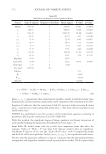
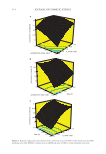
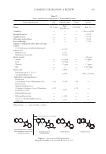
460 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Paprika Extract. Paprika extract is a red colorant obtained from the solvent extraction of the dried pod of capsicum (Capsicum annuum L.). The carotenoid composition and content of the paprika extract can vary depending on the type of red pepper and geo-climatic conditions. The identified major coloring components of this major carotenoid are capsanthin and cap- sorubin (Figure 11). In paprika extract, the pungent component, capsaicinoids, creates a serious limitation to its application (72). To use as paprika extracts as a colorant in cosmetics, they may undergo further purifications to remove the capsaicinoids. In the EU, the capsaicin con- centration is limited to 0.025%. Chlorophylls. The greenness in plants is because of chlorophyll which is composed of pheophytin che- lated with a magnesium ion. There are four types of chlorophylls: chlorophyll, chloro- phyllin, and copper complexes of chlorophyll and chlorophyllin. Generally, chlorophylls can be extracted from green plants. Chlorophylls a and b are the two major types of this pigments, and they differ only in the functional groups [methyl (a) or aldehyde (b)] attached to the C-7 carbon (Figure 12) (56). Chlorophyllin is obtained through the saponification of chlorophyll. Saponification or alkaline hydrolysis produces a water-sol- uble compound by removing the phytyl and methyl ester groups. A copper complex of O O HO OH Capsorubin O OH HO Capsanthin Figure 11. Structures of Capsanthin and Capsorubin. Figure 12. Structure of chlorophyll.
461 COSMETIC COLORATION: A REVIEW chlorophyll or chlorophyllin is obtained through the addition of copper ions to the plant extract or saponified plant extract. The major cause of chlorophyll degradation is the loss of magnesium ions because of a change in pH (56,62,73,74). As magnesium is easily isolated from the chloro- phyll structure, copper and zinc ions can replace the central magnesium ion. Copper is very effective for stabilizing the pheophytin and creates color consistency through- out the manufacturing process and storage (75). Therefore, copper chlorophyllin is the most commonly used colorant of the chlorophyll derivatives, and chlorophyll is rarely used because of its fragile nature. Copper chlorophyllin extracted from alfalfa is the only acceptable colorant made from chlorophyll derivatives in the United States (Table IX) (76). The term “chlorophyllin” is not an accepted name. However, it has been used incor- rectly by the food and cosmetic industry. Chlorophyllin contains a magnesium ion in its structure, so the term “copper-chlorophyll/chlorophyllin” is not adequate as copper replaces the central magnesium ion (75,77). Most importantly, the exact structure of the chlorophyllin-copper complex has not yet been elucidated fully. Copper chlorophyl- lin components differ in their origins, manufacturing processes, and storage conditions. The saponification process of chlorophyll is assumed to create diverse structures of cop- per chlorophyllins (e.g., Cu-chlorin e6, Cu-rhodin g7, Cu-chlorin e4, Cu-isochlorin e4, and Cu-chlorin P6 Figure 13). First, saponification hydrolyzes two ester groups to yield 132-carboxy pyropheophorbide a., and the β-ketoester of an isocyclic ring may be attacked again by the hydroxide ion to form Cu-chlorin e 6 (78–80). Oxidation at C132 or further decarboxylation has been attributed to the production of other copper chloro- phyllin products (81,82). In the EU regulations, the Cu-chlorophyllin a is described as 132-carboxy pyropheophorbide a, although it has been reported as a minor product in copper chlorophyllin mixtures (75). Table IX Comparisons in Chlorophyll Characteristics Chlorophylls Chlorophyllin Chlorophyll-Cu complex Chlorophyllin-Cu complex Manufacturing process Solvent extraction Solvent extraction + saponification Solvent extraction + addition of copper salts Solvent extraction + saponification + addition of copper salts Characteristics · ester-phytol bond (lipid-soluble) · product of saponification: → polarity↑ (water- soluble) · ester-phytol bond (lipid-soluble) · product of saponification: → polarity↑ (water- soluble) Stability Unstable Stable Europe Origin: edible plant material, grass, lucerne, nettle E 140 (i) E 140 (ii) E 141 (i) E 141 (ii) United States Origin: dehydrated alfalfa · Not listed · Not listed · Not listed §73.2125 Korea Origin: green plants (e.g., Chlorella pyrenoidosa, spinach, comfrey, spirulina) 64. (1) Chlorophylls · Not listed 64. (2) Chlorophyll- copper complex 64. (3) Chlorophyllin- copper complex
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)