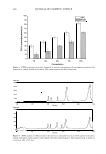
428 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE release from RBL-2H3 cells treated with IgE (0.5 µg/ml). Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract decreased the �-hexosaminidase release in a dose-dependent manner (IC 50 was around 100 µg/ml). Furthermore, 1000 µg/ml of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract completely inhibited the �-hexosaminidase release to the control level, at which the amount is spontaneously released from RBL-2H3 cells untreated with IgE (Figure 7), even though the anti-allergic activity was not comparable with that of indomethacin, a well-known topical analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug. The results suggest that the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum could be a useful active ingredient for anti-allergic cosmeceuticals. IN VIVO CLINICAL SAFETY TEST In order to evaluate the skin-sensitizing potentials of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. ja ponicum extract, a clinical test was performed after repeated epicutaneous applications under an occlusive patch (repeat insult patch test, RIPT) for 48 h. Fifty male and female subjects between the ages of 21 and 51 were selected for the study. The evaluation criteria of the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group (ICDRG) were used as the standard of the grading scale, as shown in Table I (10,11). The results were analyzed by calculating the mean irritation index (M.1.1.) of allergic reaction for the test articles according to the formula, as shown in Table II. The repeated and single cutaneous applications of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract under the occlusive patch did not provoke any cumulative irritation and sensitization reaction. f- Quantitative Determination of (3-hexosaminidase � CD (II ca CD (II ca 'i: ·e ca 0 CD 0 C 0 :c .E Figure 7. Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum on �-hexosaminidase release from RBL-2H3 cells immunologically activated by treatment with IgE (0.5 µg/ml). The data are expressed as the mean values (±standard deviations) of four experiments.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF C. ASIATICUM 429 Table I Clinical Evaluation Criteria of International Contact Dermatitis Research Group (ICDRG) (11) Symbol ± + ++ +++ Score 0 2 3 4 Table II Scoring of skin reaction: 5-point scale (1) Negative (2) Incomplete or irregular erythema (3) Regular well-defined erythema + induration (4) Significant erythema + induration + vesicle (5) Erythema purplish + induration + bullae Analysis of Results According to the Grade of the Mean Irritation Index (M.I.I.) Grade Non-irritating (1) Slightly irritating (2) Mean irritant (3) Very irritating ( 4) Very severely irritating (5) L quotation of the 8 readings (all volunteers) Mean irritation index (M.I.I.) = b f l ( . ) N um er o vo unteers X 8 readings CONCLUSIONS M.1.1. 0.00-0.24 0.25-0.99 1.00-1.99 2.00-2.99 3.00-4.00 The extract of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum! of the Amaryllidaceae family and designated as the 19th of Korea's natural treasures, was obtained by the ethanol extrac tion method, with a pH maintained at 3.5. It was confirmed that lycorine, an active molecule, was present in Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum! and its content (about 1 % ) was identified by a high-performance liquid chromatogram. In the cytotoxicity assay, the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum did not show any cytotoxicity, instead showing slightly increased cell viability. In the anti-inflammatory activity assay, the ethanol extract of Crinum asiaticum showed good anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of iNOS gene expression, followed by reduced NO production and the reduced release of PGE2 , IL-6, and IL-8 by various stimuli such as H202 , UV, and SDS. Furthermore, in the anti-allergic activity assay measured by �-hexosaminidase release from RBL-2H3 cells treated with IgE, Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract showed good anti-allergic activity to decrease the �-hexosaminidase release to the control level at a concentration of 1000 µg/ml. In an in vivo clinical test to investigate the skin-sensitizing potentials of the extract of Crinum asiaticum, the repeated and single cutaneous applications of Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract under an occlusive patch did not provoke any cumulative irritation and sensitization reaction. These results suggest that Crinum asiaticum Linne var. japonicum extract, having anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects, could be used as an appropriate ingredient for cosmeceutical prod ucts. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Energy, "The Development of Cosmeceutical Ingredients from Natural Plants Like
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)