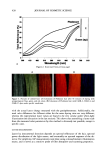
LIPOIC ACID STABILITY 453 Table II pH of the Systems at Initial (t - 0) and Final (t = 6 months)Time System pH (t - 0) pH (t = 6 m) 1 2.74 3.53 2 2.78 3.22 3 2.80 3.3O 4 2.80 3.46 5 5.80 5.90 Table III Selectivity: Degradation Conditions of Lipoic Acid Condition Time (h) % Recovered RRT of degradation products Water, refluxed 0.5 95.1 None detected Daylight 96 0.0 None detected Acid 1N HC1, refiuxed 0.5 98.1 0.65 Hydrogen peroxide, 100 vol., refluxed 0.5 0.0 None quantified RRT: relative retention time. Table IV Selectivity: Degradation Conditions of Vitamin A Condition Time (h) % Recovered RRT of degradation products Water, refluxed 0.5 83.9 0.07, 0.11, 0.15, 0.17 Daylight 72 0.0 0.07, 0.10, 0.18 Acid 1N HC1, refiuxed 0.5 0.0 0.06, 0.08, 0.09, 0.12 Hydrogen peroxide, 100 vol., reluxed 0.5 73.7 0.07, 0.15, 0.18 RRT: relative retention time. Table V Selectivity: Degradation Conditions of Vitamin E Condition Time (h) % Recovered RRT of degradation products Water, refiuxed 0.5 95.7 Daylight 96 99.9 Acid 1N HC1, refiuxed 0.17 84.6 Hydrogen peroxide 0.5 93.8 100 vol., refluxed 0.1l, 0.20, 0.21, 0.26, 0.41, 0.86, 1.90 0.11, 0.20, 0.27, 0.87 0.16, 0.21,0.22, 0.58, 0.78, 1.44, 2.24, 2.49, 2.67 0.12, 0.16, 0.22, 0.48, 0.87 RRT: relative retention time. ANALYSIS OF THE ACTIVE INGREDIENTS The analyses of lipoic acid and vitamins A and E were made by HPLC. Rlateriah and reagents. The working standards employed for lipoic acid and vitamins A and E were the same as those used in the preparation of the creams. Solvents were HPLC
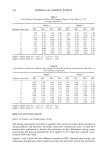
454 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE A B C D E Figure 3. Lipoic acid: (A) Standard. (B) Water degradation. (C) Photochemical degradation. (D) Acid degradation. (E) Oxidant degradation. A B C D E Figure 4. Vitamin E: (A) Standard. (B) Water degradation. (C) Photochemical degradation. (D) Acid degradation. (E) Oxidant degradation. grade. Water of HPLC grade was obtained by distillation and passing through a 0.45- micron membrane filter. Instrumentation. The HPLC system consisted of a dual-piston reciprocating pump (model KNK-500 G), a UV-Vis detector (model KNK-029-757), an integrator (model SP 4600) (all from Konik), and a Rheodyne injector (model 7125). HPLC conditions. The experiment was performed on an LiChrosphere © 100 RP-18 (5 pm) 125-4 column from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) for vitamins A and E. For lipoic acid the experiment was performed on a Microsorb-MV © 100fit C18 (5pm) column (Varian Analytical Instruments, Walnut Creek, United States). The mobile phase was methanol for vitamins A and E and methanol:water (80:20, v/v), pH 3.0, adjusted with 85% phosphoric acid, for lipoic acid. Both were filtered and &gassed under reduced pressure prior to use. Separation was isocratically carried out at
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)