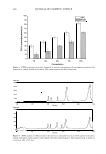
- - C, -E ::I 0 E ca (1) ti) ca � ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF C. ASIATICUM 1000 800 600 400 I I I 200 I 0 SDS -Treatment ., ______ I ...._T I I I I I I I I I I I e,o�· \ '\a �- ::f..�'o- \ \ \ \ \ •---- .... 0 -------- IL6 0 IL8 --y- PGE2 �- -- ,, :«' e c.i'� -v concentration (µg/ml) 427 Figure 6. Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on SDS-induced IL-6, IL-8, and PGE 2 synthesis in human fibroblast cells. N. con: negative control. P. con.: positive control treated with 0.05% SDS. The extract of Crinum asiaticum was treated with 0.05% SDS. factor-a, and COX-2 (13-15). COX-2 is induced in a number of cells by proinflam matory stimuli contrary to the constitutive enzyme, COX-1. Prostanoid release is ini tiated by the liberation of the substrate arachidonic acid, which is metabolized by COX to prostaglandin H2. This is further metabolized by other enzymes to prostaglandins, prostacyclin, and thromboxane A2 (16). The addition of H 2 O 2 , UV radiation, and SDS stimulates human fibroblasts 'to induce substantial PGE 2 , IL-6, and IL-8 synthesis. The treatment of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticumJ however, reduced IL-6, IL-8, and PGE 2 synthesis by those stimuli to the control level at all of the concentrations tested IL-6 synthesis, in particular, was completely inhibited (Figures 4-6). These results suggest that the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum could block the inflammatory response from various stimuli such as H 2 O 2 , UV, and SDS by inhibiting transcription factor activity. INHIBITION OF !3-HEXOSAMINIDASE RELEASE FROM RBL-2H3 CELLS Beta-hexosaminidase is located in the secretory granules of mast cells where histamine is stored, and is released along with histamine when mast cells are immunologically activated (9,17). Therefore, it is generally accepted that the �-hexosaminidase is a degranulation marker of mast cells, and the quantitative determination of the � hexosaminidase released has been used to evaluate the extent of degranulation and anti-allergic activities (18). In order to evaluate the anti-allergic activity of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract, we measured the amount of �-hexosaminidase
428 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE release from RBL-2H3 cells treated with IgE (0.5 µg/ml). Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract decreased the �-hexosaminidase release in a dose-dependent manner (IC 50 was around 100 µg/ml). Furthermore, 1000 µg/ml of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract completely inhibited the �-hexosaminidase release to the control level, at which the amount is spontaneously released from RBL-2H3 cells untreated with IgE (Figure 7), even though the anti-allergic activity was not comparable with that of indomethacin, a well-known topical analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug. The results suggest that the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum could be a useful active ingredient for anti-allergic cosmeceuticals. IN VIVO CLINICAL SAFETY TEST In order to evaluate the skin-sensitizing potentials of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. ja ponicum extract, a clinical test was performed after repeated epicutaneous applications under an occlusive patch (repeat insult patch test, RIPT) for 48 h. Fifty male and female subjects between the ages of 21 and 51 were selected for the study. The evaluation criteria of the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group (ICDRG) were used as the standard of the grading scale, as shown in Table I (10,11). The results were analyzed by calculating the mean irritation index (M.1.1.) of allergic reaction for the test articles according to the formula, as shown in Table II. The repeated and single cutaneous applications of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract under the occlusive patch did not provoke any cumulative irritation and sensitization reaction. f- Quantitative Determination of (3-hexosaminidase � CD (II ca CD (II ca 'i: ·e ca 0 CD 0 C 0 :c .E Figure 7. Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on �-hexosaminidase release from RBL-2H3 cells immunologically activated by treatment with IgE (0.5 µg/ml). The data are expressed as the mean values (±standard deviations) of four experiments.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)