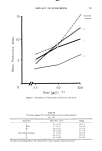
568 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS GROUP X]7. I •J ,.. • •. THORAZiNE CONTROL '• .- . . 15('1 min. UVL • :• . . . • '. .-? • . • • •'• .: •.•. ... . • • , -,: ---•. ß u . - ' • Figure 1. Hairless mice tranquilized with chlorpromazine and irradiated with UVL for 150 min--96 hr after irradiation crusted erosions were in many cases larger at 72 hr and exfoliation was under way around the edges of the treated areas. At 96 hr much of the treated area was still covered with thickened, whitish dried skin, the encrusted lesions were very prominent and in areas where exfoliation had occurred there were deep pink to red spots (Figure 1). Figure 2. Hairless mice tranquilized with chlorpromazine, painted with Product A and exposed to UVL for 150 min--96 hr after irradiation
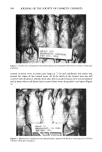
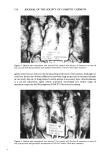
POLYMERIC FILM-FORMING SUNSCREEN 569 ß . '.¾: •' ... - • ,..-• ..• - . . . . g . •. . t- • -x •., . %.. .... •. iql.) •IIN ..• Figure 3. Hairless mice tranquilized with Innovar©-Vet, immersed in water 30 rain, injected with chlor- promazine and irradiated with UVL for 150 rain--96 hr after irradiation The three groups treated with the sunscreen preparations were similar in appearance. Erythema was visible for 48 to 72 hr with some dry, scaley skin present at this time. By 96 hr the backs of these animals appeared to be normal or nearly normal (Figure 2). WATER IMMERSION STUDY The nondrug controls and the drug controls were similar to those in the nonimmersed groups, but the number and size of encrusted erosions were greater. Much of the center of the backs of these mice was still covered with whitish, thickened skin at 96 hr and, in areas where exfoliation had occurred, deep pink to red lesions were observed (Figure 3). Of the five mice treated with Product A, four were similar to the controls, while the remaining one had fewer and smaller erosions (Figure 4). The group treated with Product B developed a few scattered erosions up to 4 mm in length and at 96 hr a large ß area of the back was still covered with the whitish, thickened skin (Figure 5). In the group treated with Product C, the treated areas were erythematous with minor, spotty edema, dry scaley skin with some exfoliation at 48 hr. At 72 hr, most of the dry scaley skin was gone and the newly exposed skin appeared almost normal except for some very faintly erythematous spots. At 96 hr the treated areas of three mice appeared normal and the remaining two had a few spots of mild erythema (Figure 6). DISCUSSION This method provides an animal model for testing potential sunscreen agents and formulations for efficacy and substantivity. The use of tranquilizers ensures that the
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)