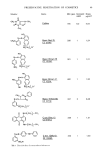
112 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Lanolin (38%, 37) hydrolysis KOH-silicagel column chromatography Lanolin alcohols Lanolin fatty acids (85%, 33) (13%, 23) esterification silica gel column chromatography I Methyl esters of Methyl esters of alkanoic acids hydroxy fatty acids (0%, 5) (20%, 5) reduction with LiA1H 4 Alkanols Alkane diols (17%, 6) (80%, 5) Figure 9. Scheme for the transformation of hydroxy fatty acids in lanolin to diols and their allergenicity (the values in the figure represent allergic reaction %, subjects). adduct method described in the experimental section. The aliphatic fraction was further purified under the same conditions three additional times to remove alicyclic compounds (steroIs and triterpene alcohols) completely. Then, the obtained aliphatic fraction was fractionated by HPLC on silica gel. Before the fractionation, the aliphatic fraction was esterified with p-nitrobenzoylchloride in order to use a UV detector in HPLC experiments. The esterified compounds gave four peaks on the chromatogram, and each peak was classified as shown in Figure 11 by comparing retention times of these peaks with those of authentic samples. Each compound was isolated repeatedly until it gave a single peak, and then hydrolyzed. Figure 10 shows the scheme for isolation of the diols and the patch test results with these isolated compounds. Alkanols showed no positive reactions. However, alkane-
ALLERGENS OF LANOLIN 113 Lanolin (38%, 37) reduction with LiA1H 4 Hydrogenated lanolin (100%, 9) Benzene fraction (non-allergenic, 0%, 9) florisil column chromatography Methanol fraction (allergenic, 100%, 9) urea adduct method I Alicyclic fraction (sterol, triterpene alcohols) I Aliphatic fraction preparative HPLC (on silica gel) Alkanols Alkane-e, •-diols Alkane-e, •-diols (0%, 9) (100%, 4) (67%, 6) Figure 10. Scheme for the isolation of alkane-.c•,fi•-diols and alkane-ot,to-diols from hydrogenated lanolin and their allergenicity (the values in the figure represent allergic reaction %, subjects). ot,/5-diols and alkane-ot,c0-diols exhibited strong positive reactions in four patients. Consequently, it was indicated that alkane-ot,/5-diols and alkane-ot,c0-diols were the allergens of hydrogenated lanolin. Incidentally, peak 3 in Figure 11 was judged to be the reduction product of a hydroxy acid possessing a tetrahydrofuran ring established by Ito et al. (15). Precise identifica- tion is under investigation. DISCUSSION Hydrolysis of lanolin gives commercially available lanolin alcohol and lanolin fatty acid, which contain the aforementioned alcohols or acids respectively. Because lanolin alcohol shows a remarkably high incidence of allergy compared with lanolin fatty acid (Figure 1), it can easily be inferred that the main allergens of lanolin are present in the alcoholic fraction. In addition, derivatization of lanolin alcohols to acetates or ethoxylates tends to decrease their allergenicity. These facts also suggest that the allergens possess at least one hydroxyl group in the molecule. Sulzberger et al. (16)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)