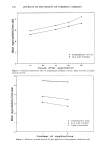
218 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Absorbance units Absorbance units 100% ETHYL ALCOHOL ,/•'•\,\ ', •.--'"-"-",-,. .• ,./' I I -- "• " I •,, 800 0 • I W•vele•th (nm)l • I • I I I i I HEINE • I ' , /,.' I 1 , O Waveleith (nm) Figure 5. UV absorption spectra of octyl dimethyl PABA showing a bathochromic shift in the h max in the UVB region (290 to 320 nm) from a non-polar solvent (hexane) to a polar solvent (ethanol). Triethanolamine salicylate, octyl salicylate, homomenthyl salicylate, and menthyl anthranilate showed only minor variations in h max in both polar and non-polar sol- vents (Table III and Figure 3). The minimum shift of the h max is due to the ortho- substituted configuration of salicylates and anthranilates. The lone pair of electrons are involved in the six-membered cyclic arrangement and, as a result, are not available for interaction with polar solvents (Figure 6). Hence, ortho-substituted compounds tend to exhibit moderate to low • max shifts in polar solvents. Although oxybenzone and dioxybenzone both may form a six-membered cyclical arrangement, similar to the salicy- lates and anthranilates, they exhibit added polarity due to the additional hydroxy and methoxy groups. A more in-depth explanation for the shifts and changes observed in the • max that occur when sunscreen chemicals are dissolved in both polar and non-polar solvents has been provided in separate reports by Shaath (10, 11).
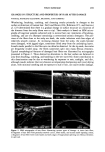
SOLVENTS AND SUNSCREEN ABSORBANCE 219 Table V Relative Lipophilicity of Sunscreen Chemicals Based Upon Their Calculated Partition Coefficients Between Octanol and Water CTFA name Other names Log P @25øc Glyceryl PABA Benzophenone-4 PABA Benzophenone-8 Cinoxate Benzophenone-3 Ethyl dihydroxypropyl PABA Amyl dimethyl PABA Butylmethoxy dibenzoylmethane Menthyl anthranilate Octyl salicylate Homosalate Octyl methoxy cinnamate Octocrylene Octyl dimethyl PABA 1,2,3-Propanetriol, 1-(4-aminobenzoate) - 0.02 Sulisobenzone - 1.51 p-Amino benzoic acid 0.74 Dioxybenzone 2.15 Ethoxyethyl methoxy cinnamate 2.55 Oxybenzone 2.63 Ethyl-4-bis(2-hydroxypropyl-aminobenzoate) 2.84 Amyl dimethyl PABA 4.53 Butylmethoxy dibenzoylmethane 4.86 Menthyl-O-aminobenzoate 5.05 2-Ethylhexyl salicylate 5.30 Homomenthyl salicylate 5.61 Ethylhexyl-p-methoxy cinnamate 5.65 Octyl cyanodiphenylacrylate 5.69 2-Ethylhexyl-p-dimethyl aminobenzoate 6.08 CHANGES IN MOLAR ABSORPTIVITY In addition to shifts in X max, both increases and decreases in the molar absorptivities (½) of sunscreen chemicals were also observed in the various test solvents. In general, and with the exception of PABA, the rest of the UVA and UVB sunscreens selected for study showed increased ½ values at X max in both polar (ethanol-water systems) and non-polar (hexane and mineral oil) solvents. In contrast, there were signif- icant decreases in ½ values at • max when the sunscreen chemicals were dissolved in semi-polar solvents such as hexylene glycol and C•2-C•5 alcohols benzoate. These data (taken from Data Tables II-IV) have been summarized in Tables VI and VII. Reduction in molar absorptivity varied between 12% and 55% for hexylene glycol and between 7% and 28% for C•2-C•5 alcohols benzoate. In addition, employing a spectro- photometric technique suggested by Vogelman et al. (12), overall reduction in the area H 6 ø I I 0 -- Menthyl 0 -- Octyl (a) (b) Figure 6. Steric configuration of ortho-substituted molecules, (a) menthyl anthranilate and (b) octyl salic- ylate.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)