TOPICAL APPLICATION OF SOY MILK EXTRACT 477 duction in human keratinocyte culture maintained at room temperature for two years (unpublished data). These observations indicate that BE is safe and stable as a cosmetic ingredient. In the forearm skin of healthy volunteers, topical application of a gel formula containing 10% BE significantly improved skin elasticity (Ua/Uf) at month 3 (Figure 5). The Ua/Uf of skin treated with the gel formula tended to be higher than that of skin treated with the vehicle formula during the test period, but some parameters of skin viscoelasticity were not affected by topical application. Some parameters measured by cutometer are used in the evaluation of skin elasticity, and, one of them, Ur, is affected by skin thickness (1). Because the results using mouse skin showed no differences among Ur, other elastic parameters (Ua, Ur/Uf, and Ua/Uf), and Ur normalized to skin thickness (Ur*), our animal study employed Ur, the simplest and most typical parameter, as a measure of skin elasticity. On the other hand, the Ur, Uf, and Ua of forearm skin were markedly varied in each human volunteer. Thus, we employed Ua/Uf (Ua normalized by Uf) for evaluation of human skin elasticity. Skin thickness, age, and environmental conditions show considerable differences between animal model and human studies. Mainly due to the activity of Gen released from Gen-Glc during the fermentation of soy milk, topically applied BE increases the amount of cutaneous HA (15), which has specific rheological characteristics, good water-holding capacity, and certain important biological roles. Beta-estradiol (Est) increases the content of HA in murine skin (17), and its activity is more than 1000-fold higher than that of Gen and Dai (11). Also, Est has more than 1000-fold higher potential than Gen and Dai to bind with the beta-estrogen receptor (18), which is abundant in human skin (19). It is hypothesized that Gen in BE 11o 105 lOO -0- Gel formula with 10% BE -0- Vehicle formula -•- No treatment * 95 0 1 2 3 Application period (months) Figure 5. Effect of topical application of gel formula containing Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract (BE) on elasticity of human forearm skin. Values are mean e SE (n = 3). *(p 0.05) indicates a significant difference from no treatment.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)