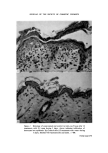
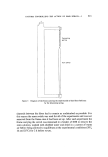
MALE PATTERN BALDNESS 527 an unidentified non-polar metabolite X. The percentage of each of these components in the skin extract is shown in Table L With the exception of the non-polar metabolite X, these steroids have all been found previously in incubations of testosterone with human skin from abdominal and sexual sites (16-18). There was no sign of a metabolite possessing the 5 [3-configu- ration in this or any other of the incubations described here. Table I The metabolism of [4-x4C]testosterone by human male scalp skin. 101aCi of [4-x4C]testosterone (specific activity 58.2 mCi/mmol) was incubated with 301.5 mg of semi- bald male scalp skin for 5 h at 37øC with shaking under air in 5 ml tissue culture medium 199. Metabolite Percentage Polar material (origin) 0.5 5a-Androstane-3a,1713-diol + other diol(s) 2 Unchanged testosterone 46 Androsterone 4 Epiandrosterone 2 Dihydrotestosterone 23 Androstenedione 8 An d ro stanedione 13 Unidentified non-polar metabolite X 1 Ancillary experiments In all experiments, hairy skin samples were taken from the occipital region of the scalp which in the majority of balding men remains hairy throughout life. In some preliminary work one hairy skin sample and one sample from a bald region of the scalp were cut parallel to the skin surface at a depth of about 2 mm so that the upper parts contained all the epidermis and substantially all the sebaceous glands and dermis while the lower parts contained mainly adipose tissue and the hair bulbs. Each piece of skin was incubated separately with testosterone under the conditions described above. Thin-layer chromatography of the skin extracts showed that both the upper and lower portions of the hairy biopsy specimen metabolized testosterone to give the metabolites found previously, both halves giving similar proportions of the metabolites. Some differences were observed in the percentages of the various metabolites in the upper and lower portions of the bald biopsy specimens but the experiment served to demonstrate that the metabolism of testosterone is not confined to sebaceous glands or any
528 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS one skin stratum. That steroid-metabolizing enzymes are not confined to the sebaceous glands has also been shown by Wilson and Walker (17) using skin from the leg and the sole of a foot. Whilst skin from only one subject was used by us, it is worth noting that the unidentified metabolite X com- prised a greater proportion of the metabolites in the extracts of the lower portions of the skin than in the extracts of the upper portions. Also another unidentified metabolite Y, of polarity intermediate between that of andro- stenedione and androstanedione was found in the extracts of the lower, but not the upper, portions of each biopsy specimen. A brief investigation of the metabolism of testosterone as a function of time showed that there was considerable metabolism after 1 h and this period was therefore used for the quantitative studies. Quantification of metabolism The second main experiment was carried out using bald and hairy skin samples taken from five balding males under local anaesthesia. The skin specimens were between 3 and 5 mm in diameter and approximately 4 mm deep. These samples were incubated with [4-•4C]testosterone for 1 h at 37øC under air within 30 min of being removed from the scalp. The bald biopsy specimen from subject PFW (see Table I1) was taken from an area which had been rubbed daily with an aqueous-alcoholic solution of testosterone (1•o) for 61 days immediately prior to the removal of the skin sample. This Table II Specific uptakes of [4-x4C]testosterone by bald and hairy human male scalp skin in vitro. Incubation of [4-x4C] testosterone with bald and hairy human scalp skin for 1 h at 37øC under air. Donor Uptake of [4-11C] testosterone in Ratio of pmol/mg extracted skin uptakes Bald Hairy (bald/hairy) PFW 318' 381 0.84 PA 344 299 1.15 JZ 398 257 1.55 AC 461 282 1.64 CB 288 185 1.56 *This biopsy specimen was taken from the site to which the non-radioactive testosterone had been applied.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)