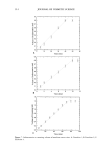
MATRIX COMPOUNDS AND OXIDATIVE HAIR DYES 237 retention time between 5 min and 30 min. Some of the tested dyes have very close retention times--4-n-l,2-pd, 2-a-4-np, and 4-a-2-ht for instance, their retention times being 15.10 min, 15.50 min, and 15.66 rain, respectively. However, since their respec- tive UV spectra show remarkable differences (8), their identification can still be carried out easily. In order to test the repeatability, five injections of each sample were carried out. The relative standard deviation (RSD) for the retention time was between 0.2% and 1.1%, while that of the peak corrected areas (defined as the peak area divided by the retention time), recorded at 290 nm, was between 1.1% and 6.0% (9). The chromatographic behavior showed good repeatability. The injections were repeated on three different columns in order to test the reproduc- ibility (Table II). For thirty-six hair dye intermediates, the relative standard deviation (RSD) on the retention time was less than 5% for nine dye intermediates, this RSD was between 6% and 10% and more than 10% for only two dyes. The reproducibility between columns was considered satisfactory. Single solutions of matrix compounds. Eight different compounds were subjected to chro- matographic separation, and their retention times and UV spectra were recorded. Results are presented in Table III. It appears that some of the tested compounds have very close retention times--BHT, OA, and ORA, for instance. However, with their respective UV spectra also showing remarkable differences (Figure 1), their identification can still be carried out easily. It must also be noted that most of the matrix compounds, with the exception of DMDM, PVP and MP, have retention times greater than 30 minutes, meaning that confusing dye intermediates with matrix products should not occur since the retention times of the hair dyes generally range from 5 to 30 minutes (1). Concerning the four dye intermediates for which retention times are out of the range of 5 to 30 min, the discrimination from the matrix compounds can also be easily made according to both retention time and UV spectrum. In order to test the repeatability, five injections of each sample were carried out. The relative standard deviation (RSD) for the retention time was between 0.02% and 0.7%, while that of the peak corrected areas was between 0.3% and 3.7%, except for DMDM. The chromatographic behavior of the matrix compounds showed good repeatability. Table III Retention Times and Corrected Peak Areas for Eight Matrix Compounds, Each in a Single Solution (n = 5) Retention time (min) Corrected peak area (AU) Matrix compound Mean RSD (%) Mean RSD (%) k of measurement (rim) DMDM 6.80 0.21 4.3 12.4 220 PVP 7.10 0.24 1.1 0.2 220 MP 26.87 0.06 1.0 1.8 290 NNO 33.80 0.70 5.2 3.4 235 EOP 35.85 0.08 5.8 0.3 290 OA 37.97 0.30 20.6 2.9 235 BHT 38.11 0.02 2.5 3.7 290 ORA 38.35 0.09 12.2 0.5 235 AU: arbitrary unit.
238 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Butylated Hydroxytoluene 1000-- 500• -s22| I 200 300 Figure 1. UV spectra of three matrix products. 400 Wavelength (nm) Sample solutions containing an additional matrix compound and three dye intermediates. From the forty-seven dye intermediates tested, four were chosen for further investigation based on how representative they were of their different classes of hair dyes as well as on their use in formulations. Three sample solutions were prepared, each containing a mixture of three selected dye intermediates (1,4-pd or 4-ap, res, and 2-n-l,4-pd), the intrinsic matrix compound NaAsc as an antioxidant, and another major matrix compound, BHT, DMDM, or EOP, respectively. BHT is an important antioxidant, DMDM a commonly used preservative, and EOP a perfume solubilizer. The retention time of BHT and EOP is more than 30 min, while DMDM is eluted within about 7 min. Three control solutions, mixtures of the respective dyes without the major matrix compound, were also prepared. All the components were at the concentrations used in formulations according to COLIPA, and five injections of each type of solution were made. For each series of measurements of control and mixture, a new column was used, as it has been shown in a preliminary study that after 50 injections, the efficiency of the column is dramatically decreased (data not reported). Table IV gives the statistical results obtained for the retention times and the corrected peak areas for each of these compounds. Comparison of the data between mixture ! (BHT) and control 1, mixture 2 (DMDM) and control 2, and finally mixture 3 (EOP) and control 3 leads to several observations. First of all, as shown by the results, DMDM or EOP do not interfere with the dye intermediates or with the column in a way that would change the chromatographic
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)