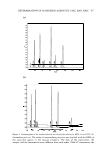
524 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE lrritancy ranking of 31 cleansers in the Indian market in a 24-h patch test C. Lakshmi*, C. R. Srinivas*, C. V. Anand_ and A. C. Mathew_ *Departments of Dermatology, _Biochemistry and _ Community Medicine, PSGIMSR, Peelamedu, Coimbatore-641004, India Correspondence: Chembolli Lakshmi, Department of Dermatology, PSGIMSR, Peelamedu, 'coimbatore-641004, India. Tel.: +91 422 2570 170 fax: +91 422 2594 400 e-mail: cl coimbatore@yahoo.co.in Cleansing trends promise freshness, sensory and health benefits but may also be accompanied by an increase in soap-induced skin irritation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the irritant effect of 31 cleansers (28 bar soaps and 3 liquid cleansers) available in the Indian market. Eight percent w/v solutions of the soaps/cleansers were made and 30 IL of each of the solutions were applied to Finn chambers and occluded for 24 h along with distilled water (negative control) and 20% sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) as positive control. The sites were graded for erythema and scaling 30 min after removing the patches. The pH of each of the soap solutions was determined. Mean with SD and ANOVA (F-value) was computed separately for each soap/cleanser with respect to the two parameters, erythema and sealing. The total of the means for both the parameters, erythema and scaling was also computed. The cleansers were listed based on this total from the least irritant to the most irritant. The differences between soaps (F-value) was significant for erythema and scaling [ erythema = 4.106 (P = 0.000) scaling = 6.006 (P = 0.000)]. Cetaphil cleansing lotion had the lowest erythema score of 0.25. Lowest scaling score of zero was recorded for Cetaphil cleansing lotion and Elovera moisturizing body wash. Aquasoft and Lifebuoy soaps had the highest erythema score of 2.13. Acnex had the highest scaling score o f 1.75 Aquasoft, Hamam scrub bath soap and Naturepower sandal soaps were the next with a scaling score of 1.63. Cetaphil cleansing lotion, Aquaderm liquid soap, Dove bar soap and Elovera moisturizing body wash proved to be the least irritant cleansers with a total score of less than I. The four most irritant soaps/cleansers had an average score of 3.65. The irritant potential of the majority of the cleansers fell between these extremes. The pH of all the soap/cleanser solutions was neutral to alkaline (pH 7-9) except that of Dove bar, Cetaphil cleansing lotion, Aquaderm liquid soap and Elovera moisturizing body wash which tested acidic (pH 5-6). The pH of the positive control-20% SDS, was acidic (pH 6). The difference in the irritancy potential between soaps/ cleansers as determined by the 24-h patch test was significant. There were individual variations in the irritant potential of the soaps/cleansers in the volunteers, thus when the patient queries on what soap to use, it may be advisable to test each patient separately and educate him/her regarding the soaps/cleansers less likely to cause irritation. The limitations of the study was that it was single blind and non-randomized as all the 14 soap solutions were applied on 15 volunteers in the first panel and subsequently all the 17 soap solutions were applied on eight volunteers in the second panel. However, we could compare the irritant potential of 31 cleansers. The results of 24-h patch testing of 31 soaps/cleansers in the Indian market in two panels of 14 and 17 soaps/cleansers on 15 and eight volunteers, respectively, are presented. In vitro evaluation of sun protection factors of sunscreen agents using a novel UV spectrophotometric technique M. D. Bleasel and S. Aldous School of Pharmacy, University of Tasmania, Private Bag 26, Hobart, 7001 Tasmania, Australia Correspondence: Stephen Aldous, School of Pharmacy, University of Tasmania, Private Bag 26, Hobart, Tasmania 7001, Australia. Tel.: +61 36 226 2190 fax: +61 36 226 2870 e-mail: stephen.aldous@utas.edu.au A method for the in vitro determination of lowand high value sun protection factors (SPF) of sunscreens using artificial substrates and a novel pseudo double beam (PDB) mode of operation of a standard double beam UV spectrophotometer is described. The method allows transmittance to be calculated from detector responses of reference and sample beams measured at different gain levels and facilitates the accurate quantification of low levels of electromagnetic radiation transmitted through highly absorbing samples. The spectrophotometer was modified to hold quartz diffusing plates on which a substrate [Transpore_ adhesive tape or human stratum comeum obtained from a skin surface biopsy (SSB)] and the sunscreens to be tested were applied. The PDB mode of operation increased the effective linear range of the detector response of the spectrophotometer by a factor of approximately 20000-fold, enabling the in vitro SPF determination technique to be applied to both high and low SPF value sunscreens. Eight commercial sunscreens with known SPF values ranging from 4 to 77, previously determined by in vivo methods, were tested in vitro using both test substrates and correlations between the in vivo and in vitro values were determined. SPF values determined using the in vitro method correlated well with the known in vivo results (Transpore_ tape, R2 = 0.611 SSB, R2 = 0.7928). The in vitro SPF obtained for one of the tested products differed substantially from the cited in vivo SPF value. Independent in vitro and in vivo re evaluation of the SPF of this product matched the value predicted by the present method much more closely than the originally cited in vivo value. All determined SPFs were ordered correctly in comparison to in vivo ranking and the technique appeared to correctly identify a sunscreen that had a labelled SPF value that was significantly higher than its true SPF.
ABSTRACTS 525 Development of chitosan-coated \iposomes for sustained delivery of tamarind fruit pulp's extract to the skin M. Phetdee*, A. Polnok*,_ and J. Viyoch*,_,_ *Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok 65000, _HerbTech, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok 65000 and Cosmetic and Natural Product Research Center, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok 65000, Thailand Correspondence: Jarupa Viyoch, PhD, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok 65000, Thailand. Tel.: +66 55 261000 4 (ext 1875) fax: +66 55 261057 e-mail: jarupav@nu.ac.th (or) jarupav@hotmail.com In this study, chitosan-coated liposomes were developed. To entrap lyophilized tamarind extract containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) together with tartaric acid, the reverse phase evaporation method was used to obtain well formed liposomes loaded with the extract. The highest entrapment efficiency of 68.3 ± 3.0% into the liposomes was obtained with liposomes consisting of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol in a molar ratio of2: 1 after the extrusion process. The average particle size of the prepared liposomes was 158 ± 26 nm showing a negative zeta potential of)6 mV. For the preparation of the chitosan coated liposomes, two selected independent parameters were varied: chitosan concentrations of 0 .1, 0 .5 and 1.0% w/v and volumes of the chitosan solutions of 1 2 and 3 mL to study the effects of such parameters on th� entrapmen� efficiency of the extract-loaded liposomes. Variation in the volumes of the chitosan solution did not affect the entrapment efficiency of the liposomes. However, the entrapment efficiency of the AHAs in the chitosan-coated liposomes significantly increased with increasing chitosan concentrations. The size of the chitosancoated liposomes was in the range of 200-300 nm with a positive zeta potential in the range of6--29 mV. An in vitro release study using dialysis technique was performed to evaluate the release profile of the tartaric acid from the chitosan-coated liposomes. The obtained results showed the effect of the chitosan-coated liposomes on the lower release rate and on the amount of tartaric acid in comparison with that of the uncoated liposomes. The study in an in vitro skin cell model indicated that the developed system could enhance the pot ential of tamarind's AHAs on the stimulation of human keratinocyte proliferation being two-fold higher than the solution of the tamarind extract. Analysis and quantification of parabens in cosmetic products by utilizing hollow fibre-supported liquid membrane and high performance liquid c hromatography with ultraviolet detection T. A. M. Msagati*, T. Barri, N. LarssonandJ. A0 • Jo"nsson *School of Chemistry, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Private Bag X54001 Westville Campus, Durban 4000, South Africa and Department of Analytical Chemistry, Lund University, PO Box 124, SE-221 00 Lund, Sweden Correspondence: Jan AO ke Jo"nsson, Department of Analytical Chemistry, Lund University, PO Box 124, SE- 221 00 Lund, Sweden. Tel.: +46 46 222 8169 fax: +46 46 222 4544 e-mail: jan ake.jonsson@analykem.lu.se A simple and direct method based on hollow fibresupported liquid membrane (HFSLM) extraction and liquid chromatography equipped with a UV detector was developed for analysis and quantification of parabens in cosmetic products. The parabens analysed included methyl, ethyl, propyl, isobutyl and butyl paraben. The HFSLM extraction was carried out by employing di-n-hexyl ether as organic liquid that was immobilized in the hollow fibre membrane. The HFSLM extraction is simple, cheap, minimizes the use of solvents and uses disposable material. In an investigation of 11 paraben-containing cosmetic products, the levels of parabens (sum of all parabens in a product) ranged from 0 .43% to 0 .79% (w/w) for skin care products, 0 .07-0.44% for hair fixing gels and 0.30-0.52% for soap solutions. The levels of individual parabens in individual cosmetic products ranged between 0.03% and 0 .42% w/w for skin care products, 0 .07% and 0.26% w/w for hair fixing gels and between 0 .11 % and 0 .34% w/w for soap solutions. Parabens were found in the highest concentrations in skin care products followed by soap solutions and the least amounts were found in hair fixing gels. Of the paraben-containing products tested, all of them contained methyl paraben and about 90% contained propyl paraben in addition to methyl paraben. One product contained all the parabens analysed.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)