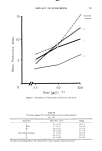
528 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS skin by clear occlusive tape (Blenderm, 3M). Two hours later, the test sunscreens were applied at a dose of 5.0/xl/cm 2 and exposed to UV-A at 30-sec increments. The Minimum Phototoxic Dose (MPD) is the least exposure that produces erythema 24 hr later. The P.F. in this case is the ratio between the MPD in sunscreen treated and untreated skin. COMPARISON OF LIGHT SOURCES The S.P.F. values obtained by the solar simulator were compared to those from fluorescent suniamp tubes. A bank of five Westinghouse FS20 fluorescent bulbs housed in an aluminum reflector was used at a distance of 15 cm. The UV-B flux (280 to 320 nm) at skin surface was 0.54 mW/cm 2. RESULTS IMMEDIATE PROTECTION Fifteen proprietory sunscreens were evaluated. The S.P.F. values ranged from 3.8 to 13.5 (Table I). Nine of fifteen products had S.P.F.'s exceeding 8.0, indicative of Table I Sun Protection Factors a (n = 10) Active Mean Sunscreen Ingredients S.P.F. - S.E. Range A isoamyl-p-dimethyl 3.8 --- 0.22 3-5 aminobenzoate B amyl dimethyl PABA 5.1 ___ 0.35 4-7 C homomenthyl salicylate 5.3 + 0.28 4-7 8.0% D padimate and dioxybenzone 6.3 + 0.47 5-9 E titanium dioxide, 5.0% and 6.6 + 0.34 5-8 menthyl anthranilate, 5.0% F octyl dimethyl PABA 7.3 + 0.30 6-9 3.3% G oxybenzone, 3.0% and 8.8 + 0.64 5-11 dioxybenzone, 3.0% Zinc Oxide Ointment zinc oxide 8.8 + 0.67 7-11 (U.S.P.) H cinoxate, 4.0% and 9.0 + 0.61 8-11 menthyl anthranilate, 5.0% I para aminobenzoic acid 9.1 + 0.62 7-11 5.0% J sulisobenzone, 10.0% 9.2 + 0.68 5-11 K methoxy cinnamate 9.8 --- 0.93 8-15 Red Veterinary 12.6 + 0.71 11-16 Petrolatum L 13.1 --- 0.76 12-18 13.5 -+ 0.48 12-15 glyceryl PABA, 3.0% and octyl dimethyl PABA, 3.0% para aminobenzoic acid, 5.0% aIn order of increasing efficacy.
EFFICACY OF SUNSCREENS 529 Table II Resistance to Wash Off Sunscreen Average Erythema a + S.E. Range J 2.8 _+ 0.16 0-3 Red Vet Petrolatum 2.2 _+ 0.30 1-3 I 1.7 -+ 0.12 1-2 Zinc Oxide Ointment 1.2 _+ 0.27 0-3 H 1.2 _+ 0.16 2-3 D 0.4 -+ 0.20 0-1 C 0.4 + 0.15 0-1 M 0.3 -+ 0.25 0-2 F 0.1 m 0.06 0-1 aErythema 24 hr after three MED's: 0 = normalskin (complete protection) 1 + = minimal erythema 2 + = moderate erythema 3 + = intense erythema (little or no protection) In order of increasing efficacy. moderate-to-high protection. The highest values were obtained with formulations containing PABA and its esters. Nonetheless, the least effective (S.P.F.'s of 3.8 and 5.1) were also preparations containing PABA esters. S.P.F. values below 4.0 are indica- tive of poor protection. The benzophenones were intermediate. Zinc oxide ointment was quite effective as was red veterinary petrolatum. RESISTANCE TO IMMERSION Again, the test agents differed considerably (Table II). F provided virtually complete protection against three MED's in contrast to J and red veterinary petrolatum, which possessed but slight resistance to wash-off. It is noteworthy that four of the test agents penormeu very well with mean erythema values -c •, /. •,t t,.•, or less. RESISTANCE TO SWEATING Most of the agents withstood sweating well, with the exception of red veterinary petro- latum (Table III). The preparations containing PABA and its esters were the most ef- fective. Table III Resistance to Sweating Sunscreen Average Erythema a -+ S.E. Range Red Vet Petrolatum 2.3 -+ 0.25 1-3 H 1.3 -+ 0.45 0-3 J 1.1 _+ 0.14 1-2 C 1.0 -+ 0.21 0-2 Zinc Oxide Ointment 0.9 -+ 0.29 0-2 D 0.7 + 0.21 0-2 F 0.4 - 0.14 0-1 L 0.3 -+ 0.16 0-1 M 0.2 -+ 0.14 0-1 I 0.2 _+ 0.11 0-1 •Erythema 24 hr after three MED's.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)