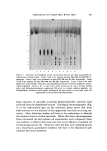
CHEMICAL DIFFERENTIATION IN EPIDERMIS 589 Preliminary data indicate that the HP has a single N-terminal amino acid residue, lysine with its •-amino group blocked in some, as yet un- known, manner. There also appears to be only one C-terminal residue which is arginine (12). The same terminal residues are present in the "urea-soluble" fraction prior to treatment with PCA. On the other hand, the "0.1N PCA-insoluble" fraction shows new N-terminal residues. These are glycine, serine, threonine, and possibly aspartic acid. The C-terminal residue of the "O.1N PCA-insoluble" fraction is arginine. Surprisingly, therefore, no new C-terminal residue has been detected to coincide with the finding of the new N-terminal residues. It may be that the HP is attached to the protein which remains insoluble in 0.1N PCA by peptide linkages between the newly uncovered N-terminal residues of the insoluble fraction and a y-carboxyl of glutamic acid or a fi-carboxyl of aspartic acid in the HP. However, the y-carboxyl-linked glutamyl residue of glutathione is not released by exposure to 0.1N PCA at room temperature. The "urea-extractable" protein which contains the HP is now being extensively purified so a definitive study of the nature of the "PCAdabile" linkage can be done. "NONHISTIDINE" IMIDAZOLE IN EPIDERMAL UREA-EXTRACTABLE PROTEIN Comparison of the titration curves of the "urea-extractable" protein before and after exposure to PCA indicates that a fivefold increase in titratable imidazole results from the PCA treatment (13). Surprisingly, after the protein is exposed to 0.1N PCA at 24øC for 30 minutes, there is five times more titratable imidazole than there is histidine by amino acid analysis. The Pauly analytical technique, which is relatively specific for the iInidazole group (14), confirms the titration data. Table III gives the results of a particular experiment in this regard. The "non- histidine" imidazole is dialyzable after the PCA treatment. Table III Imidazole in Epidermal Protein of the Newborn Rat Urea-Extractable Protein (t•moles imidazole/g) Dialyzed urea extract By titration with HC1 By amino acid analysis for histidine Cold PCA extract By amino acid analysis for histidine By titration with HC1 Bv Pauly reaction with urocanic acid as std. 230 25O 157 74O 75O
590 .JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS The presence of large amounts of urocanic acid in the epidermis (15, 16) makes this compound a prime candidate as the "nonhistidine" imidazole in the "urea-extractable" protein fraction. The substance can be removed from the dialyzate by adsorption on Dowex-1 (formate). After elution from the ion exchanger resin, the compound shows similar absorption spectra, at various pH values, with authentic trans-nrocanic acid. There is no free amino group. Conclusive identification has not yet been achieved, however. COPPER IN EPIDERIX4AL UREA-EXTRACTABLE PR()TEIN The presence of large amounts of iinidazole in the "urea-extractable" protein suggests the presence of metal ions. Emission spectroscopy indi- cates the presence of copper as the only metal ion which is nondialyzable against EDTA in the "urea-extractable" protein fraction (13). As shown by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, treatment of this protein fraction with 0.1N PCA at room temperaure makes all the previously bound copper ion dialyzable. As a working hypothesis, it is being as- sumed that the liberation of copper ion is related to the splitting out of the HP and the appearance of titratable imidazole. Obviously, these three phenomena may not be related and much more work will be nec- essary to substantiate this hypothesis. RELATION OF THE "HISTIDINE-RICH" PROTEIN TO KERATOHYAI,IN Demonstration that keratohyalin contains a great deal of histidine (14), that administered tritiated histidine finds its way into keratohyalin (17), and that, kinetically, this labeling of keratohyalin appears to occur after formation of labeled protein in the cytoplasm outside the kerato- hyalin granules (18) makes it attractive to postulate (18) that the HP is a precursor of keratohyalin. If this were so, a "handle" would be available to study the role of the HP in epidermal differentiation and, possibly more important, to investigate the role of keratohyalin in the keratinization process. As •neasured by autoradiogTaphy at the ultrastructural level, 30 minutes after the intradermal administration of histidine-all only about 25% of the silver grains in the granular cells appear over the kerato- hyalin granules, while by six hours, the number increases to about 75% (18). Fractionation of protein (Fig. 2) from a "granular-cornified" cell preparation (8) at 30 minutes and at six hours after the intraperitoneal injection of histidine-all shows that, at both times, 75-85% of the labeled
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)