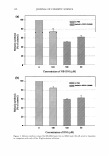
]. Cosmet. Sci., 59, 159-161 (March/April 2008) Abstracts International Journal of Cosmetic Science Vol. 29, No 6, 2007* In vitro assessment of water resistance of sun care products: a reproducible and optimized in vitro test method M. Pissavini*, V. Alard_, U. Heinrich_, K. Jenni§, V. Perier-, V. Tournier**, D. Lutz__, M. Meloni__, D. Kockott§§, L. Ferrero*, B. Gonzalez_, L. Zastrow* and H. Tronnier_ *Coty-Lancaster, International Research & Development Center, 2 rue de la Lujemetta, 98000 Monaco, Monaco, _L VMH Recherche, Branche Parfums et Cosme'tique, 185, Avenue de Verdun, 45804 St Jean de Baye, France, _Dermatronier, Institut ft( r Experimentelle Dermatologie, Universita .. t Witten/Herdecke, 58455 Witten, §Degussa GmbH, Business Line Goldschmidt Personal Care, 45127 Essen, Germany, -Pierre Fabre Derrno-Cosme'tique Centre de Recherche & De'veloppement, Alle'e Camille Soula, Vigoulet, **Dipta, 505 rue Pierre Berthier, 13855 Aix--en- Provence cedex 3, _Helioscience, 36 rue Borde, 13008 Marseille, France, _ VitroScreen, 17 Piazza Giulio Cesare, 20145 Milan, Italy and §§UV-Technik, 27 Vogelsbergstrabe, D-63456 Hanau-Steinheim, Germany M. Pissavini, Coty-Lancaster, International Research & Development Center, 2 rue de la Lujernetta, 98000 Monaco, Monaco. Tel.: +00 377 92 05 47 05 fax: +oo 377 92 05 47 47 e-mail: marc_pissavini@cotyinc.com The aim of the study was to develop a simple reproducible and reliable in vitro water resistance (WR) method to assess the sun care products. This paper is the result of a scientific collaboration between seven different international industrial laboratories and testing institutes. The same group has already achieved an in vitro protocol for the sun protection factor (SPF) determination [ 1]. The in vitro WR of sunscreens was tested by applying the same principle as in vivo, which determines the percentage of retention of sunscreen products by assessing the SPF before and after water immersion. Special care was taken to study the parameters influencing the WR and the possibility to follow the kinetics of sunscreen retention during water immersion. The influence of different water qualities has been tested, and osmosed water (1-3 IS cm-I) was chosen for the main ring study. Measurement was carried out after 5, 20 and 40 min of immersion. Histograms of selected products demonstrate the percentage of WR at all measuring times and centres, and the regression coefficient to the in vivo determination was shown and statistical calculations clearly demonstrate the reproducibility of the results between the different evaluation centres. The presented method is a practical, convenient and relevant tool for WR screening of sun care and skin care products. It even has the potential to be the starting point for the replacement of the in vivo method in future. Evaluation of black tea gel and its protection potential against UV M. Turkoglu* and N. Cigirgil_ *Faculty of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical Technology Department, Marmara University, 34668 Haydarpasa, Istanbul and _KOPAS Cosmetics, Inc., Istanbul, Turkey Murat Turkoglu, Faculty of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical Technology Department, Marmara University, 34668 Haydarpasa, Istanbul, Turkey. Tel.: (90) (216) 418 5029 fax: (90) (216) 345 2952 e-mail: turkoglu@marmaraedu.tr In this study, aqueous and alcoholic extracts of black tea were obtained. The black tea extracts were tested in vitro for their ultraviolet (UV) absorption profile. It was found that both extracts showed UV absorption and followed the same path based on the wavelength. Aqueous extract showed a stronger absorptivity per weight basis than the alcoholic extract of black tea. A peak was obtained between 250 and 300 nm. After 300 nm, UV absorption decreased fast towards 400 nm with a low absorptivity. The black tea aqueous extract was formulated as a gel with the help of a * These abstracts appear as they were originally published. They have not been edited by the journal of Cosmetic Science. 159
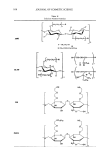
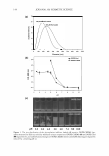
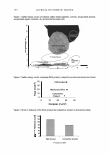
160 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE carbomer resin and tested in vivo in six subjects for evaluating its protection potential against the UV (200--400 nm) using an artificial UV source consisting of a high pressure metal halide discharge lamp. Based on erythema evaluation, it was found that erythema appeared after 4 h and reached a peak at 24 h o n control site. On the contrary, no erythema was observed in any of the six subjects on black tea gel applied sites. Therefore, it was concluded that black tea gel protected the skin from a broad range UV (200--400 nm) radiation. The black tea gel can be safely applied in large amounts on large skin surfaces without any toxicological concerns. Influence of different parameters on droplet size and size distribution of sprayable sunscreen emulsions with high concentration of UV-filters L. Durand*, N. Habran_, C. Denis_, L. Meulders_, V. Henschel* and K. Amighi* *Laboratory of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, Universite· Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, _Eurocos Consult, Dion-Valmont and _Lambiotte & Cie S.A./N.V., Bruxelles, Belgium K. Amighi, Laboratory of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, Universite' Libre de Bruxelles, 1050 Brussels, Belgium. Tel.: +3226505252 fax: +3226505269 In vivo persistent pigment darkening method: proposal ofa e-mail: kamighi@ulb.ac.be new standard product for UV A protection factor determination D. Moyal*, M. Pissavini_, F. Boyer_, V. Perier and J. H. FreAlon§ - *L'Ore'al Recherche, 25/29 Quai Aulagnier, 92665 Asnie'res Sur Seine, France, _Coty-Lancaster, International Research & Development Center, 2 Rue de la Lujemetta, 98000 Monaco, _Pierre Fabre Dermo Cosme'tique, Alle'e Camille - Soula Vigoulet Auzil, 31322 Castanet Tolosan, France and §Fe'deration des Industries et de Ia Parfumerie, 33 Champs Elyse· es, 75008 Paris, France Dominique Moya!, L'Ore'al, 25/29 Quai Aulagnier, 92600 Asnie'res Sur Seine, France. Tel.: +33 147568134 fax: +33 147567995 e-mail: gmoyal@rd.loreal.com The European Commission (EC) has recommended assessing the level of ultraviolet A (UV A) protection afforded by sunscreen products using the in vivo persistent pigment darkening (PPD) method or other methods giving equivalent results. In this context, the reproducibility of the in vivo PPD method is ofimportance. To check the validity of the UV A protection factor (UVAPF) tests, the Japanese Cosmetic Industry Association (JCIA) recommends using a standard product (JCIA standard) with an expected UV APF 3.75 (SD 1.01). However, considering the increase in UVA efficacy of the new sunscreen products available in the market, with UV APF up to 30, it seemed useful to develop a new standard product to be used when testing products with expected UVAPF tl0. The PPD method was used in six centres to determine the UVAPF of the two products. Reproducibility of results was also studied by testing two batches of the new product at two different times. There was no statistical difference between the six centres with regard to the JCIA standard. The ring study showed that the mean value ofUVAPF (4.3) was higher than that given by JCIA (3.75). These data enable the proposal of a new acceptance range for the JCIA standard product (3.4-5.2) derived from actual results from European laboratories. Whereas this range is different from that proposed by JCIA (2.74-4.76), there is an overlapping of the values. Data on the new standard product show that reproducibility is not influenced by the batches of this product. The mean UV APF value obtained is 12.1. An acceptance range (9.6- 14.6) is proposed for the new standard. Data presented here demonstrate that if an identical protocol is used, reproducible results can be expected and that the PPD method is reproducible and reliable. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the possible influence of different formulation and technological parameters such as sunscreen type and concentration, viscosity, propellant gas, actuator and valve type on size and size distribution of droplets in emulsions of waterproof sunscreens conditioned in aerosol cans. Different kinds of emulsion, W/Si and W/O, were prepared with high concentrations of organic and inorganic UV-filters. These formulations were incorporated in aerosol cans with gas (a blend of butane, propane and isobutane). The size and size distribution of the droplets were analysed by laser diffraction using a Malvern_ Spraytec. The results showed that the sprayability of the formulation and the particle size characteristics of the emitted sprays are dependent on the physicochemical properties of the formulations. Sprayable waterproof sunscreen emulsions, with a high sun protection factor and negligible percentage of emitted droplets below 30 Im, were successfully developed by optimizing formulation parameters and using appropriate actuators and valves. Review Article Global and systematic demonstration for the practical usage of a direct in vivo measurement system to evaluate wrinkles T. Fujimura, K. Haketa, M. Hotta and T. Kitahara Biological Science Laboratories, Kao Corporation, 2606, Akabane, lchikai-machi, Haga-gun, Tochigi 321-3497, Japan Tsutomu Fujimura, Biological Science Laboratories, Kao Corporation 2606, Akabane, lchikaimachi, Haga Tochigi 321-3497, Japan. Tel.: +81 285 68 7871 fax: +81 285 68 7469 e-mail: fujimura.tsutomu@kao.co.jp The global and systematic demonstration for the practical usage of a direct three-dimensional in vivo measurement system (PRIMOS) to evaluate wrinkles was investigated. Ten repetitive measurements of the comer of the eye of a subject showed that the coefficient of variation (CV)% value was 7 .0% in a typical line-length roughness parameter Ra (the arithmetic mean of roughness), and that the CV% value in a typical surface area roughness parameter Sa was 2.4%. The relationships between the roughness values obtained from the comers of the eye and the age or wrinkle scores of Japanese women aged 10-70
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)