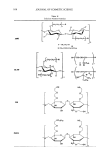
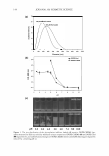
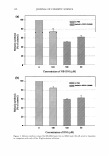
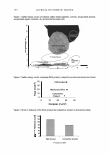
164 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE A New Decorin-like Tetrapeptide for Optimal Organization of Collagen Fibers Arturo Puig, Jose Marfa Garcia Anton, Montserrat Mangues Lipotec SA, Isaac Peral 17, 08850 Gava, Barcelona, Spain Decorin interacts with collagen via its protein core and influences collagen fibrillogenesis, thus regulating excessive bundle-I ike aggregation of collagen. As skin ages, there is a lack of functional decorin which results in disrupted collagen fibers and a reduction in the tensile strength of the skin. Therefore, a substitute for decorin would make up for the non-functional decorin that is present as we age. Two tetrapeptide sequences were identified as the specific binding sites of decorin to collagen fibrils. These sequences were engineered in order to generate new tetrapeptides with improved affinity that would present a decorin-like activity. A focused library of several candidates was synthesized containing only tetrapeptides that mimicked the binding sequences of decorin. The candidates were screened with an in vitro collagen fibrillogenesis assay, and the tetrapeptide with the INCi name Tripeptide-10 Citrulline achieved the best results. Like decorin, this synthetic tetrapeptide proved in in vitro tests to regulate collagen fibrillogenesis and influence the diameter of collagen fibers, making them thinner and more uniform. Tri peptide-IO citrulline is a new cosmetic active to specifically target collagen fiber organization. Skin collagen quality is addressed rather than skin collagen quantity. Tripeptide-10 citrull ine ensures uniformity of fibril diameter and increases skin suppleness due to a better cohesion of collagen fibers. Winner of the Award for the best Podium Presentation at the IFSCC Conference 2007, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Water Management of Human Hair Franz-J. Wortmann1 , Alexandra Hullmann2, Crisan Popescu3 1 School of Materials, University of Manchester, Sackville Street, Manchester M60 1 QD, UK 2 Kao Professional Salon Services GmbH, Pfungsutdter Str. 92-l00, D-64297 Darmstadt, Germany 3 DWI e.V. and Institute of Technical and Macromolecular Chemistry, RWTH Aachen University, Pauwelsstr. 8, D-52074 Aachen, Germany and University »Aurel Vlaicu«, Bd. Revolutiei 77, RO-310130 Arad, Romania Temperature dependent isotherms for the water ab- and desorption of human hair were determined (25-65°C) together with the related diffusion coefficients and hysteresis effects. Special care was taken to standardize the physical history of the samples. With increasing temperature, isotherms, while preserving their shape, shift to lower regains while the hysteresis effect decreases. This is in accordance with expectations derived from the Rosenbaum-model for water sorption. The differential heat of water sorption changes from dry to wet hair between 1020 and 50 Jig H2O. Diffusion coefficients are of the order of I 0·9 cm2/s. The coefficients increase with temperature and show a pronounced maximum in the range of medium regains. The temperature dependence follows the Arrhenius equation and exhibits activation energies that change from dry to wet hair between 55 and 30 kJ/mol. The sorption performance of strongly bleached hair, with and without an additional treatment with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, was investigated. No significant effects either of the cosmetic treatment or of the ingredient were found. It is concluded that human hair exhibits a rather robust static and dynamic water sorption performance that, against initial expectations, is not readily changed by cosmetic processes and ingredients. Super Mild Oxidation Coloring: Preventing Hair Damage at the Molecular Level Thomas Doering, Claudia Brockmann, Annin Wadle, Detlef Hollenberg, and Thomas Forster Henkel KGaA, 40191 Dusseldorf, Germany Hydrogen peroxide is widely used for oxidation hair coloring or bleaching. It displays a high redox potential and easily penetrates into the hair fiber. This renders hydrogen peroxide capable of non-specific interactions with cortex and cuticle proteins resulting in irreversible cleavage of cystine crosslinks. Various classes of antioxidants were screened for their anti-hair damage effect in a permanent hair dye formulation using NIR spectroscopy. In parallel, the effect on the coloring and lightening performance was studied to exclude unwanted side effects on primary product performance. The screening criteria were fulfilled by organic disulfides such as a-lipoic acid but interestingly not by powerful antioxidants such as tocoperol, dibutylhydroxytoluene, or beta-carotene. Alpha-lipoic acid significantly protected human hair during oxidation coloring as demonstrated by (i) amino acid and protein analysis, (ii) surface polarity measurement, (iii) lipid analysis, (iv) differential scanning calorimetry, and (v) combing work measurement. Our results show that radical scavenging properties alone do not render antioxidants suitable for hair protection during oxidative treatments. The presence of disulfide bonds appears to be very favorable and it is likely that the intramolecular cross-link within a-Iipoic acid provides a kinetically controlled protection for cystine crosslinks during oxidation coloring.
J. Cosmet. Sci., 59, 165-166 (March/April 2008) Abstracts Journal of the Polish Society of Cosmetic Science, "Wiadomosci PTK" Vol. 10, No. 4, 2007* Safety Asspects of the Sunscreen Products Use Stanislaw Krus, Jacek Arct, Katarzyna Pytkowska Academy of Cosmetics and Health Care, Division of Cosmetic Chemistry, Warsaw, Poland Sunscreen products are the important part of the cosmetic market. UV filters are used in sun care products, a well as in used every day personal care cosmetics. UV filters are also important in professional cosmetics, and cosmetic dermatology, used for skin protection after invasive treatments. Sunscreens should mainly protect skin against photoaging and DNA damage, which may cause skin neoplasm. Sun care products should also protect against skin irritation - an effect of UVB radiation. High value of the protection factors of sunscreen is associated with high concentration of organic filter that sunscreen product contains. Alternatively the inorganic sunscreen - micronized pigments, especially Titanium Dioxide may be used. Unfortunately, both organic filters and micropigments, may cause side effects in human. Organic filters (e.g. hydroxyl benzophenone derivatives) are supposed to have estrogenic activity. Affinity of those substances to estrogen receptor is weak nevertheless they can be dangerous, especially in children. Another problem is photostability of UV filters. Knowledge on structures, properties of the UV filters decomposition products of is stilt inadequate. Micropigments also may undergo changes when exposure to UV radiation. On the surfaces of micropigmcnt active centers may be formed. Thus, such ingredient may act as sensitizer. Insufficient stability of the products, cause by catalytic activity of micropigment, or reaction between ingredients of the cosmetic product also may occur. Coatings of micropigments with inert films may eliminate such activity. Side effect of sunscreens are not proven, parallel there are evidential negative UV effects in human. Furthermore there are not alternative methods of protection against UV radiation. Because of that we arc made to use of UV filters, micropigmcnts, not I 00% safe, but only ones that may protect us before UV. Nanotechnology And Wellness Pierfrancesco Morganti 1 • 2 • 3 , Gianluca Morganti 3 1 II University of Naples, 2 China Medical University Shenyang, 3 Mavi Sud s.r.l. The new frontier of material research have been taken, probably, the more high level by the development of material systems made up of components with nanoscale dimensions and by the availability of technologies allowing the tailoring of material structure at the nanoscale. Thus many research centres, for example, are focusing their studies on developing new knowledge-based multifunctional surfaces and materials with tailored properties and predictable performance, for new products and processes targeting a wide range of applications, such as human tissue like physical and mechanical behaviour. Originally published in the SOFW-Joumal 133(5) 2007 *These abstracts appear as they were originally published. They have not been edited by the Journal of Cosmetic Science. 165
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)