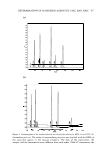
DPPH FREE-RADICAL SCAVENGING ABILI1Y 517 Table III Variation in Content of Essential Oil Components from Cinnamon Leaf Peak number Ra t Compoundb Mol. wt.c Mol. f.d Area(%) 9.04 a-Pinene 136 C10H16 2.05 2 12.10 a-Phellandrene 136 C10H16 0.59 3 12.93 p-Cymene 134 C10H14 1.37 4 16.41 J3-Linalool 154 C10H1sO 1.33 5 24.45 Cinnamaldehyde 154 C 9 H8O 0.19 6 25.13 Safrole 162 C10H18O2 0.96 7 27.87 Eugenol 164 C10H1202 82.87 8 28.75 Copaene 204 C1sH24 0.78 9 30.61 J3-Caryophyllene 204 C1sH24 3.40 10 31.83 Cinnamyl acetate 176 C11H1202 0.74 11 32.10 a-Caryophyllene 204 C1sH24 0.50 12 34.63 Eugenol acetate 206 C12H1403 2.00 13 44.03 Benzyl benzoate 212 C14H1202 1.86 * Unknown 1.36 a R,: Retention time (min). 6 The components were identified by their mass spectra and retention indicators (Rls), the Wiley and NIST mass spectral databases, and the previously published Rls. c Mol. wt: molecular weight. d Mol. f.: molecular formula. 100 80 t -� 60 "i 71.1 63.3 40 20 1.S 4.18 0 a-Pilcne f}-Carophylk:ne Cinumn leaf Concentratm (0. lm&'mL) Figure 4. DPPH radical scavenging activity of three pure chemical components of cinnamon leaf compared with its essential oils at a concentration of 0.1 mg/ml. acetate �-caryophyllene and that the eugenol is also the major component of the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity in clove bud essential oil. The DPPH free-radical scavenging activity, GC-MS, and work-up of jasmine absolute and thyme red essential oils were similar to those used in cinnamon leaf and clove bud essential oils. In Table V, there are twelve compounds: benzyl alcohol, p-cresol, �-linalool, benzyl acetate, indole, eugenol, jasmone, J3-farnesene, benzyl benzoate, isophytol, phytol, and squalene in jasmine absolute essential oil, and the two major compounds are benzyl
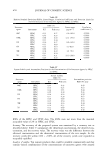
518 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table IV Variation in Content of Essential Oil Components from Clove Bud Peak number Ra I Compound6 Mol. wt.c Mol. f.d Area(%) 27.87 Eugenol 164 C10H12O2 82.32 2 30.62 13-Caryophyllene 204 C15H24 4.75 3 34.62 Eugenol acetate 206 C12H14O3 11.17 * Unknown 1.76 a R,: Retention time (min). 6 The components were identified by their mass spectra and retention indicators (Rls), the Wiley and NIST mass spectral databases, and the previously published Rls. c Mol. wt: molecular weight. d Mol. f.: molecular formula. 100 � 80 71.1 -� 60 ·.c u ca c:: "iii) 40 c:: ca u 20 0 Eugenol 4.18 P-Carophyllene Eugenol acetate Concentration (0. ImwmL) 64.6 Clove bud Figure 5. DPPH radical scavenging activity of three pure chemical components of clove bud compared with its essential oils at a concentration of 0.1 mg/ml. benzoate (32.2%) and benzyl acetate (17.24%). In Figure 6, it is clear that the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity is in the following order: eugenol jasmine absolute essential oil p-cresol J3-farnesene indole jasmone benzyl alcohol benzyl acetate benzyl benzoate J3-linalool. The total contribution (percentage of content multiplied by the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity) of the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity is in the following order: benzyl acetate benzyl benzoate p-cresol eugenol indole J3-farnesene jasmone benzyl alcohol J3-linalool. Benzyl acetate is the major component of the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity in jasmine absolute essential oil. In Table VI, there are eight compounds: cx-pinene, camphene, p-cymene, d-limonene, crithmene, J3-linalool, thymol, and carvacrol in thyme red essential oil, and the two major compounds are thymol (63.65%) and p-cymene (23.8%). In Figure 7, it is clear that the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity is in the following order: thymol thyme red essential oil p-cymene and that thymol is the major component of the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity in thyme red essential oil. From the above description, it is clear that the phenol compound is always effective in the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity. It is conclusive that the phenol compound
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)