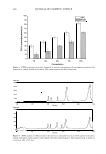
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF C. ASIATICUM 423 µl of substrate (1 mM p-nitrophenyl-N-acetyl-13-D-glucosaminide) for 1 h at 37 ° C. Stop solution (0.1 M Na 2 CO 3 /NaHCO 3 ) was added, and the absorbance at 405 nm was measured with an ELISA reader. IN VIVO CLINICAL SAFETY TEST The evaluation of contact sensitization potential was carried out according to the meth ods previously reported by Shelanski and Shelanski (10). Fifty healthy Korean subjects were studied, and written consent was obtained in each case. The average age was 3 5 years (range: 21 to 51, males and females). The subjects had no skin disease, nor had they used topical or systemic irritant preparations in the previous month. All subjects were nonsmokers and signed an informed consent form in accordance with the Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and Declaration of Helsinki. Repeated epicutaneous applications under occlusive patch (repeat insult patch test, RIPT) for 48 h were performed using a Finn Chamber® (Epitest Ltd Oy, Finland) secured to the back site with Scanpore tape. These chambers are made of inflexible aluminum, and have a diameter of 12 mm and a depth of 0.5 mm. The round border of the chamber was placed firmly against the skin, causing a tight occlusion of the test materials. Sixty microliters of 1 % and 5% aqueous solutions of Crinum asiaticum extract were applied. The patches (chambers) stayed in place for 48 h for each application. The subjects abstained from showering or performing any work or exercise that might wet or loosen the patches. Eight applications were carried out for Cytotoxicity Assay 180 160 140 ;i' � 120 � 100 :Ei ftl 80 · "ii 60 40 Figure 1. Cytotoxicity of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum to Raw 264.7 macrophage cells. N. con.: negative control (DMSO). P. con.: positive control treated with 1 µg/ml LPS. Indomethacin and the extract of Crinum asiaticum were treated with 1 µg/ml LPS. The data are expressed as the mean value (±standard deviations) of four experiments.
424 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Nitrite Amount released 120 100 80 60 ·;._ ::::e 0 40 20 o o�· �-0 ..... � """'fJ �'(?G � e d'�-v concentration (µg/ml) Figure 2. Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on LPS-induced nitrite production in Raw 264.7 macrophage cells. N. con.: negative control (DMSO). P. con.: positive control treated with 1 µg/ml LPS. Indomethacin and the extract of Crinum asiaticum were treated with 1 µg/ml LPS. The data are expressed as the mean value (±standard deviations) of four experiments. Inhibition of iNOS mRNA expression Lane 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 11 12 13 iNOS GAPDH Figure 3. Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on LPS-induced mRNA expression of iNOS in Raw 264.7 macrophage cells. Lane 1: negative control (DMSO). Lane 2: 1 µg/ml LPS. Lane 3: 50 µg/ml indomethacin. Lane 4: 100 µg/ml indomethacin. Lane 5: 25 µg/ml EGCG. Lane 6: 3.4 µg/ml quercetin. Lane 7: 50 µg/ml vitamin C. Lane 8: extract of Crinum asiaticum, 1 µg/ml. Lane 9: extract of Crinum asiaticum, IO µg/ml. Lane 10: extract of Crinum asiaticum, 25 µg/ml. Lane 11: extract of Crinum asiaticum, 50 µg/ml. Lane 12: extract of Crinum asiaticum, 100 µg/ml. Lane 13: extract of Crinum asiaticum, 200 µg/ml. the induction period. Once the patches were removed, a reading was done after 30 min. A single challenge application at day 36 was performed following approximately two weeks (rest period) after application of the last induction patch. A challenge patch was applied to a previously unpatched (virgin) site, not adjacent to the original induction patch site, for 48 hr. The challenge site was scored at 30 min, 24 h, and 48 h after the removal of the patch. The patch test was conducted in accordance with the standards of the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group (ICDRG) (11).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)