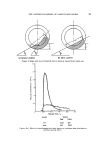
THE CONTINUOUS MIXING OF PARTICULATE SOLIDS 29 It is shown in the appendix that where a set of equations can be fitted to the residence time distribution function the variance reduction ratio can be calculated. Assuming that the correlation coefficient for the feed material 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0 0.5 I-0 1.5 2.0 2-5 Reduced time, t R Symbol Drum inclln(ffion --o-- 0ø15 ' •a-- I ø 30' --o-- 3 o 00' Figure 9(a) Effect of drum inclination on residence time distribution (at drum speed--60 rev min-l) R{r) is of the form a r, where "a" is taken as 0.11, implying almost random fluctuations, values of the variance ratio for drum speeds of 50, 60, 80, 100 and 120 rev min- 1 have been calculated and are shown in Table VII. For comparison the values of t•o2/t•i 2 for perfect mixing have also been included in Table VII. Values of t•o2/•i2 for speeds of 20 and 40 rev min- 1 will be greater than any value in Table VII they could be found by stepwise evaluation of the integral in equation XI. Examination of the results reveals that the values of t•o2/•i2 for runs at 60, 80 and 100 rev min-• are approximately equal to that for perfect
30 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS mixing the slight variation of the value of C•o2/(•i2 from run to run may be considered to be within experimental error. In fact, this has been sub- stantiated by repeating these experiments. Value of C•o2/(•i2 for runs at speed 50 and 120 are greater than for ideal mixing. 2'5 w 2.0 I 0 2-5 0.5 o 1.0 I-5 2.0 Reduced time', t R Symbol Drum inclin(3tion • 0ol5 ' • I 0 ø 30' •e• 3 ø O' Figure 9(b) Effect of drum inclination on residence time distribution (at drum speed--80 rev min-l) It is expected that there would be good agreement between the values of C•o2/(•i2 calculated from response functions and those obtained by direct measurement. The condition for this is that the system must be strictly continuous, i.e. inflow and outflow in any finite time interval is equal and constant and the hold up is constant. Since the present system does not satisfy these conditions direct measurement of C•o2/C•i2 would be expected to give higher values. In practice the value of C•o2/C•i 2 will also depend on the local inhomogeneity of both inflow and outflow. Since in a drum mixer the radial mixing is very rapid (16) the outflow with non-segregating com-
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)