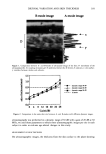
FLUORIDES IN ORAL HYGIENE PRODUCTS 403 Table 1. Recovery and Reproducibility in the Analysis of Toothpastes and Mouthwashes by Ion Chromatography (5 determinations for each aspect of procedure) Sodium fluoride Sodium monofluorophosphate Added Found Recovery Added Found Recovery (mg 1 -•) (mg 1 •) (%) (mg 1 t) (mg 1 -•) (%) Toothpaste A 2.00 2.07 103.5 (1.4) a 5.00 5.10 102.0 (2.3) Toothpaste B -- -- -- 5.00 5.07 101.5 (5.0) Mouthwashes A 5.00 4.87 97.3 (3.3) -- -- Mouthwashes B 4.00 3.99 99.8 (1.3) -- -- Standard deviation. shown in Table I, excellent recoveries and precision were observed (recoveries ranging from 97.3% to 103.5%). APPLICATION TO ORAL HYGIENE PRODUCTS The proposed IC method was applied to the determination of chemotherapeutic agents in oral hygiene products (toothpastes and mouthwashes). A representative chromato- gram of a commercial toothpaste is shown in Figure 2. Analytical results are given in 0 4 8 12 Time( min ) Figure 2. Chromatogram of typical toothpaste using sodium carbonate buffer (pH 9.85). Mobile phase. Peaks: a = fluoride b = rnonofluorophosphate.
404 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table II Analytical Results for the Determination of Fluoride and Monofiuorophosphate in Commercial Toothpastes and Mouthwashes by Ion Chromatography (IC) and Fluoride-Ion Selective Electrode Concentration (w/w, %) IC (n = 5 •) F- electrode (n = 6 •) F- FPO32 Total F- Toothpaste 1 0.075 0.074 (4.3%) b (2.5%) Toothpaste 2 0.244 0.129 0.376 (1.1%) (1.4%) (5.0%) Toothpaste 3 0.245 0.386 0.632 (0.7%) (2.4%) (2.2%) Toothpaste 4 0.369 0.239 0.605 (3.3%) (4.1%) (2.3%) Toothpaste 5 0.390 0.231 0.620 (5.0%) (4.0%) (0.5%) Toothpaste 6 0.314 0.360 0.669 (3.7%) (4.4%) (4.4%) Toothpaste 7 0.245 0.239 0.474 (2.0%) (4.4%) (0.76%) Toothpaste 8 0,144 0.467 0.618 (0.9%) (5.1%) (0.7%) Toothpaste 9 0.211 0.355 0.588 (2.4%) (3.7%) (1.8%) Toothpaste 10 -- 0.667 0.675 (2.5%) (3.9%) Toothpaste 11 -- 1.09 1.055 (3.6%) (5.6%) Toothpaste 12 0.064 0.690 0.768 (5.3%) (5.5%) (1.6%) Mouthwash 1 0.021 -- 0.028 (1.2%) (1.5%) Mouthwash 2 0.068 -- 0.070 (2.8%) (2.6%) Number of determinations. Relative standard deviation. Table II. These results agree with those obtained by a fluoride-ion electrode method, performed with a TISAB II solution, after treatment with hydrochloride acid hydrolysis. CONCLUSIONS The IC procedures described here are applied directly to the analysis of cosmetic samples without the need for MFP acid hydrolysis. The direct determination of fluoride not only offers more precision than indirect determination but also saves more time and is applicable to actual samples. ACKNOWLEDGMENT Financial support for this work by the National Science Council of the Republic of China is gratefully acknowledged (no. NSC 87-2113-M-041-002).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)