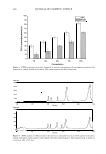
SIMULTANEOUS DETERMINATION OF HEAVY METALS 447 Table V Determination of Metals in Cosmetic Products Concentration (µg ml - 1 ) Samples Pb Fe Cu Ni Zn Eyeshadow ,pink 3.7 2.5 679.3 Eyeshadow blue 66.9 715.8 Eyeshadow yellow 7.3 0.3 508.2 Eyeshadow purple 2.2 181.3 Makeup base A 1.3 173.2 Makeup base B 0.5 59.4 Makeup base C 62.7 Foundation A 0.8 116.7 Foundation B 2.2 32.6 Foundation C 8.4 0.5 88.7 Gloss A 1.1 25.6 Gloss B 2.9 2.6 26.9 Gloss C 0.6 26.6 Lipstick A 2.4 0.4 24.1 Lipstick B 17.5 Lipstick C 2.0 23.5 Mascara A 55.7 27.8 Mascara B 52.5 57.3 Mascara C 224.1 68.3 Eyeliner A 342.5 118.0 Eyeliner B 115.7 33.2 Eyeliner C 683.1 78.2 Above are the average concentration values of 3-time injection. Co Cd Mn 3.9 1.7 9.6 metals because of the interference of residual organic materials. The HPLC method is not suitable for the determination of heavy metals. Even though the interference of residual organic materials can be ignored because it is the determination method for organic materials, the HPLC method is not sensitive in analyzing trace heavy metals due to the ion-exchange column in the stationary phase in the system. On the other hand, the Dionex IonPac CSSA analytical column for IC is dedicated to the analysis of heavy metals. The limit of detection (LOD) of IC is higher than in the HPLC method and IC can improve the quality control process in the manufacturing of cosmetics. In this study we have found that the flow rates of the eluent and the post-column reagent are critical to the analysis of heavy metals in cosmetics. The flow rate of the eluent should be two times the flow rate of the post-column reagent, which enables microanalysis because the baseline is most stable under this condition. The concentration of the eluent (PDCA) and the post-column reagent (PAR) are important for the sensitivity and selectivity of the peaks of heavy metals. The sensitivity of the detection can be changed by the concentration combination of PDCA and PAR, and so it is important to look for an optimum concentration combination. CONCLUSIONS We have developed a simultaneous determination method for water-soluble trace heavy metals in cosmetic products and coloring agents. The proposed techniques show that ion
448 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE chromatography with an IonPac CSSA column and a post-column reaction system can be used for fast and accurate determination of water-soluble heavy metals in cosmetic samples. Consequently, this process is fast and sensitive, with the simultaneous deter mination of heavy metals, and it provides accurate results due to rare interference, which can improve the safety and quality control process for cosmetic products. REFERENCES (1) P. N. Nesterenko and P. Jones, Single-column method of chelation ion chromatography for the analysis of trace metals in complex samples, J. Chromatogr. A, 770, 129-13 5 (1997). (2) E. Sainio, R. Jolanki, E. Hakala, and L. Kanerva, Metals and arsenic in eye shadows, Contact Dermatitis, 42, 5-10 (2000). (3) J. Hostynek, Chromium, cobalt, copper and iron: Metals in personal-care products, Dermatologic View, ll5, 52-65 (2000). (4) H. Maibach and T. Menne, Nickel and the Skin: Immunology and Toxicology (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1989), pp. 223. (5) H. Kerosuo, A. Kullaa, E. Kerosuo, L. Kanerva, and A. Hensten-Pettersen, Nickel allergy in adoles cents in relation to orthodontic treatment and piercing of ears, Am.]. Orthodon. Dentofac. Orthoped., 109, 148-154 (1996). (6) W. Zeng, Y. Chen, H. Cui, F. Wu, Y. Zhu, and S. J. Fritz, Single-column method of ion chroma tography for the determination of common cations and some transition metals,]. Chromatogr. A, 1118, 68-72 (2006). (7) M. R. Cave, 0. Butler, R. N. Chenery, J.M. Cook, M. S. Cresser, and D. L. Miles, Atomic spectrom etry update. Environmental analysis, J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom., 16, 194-235 (2001). (8) G. L. Long and J. D. Winefordner, Reduction of electronic noise in inductively coupled plasma atomic emission and fluorescence spectrometric measurements, Anal. Chem., 55, 1432-1434 (1983). (9) N. Cardellicchio, S. Cavalli, P. Ragone, and J.M. Riviello, New strategies for determination of transition metals by complexation ion-exchange chromatography and post column reaction,]. Chro matogr. A, 847, 251-259 (1996). (10) P. L. Buldini, S. Cavalli, A. Mevoli, and E. Milella, Application of ion chromatography to the analysis of high-purity CdTe,J. Chromatogr. A, 739, 131-137 (1996). (11) H. T. Lu, S. F. Mou, U. Uan, S. Y. Tong, and J.M.Riviello, On-line pretreatment and determination of Pb, Cu and Cd at the µg 1 - i level in drinking water by chelation ion chromatography,]. Chromatogr. A, 800, 247-255 (1998). (12) P. Jones, K. Barron, and L. Ebdon, A dithizone post-column detector for the high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of trace metals, Anal. Chim. Acta, 149, 39-46 (1983).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)