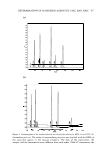
DPPH FREE-RADICAL SCAVENGING ABILITY 519 Table V Variation in Content of Essential Oil Components from Jasmine Absolute Peak number Ra I Compound6 Mol. wt.c Mol. f.d Area(%) 12.45 Benzyl alcohol 108 C7H8O 2.47 2 13.87 p-Cresol 108 C7H8O 3.66 3 14.77 J3-Linalool 154 C10H1sO 2.72 4 17.09 Benzyl acetate 150 C9H10O2 17.24 5 21.68 Indal 117 C8H7N 3.44 6 23.61 Eugenol 164 C10H12O2 0.87 7 24.94 Jasmone 164 C11H6O 2.32 8 28.34 Farnesene 204 C15H24 2.52 9 36.38 Benzyl benzoate 212 C14H12O2 32.2 10 44.90 Isophyrol 296 C20H40O 7.38 11 48.83 Phytol 296 C20H40O 16.97 12 58.28 Squalene 410 C30H50 5.29 * Unknown 2.92 a R,: Retention time (min). 6 The components were identified by their mass spectra and retention indicators (Ris), the Wiley and NIST mass spectral databases and the previously published Ris. c Mol. wt: molecular weight d Mol. f.: molecular formula. - 80 � ... :� 6() ... C J ffl 20 Benzylalcohol jKn:sol Linalool Benzylacetate 88.1 36 lndol f.ugenol Jasrronc Faamescoe Benzyl benmale Jasninc absolute Coacenllllioo ( Jmg/a) Figure 6. DPPH radical scavenging activity of nine pure chemical components of jasmine absolute com pared with its essential oils at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. shows hydrogen-donating ability and that the resonance structures are stabilized by the benzene ring (Figure 8). Correlation of the phenolic content and the scavenging activity of essential oils is shown in Figure 9. Below 500 mg/g of GAE, it is clear that the total phenolic content and the DPPH free-radical scavenging activity are in direct proportion. CONCLUSION This research reports the DPPH radical scavenging activity and the total phenolic content of forty-five kinds of commonly used essential oils. GC-MS was employed to analyze the main chemical compositions of these essential oils.
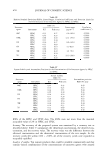
520 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table VI Variation in Content of Essential Oil Components from Thyme Red Peak number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 * R/ 8.8 9.37 12.04 12.18 13.24 14.77 21.66 21.86 a R/ Retention time (min). Compound6 Mol. wt.c Mol. f.d a-Pinene 136 C10H16 Camphene 136 C,oH,6 p-Cymene 134 CIOHl4 d-Limonene 136 CIOHl6 Crithmene 136 C,0H 1 6 �-Linalool 154 CIOH18O Thymol 150 C 10 H 1 4O Carvacrol 150 C10H14O Unknown Area(%) 1.26 1.32 23.8 2.82 0.77 2.66 63.65 2.27 1.45 6 The components were identified by their mass spectra and retention indicators (Rls), the Wiley and NIST mass spectral databases, and the previously published Rls. c Mol. wt: molecular weight. J Mol. f.: molecular formula. 60 50 0 20.9 p-Cyrnene 50.7 48.02 Th)'1110l Thyme red Concentration (lmg/mL) Figure 7. DPPH radical scavenging activity of two pure chemical components of thyme red compared with its essential oils at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. Figure 8. The delocalized structures of the phenol radical. Cinnamon leaf and clove bud are the best two essential oils in DPPH free-radical scavenging activity, and their EC 50 are 5 3 and 36 µg/ml, respectively. They are also the best two essential oils in terms of total phenolic content. In a concentration of 1 mg/ml, the total phenolic amounts are 420 and 480 (mg/g of GAE), respectively. By means of
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)