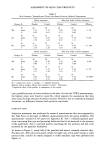
TRANS-3-METHYLBUTYL 4-METHOXYCINNAMATE 45 0.0 -0.5 -1.0 = -1.5 •., -2.0 • -2.5 -3.5 -4.0 COOR OCH 3 trans I COOR cis 1 -- - •,• ,,,,,,,'"' ,,,,,,,'" Solar-Simulat , ,,"" ,,'" • Red Limit ß ß 288 292 296 300 304 308 312 316 320 Z, [nm] Figure 2. Emission spectrum of the solar simulator in the UV-B range. CH30 • •- RO0•'•,,,"' % )CH 3 9'_COOR .- Ar•' 6 7 ,oo, I]i / j 9' , 7••3 H 0 CH30 , ..... a• 0•,, ........... •OH 7•..,COO R dienophile •cb•oR diene • •c• •' Ar '"'"' '•COO R ROOC .... '• Ar Ar • "ß•CO O R _s _s 7 OCli3 11 la Figure 3. Sunlight-induced reaction products of 3-methylbutyl 4-methoxycinnamate.
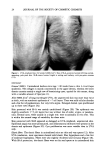
46 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table I NMR Data of 2 -- Coupling •H-NMR constants •3C-NMR 8 [ppm] NOE J [Hz] 8 [ppm] COLOC H-2 H-3 6.34 (brd) H-7 (5%) 6.5 C-1 130.2 (s) H-7' (2%) 3.10 (ddd) H-8' (5%) 9.5 6.5 1.5 C-2 134.6 (d) H-2'/6' (3%) H-2 (7%) H-5 H-8 H-3 H-5 5.82 (brd) 10.5 C-3 46.1 (d) H-7" H-8' H-6 6.66 (dd) 10.5 1.5 C-4 73.0 (s) H-2 H-3 H-8' 4-OMe H-7 7.24 (d) 16 C-5 124.8 (d) H-8 6.08 (d) 16 C-6 126.2 (d) H-10 4.20 (t) 7 C-7 143.6 (d) H-11 1.60-1.50 (m) C-8 116.6 (d) H-12 1.72 (m) C-9 167.2 (s) H-13 0.94 (d) 7 C-10 63.2 (t) H- 14 0.94 (d) 7 C- 11 37.3 (t) 4-OMe 3.16 (s) H-8' (2%) C-I' 133.1 (s) H-5 (4%) H-2'/6' 7.21 (d) 8 C-2' 127.9 (d) } AA' BB' system C-3' 114.0 (d) H-3'/5' 6.87 (d) 8 C-4' 158.7 (s) H-7' 3.25 (dd) H-2'/6' (3%) C-5' 114.0 (d) H-2'/6' (3%) 10 9.5 C-6' 127.9 (d) H-3 (3%) H-10' 4.15 (m) C-7' 41.5 (d) H-11' 1.60-1.50 (m) C-8' 59.1 (d) H-12' 1.65 (m) C-9' 63.5 (t) H-13' 0.90 (d) 7 C-11' 37.4 (t) H-14' 0.90 (d) 7 C-12' 25.1 (d) 4'-OMe 3.80 (s) C-13' 22.4 (q) C-14' 22.4 (q) 4'-OMe 55.3 (q) H-2 H-2 H-3 H-2' H-7 H_7 • H-2" 4'-OMe H-7' H-8' The UV spectroscopic data were determined densitometrically with the aid of the (Camag) HPTLC. The •H NMR (400 MHz) and the •3C NMR (400 MHz) spectra were recorded using the Bruker AC 400 instrument. RESULTS The •H NMR spectrum of the crude mixture from irradiation shows, besides the signals for the parent material, those of the corresponding cis derivatives as the main reaction product. The trans/cis ratio is 25:1, easily determined by integrating the olefinic signals of each of the isomers. The signals of the rest of the reaction products are also already detectable. Subsequent separation revealed photochemical products identified using NMR spectroscopy (Figure 3). Photochemical product 2 represents the main component of the reaction product. The
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)