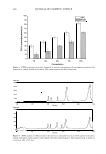
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF C. ASIATICUM 425 RES UL TS AND DISCUSSION PREPARATION AND ANALYSIS OF LYCORINE, THE ETHANOL EXTRACT OF CRINUM ASIATICUM Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract was obtained in the form of yellow powder by extraction with 95% ethanol at 75°C (28.3 g, yield = 8.32%). It has previously been reported that lycorine is the active component for anti-inflammatory activity in the Amaryllidaceae family (3,4). Therefore, we attempted to measure the lycorine content of the ethanol extract of Crinium asiaticum. As expected, the HPLC results showed that the main component of Crinum asiaticum was lycorine (up to 1 % ) and that the content of lycorine, well-known as an immunosuppressor, varied depending on the type of tissue analyzed and the extraction method used (7). Therefore, it was hypothesized that the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum would show an anti-inflammatory effect, and in flammation-related experiments were conducted. EFFECT OF THE ETHANOL EXTRACT OF CRINUM ASIATICUM ON CELL VIABILITY AND LPS-INDUCED NITRITE SYNTHESIS To evaluate the cytotoxicity of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum, the cytotoxicity assay was carried out by the MTT method (5). The results of this investigation are shown in Figure 1. The ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum did not show any cytotoxicity up to 100 µM in the presence of LPS on the contrary, it showed cell proliferation activity as the concentration increased. 500 - 400 e C) E: ... 300 C: :::J E ca 200 Q) ,,, ca Q) 100 H 2 O 2 - Treatment .,., I \ -------- . ··O· I \ I \ --.- I I \ I \ I \ I \ I \ I \ I \ I \ I �----....._ --� I ----y- • 0. / IL-6 IL-8 PGE2 .,.,� / / Figure 4. Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on H2O2-induced IL-6, IL-8, and PGE2 synthesis in human fibroblast cells. N. con.: negative control. P. con.: positive control treated with H 2 O2 5 x 10-4 M. The extract of Crinum asiaticum was treated with H2O2 5 x 10-4 M.
426 - C. - C: ::J 0 E cu Cl) cu Cl) 500 400 300 200 100 0 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE UV - Treatment 0 ____..,__ IL6 · o ILB -�- PGE2 - 0 Figure 5. Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on UV-induced IL-6, IL-8, and PGE2 synthesis in human fibroblast cells. N. con: negative control. P. con.: positive control treated with UVA 2 J!cm 2 + UVB 0.2 J/cm2. The extract of Crinum asiaticum was treated with UVA 2 J/cm2 + UVB 0.2 J/cm2. The addition of LPS stimulated Raw 264.7 macrophages to cause a substantial release of nitrite (Figure 2). The ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum) especially at 100 µM, sig nificantly reduced the LPS-induced nitrite production. Compared to cell viability, the inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on LPS-induced nitrite was not due to the lessening of cell viability. EFFECT OF THE ETHANOL EXTRACT OF CRINUM ASIATICUM ON LPS-INDUCED mRNA EXPRESSION OF iNOS The expression of iNOS is induced in stimulated macrophages, neutrophils, and endo thelial and smooth muscle cells, and catalyzes large amounts of NO production (8). The levels of iNOS and GAPDH mRNA expression were measured by RT-PCR. As shown in Figure 3, 100 µM of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum decreased LPS-induced mRNA expression of iNOS to the control level. This result indicates that the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum reduced iNOS synthesis and subsequent NO production, followed by an anti-inflammatory effect. EFFECT OF THE ETHANOL EXTRACT OF CRINUM ASIATICUM ON VARIOUS STIMULI-INDUCED PGE2, IL-6, AND IL-8 SYNTHESIS In response to specific inflammatory stimuli such as H202 , UV, and SDS, the tran scription factors NF-KB, JunD/c-fos, and p53 are subsequently activated (12,13). In turn, NF-KB induces target genes such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-a (tumor necrosis
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)