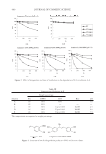
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 458 either the integrated intensity of diffuse refl ection (RD) or the half width of specular re- fl ection of the mounted hair tress (HWspecular) in the denominator of the fraction. Figure 5 shows the increase of the objective shine value achieved with a leave-in hair care prod- uct (care and style treatment) on blond hair tresses, as well as the effect of treatment on the single components—half width of specular refl ection, integral specular refl ection, and integral diffuse refl ection—that make up the objective shine value according to Figure 3. Determination of sparkle. The upper four photographs show the absolute intensities recorded for the same hair tress under four slightly different incident angles. The lower picture shows the standard devia- tions of the means of all individual pixels from the upper four pictures.
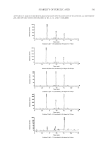
AUTOMATED DEVICE TO ASSESS HAIR SHINE 459 Reich/Robbins equation. The increase of the objective shine value in this case is mainly achieved by a reduction (-22%) of the half width of specular refl ection (HWspecular). This is accompanied by a slight reduction (-12%) of the integral specular refl ection (RS), which itself is more than compensated by a substantial decrease (-31%) of the integral diffuse refl ection (RD). In total, these changes add up to an increase in the objective shine value of 50%. The appropriateness of the equation of Reich/Robbins (eq. 1) has been correlated with eye-tracking investigations (5) of panelists assessing the shine of hair tresses mounted on Figure 4. Determination of combing values. To quantify the parallelism of a given hair tress, the entire object is divided into a defi ned number of vertical rows. At each position on a given row, the average hori- zontal intensity is calculated (upper panel). To assign a combing value to a given hair tress, vertical positions of iso-intensities (100%, 66%, 50%, 33%, and 25% of maximum intensity) of each individual row are de- termined (lower panel), and the means ± SDs of vertical position numbers for the respective iso-intensities from all rows are calculated. The combing value is determined as the mean of all standard deviations of the respective iso-intensities. The lower this value, the higher the parallelism of the hair fi bers.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)