LIPOIC ACID STABILITY 451 ultraviolet radiation (12). The purpose of this work is to study the stability of lipoic acid in the presence of vitamins A and E in o/w emulsions for cosmetic application. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS Vitamin A (as palmitate) and vitamin E (as acetate) were provided by Merck (Germany) and lipoic acid was provided by Labochim (Laboratorio Chimico Internazionale, Italy). The emulsions consisted of silicone fluid (Dow Corning, Brazil) mineral oil, and pe- troleum jelly (R.A.A.M., Argentina) and acetylated lanolin, Acelan L (Fabriqu•mica, Argentina) as oil phase polyoxyethylenated fatty alcohol, Ceral PW (Fabriqu•mica, Argentina) as surfactant methyl p-hydroxybenzoate and propyl p-hydroxybenzoate (Clariant, United Kingdom) as preservatives and propylene glycol (Dow Chemical, USA) and demineralized water as hydrophilic phase. Oil-in-water-type emulsions con- taining lipoic acid (system 1) lipoic acid and vitamin A (system 2) lipoic acid and vitamin E (system 3) lipoic acid and vitamins A and E (system 4) and a drug-free emulsion (system 5) (Table I) were prepared. PREPARATION OF THE EMULSIONS 1. The non-ionic emulsifier was melted into a stainless steel container then acetylated lanolin, silicone fluid, propyl p-hydroxybenzoate, and mineral oil were added. It was mixed by slow agitation, avoiding the incorporation of air and keeping the tempera- ture between 72øC and 74øC. Lipoic acid was then added. It was stirred, and the temperature was maintained until a full dispersion was obtained. 2. Demineralized water, propylene glycol and methyl p-hydroxybenzoate were mixed into another stainless steel container. This mixture was heated to 75øC. 3. Both phases were filtered by gravity filtration. Then mixture 1 was incorporated into mixture 2, and stirred at 900 rpm for five minutes. Cooling was then started and stirring was slowed down. Table I Composition of Emulsions Systems Materials (g/100 g) 1 2 3 4 5 Polyoxyethylenated fatty alcohols 7.000 7.000 7.000 7.000 7.000 Silicone fluid 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 Mineral oil 5.000 5.000 5.000 5.000 5.000 Acetylated lanolin 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 Methyl p-hydroxybenzoate 0.200 0.200 0.200 0.200 0.200 Propyl p-hydroxybenzoate 0.100 0.100 0.100 0.100 0.100 Vitamin A palmitate 0.120 -- 0.120 -- Vitamin E acetate -- 0.400 0.400 -- Lipoic acid 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 -- Propylene glycol 9.000 9.000 9.000 9.000 9.000 Demineralized water 100.000 100.000 100.000 100.000 100.000
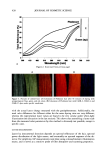
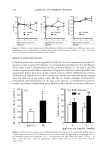
452 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 4. Vitamins A and E were incorporated at 55øC. The emulsions were stored for six months at room temperature and were analyzed under the same conditions in all cases. PHYSICAL STABILITY OF THE SYSTEMS The centrifuge model was performed to study the physical stability of the systems. The centrifuge technique, based on theorical principles reflected in the Stokes formula, was used as one of the ways for predicting the vulnerability of the emulsion-to-oil coales- cence. Centrifugation was performed for 30 minutes at 3500 rpm at room temperature on a Rolco (Argentina). centrifuge. Ten-milliliter samples in graduated centrifuge tubes were used. The rating adopted was: Good: no creaming or phase separation was observed. Poor: a considerable creaming and/or phase separation was observed. pH DETERMINATIONS The pH data for all the systems were obtained with model Antares IV Parsec equipment. The pH was measured as directed in USP 26 (791), using an indicator glass electrode. The buffers solutions for standardization were from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) at pH 4.00 and 7.01. RHEOLOGICAL DETERMINATIONS Rheometric data for all the systems were obtained by means of a Brookfield rotational viscometer (model RVT with Hellpath), employing spindle T-B at 5 rpm at room temperature. 100000 90000 80000 70000 60000 50000 40oo0 •oooo 20000 lOOOO System 1 System 2 System 3 --•- System 4 --•-- System 5 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Figure 2. Viscosity of systems 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. lOO
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)