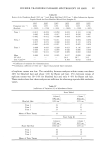
COMPONENT DISTRIBUTIONS IN KERATINS FROM AMINO ACIDS 27 3. These fractions are combined with a weight fraction, a, of component 1, b of component 2, and, since the fractions must total unity, a fraction 1 - a - b of component 3. This combination must equal the fraction x of the same amino acid in the original keratin. Since there are more amino acids than components, or should be, we define the statistical residual Re = • Ix - x 3 - a(x• - x 3) - b(x 2 - x0] 2 where the sum is taken over all the amino acids present. When all the weighting factors are properly chosen, this residual will be at a minimum. The position of this minimum is found by successively differentiating Re with respect to each of the weighting factors, setting each derivative to zero, and solving the resulting set of simultaneous equations. For the case of N = 3, two simultaneous equations must be solved: • (x -- x3)(Xl -- x 3) -- a • (x• -- x3) 2 -- b • (x• - x3)(x 2 -- x3) = 0 • (X -- X3)(X 2 -- X3) -- a • (x• -- x3)(x 2 -- x3) -- b • (x2 - x3) 2 = 0 Generalizing the method to any number of components is straightforward. Data for the component compositions is listed in Table II, and the keratin sample compositions used are listed in Appendix II. In the computation procedure, all com- binations of components were taken, 2, 3, 4, and all 5 at a time. The combination chosen had the minimum Re, with all coefficients positive. A component proportion produced by this method from input data in the form of mole fractions is actually a mole percent itself, and should strictly speaking be converted to a weight fraction. However, there is relatively little difference in the average molec- ular weight of most proteins, and so this conversion was not included in the present calculations. APPENDIX II: AMINO ACID COMPOSITIONS OF KERATIN SAMPLES Amino acid compositions for all samples listed in Table V are given in compressed form. Following the identification number from Table V in parentheses, normalized mole percents of the amino acids are listed in the following order: lys, his, arg, hcy, asp, thr, ser, glu, pro, gly, ala, val, ile, leu, tyr, and phe. (1) 2.72, 0.91, 5.85, 17.94, 4.94, 6.85, 11.79, 11.49, 8.47, 6.45, 4.64, 5 85, 2.62, 5.85, 2.01, 1.61, (2) 2.41, 0.80, 6.34, 16.70, 5.33, 7.44, 11.97, 12 57, 8.25, 5.84, 4.53, 5.43, 2.62, 5.93, 2.11, 1.71, (3) 2.44, 0.75, 5.99, 17.80, 5 35, 7.43, 12.16, 12.59, 8.00, 5.92, 4.45, 5.18, 2.40, 6.06, 1.90, 1.57, (4) 2.26, 0 79, 6.04, 18.05, 5.27, 6.88, 10.80, 11.24, 9.56, 6.50, 4.38, 6.22, 2.69, 5.89, 1 60, 1.82, (5) 2.51, 0.90, 6.53, 15.98, 5.43, 7.64, 12.26, 12.26, 8.44, 5.83, 4 32, 5.53, 2.31, 6.13, 2.21, 1.71, (6) 2.56, 0.73, 6.35, 13.67, 5.63, 7.25, 11.47, 12 65, 8.75, 6.69, 5.04, 6.30, 2.98, 6.50, 1.84, 1.58, (7) 2.49, 0.81, 6.19, 16.70, 5 33, 7.25, 11.75, 12.14, 8.58, 6.21, 4.56, 5.75, 2.61, 6.06, 1.95, 1.62, (8) 3.64, 0 91, 5.76, 8.08, 8.38, 5.45, 9.59, 14.34, 5.76, 6.77, 7.17, 6.26, 3.53, 9.19, 2 73, 2.42, (9) 4.24, 1.11, 6.66, 6.05, 8.78, 5.45, 9.38, 14.83, 5.45, 6.36, 7.06, 6.86, 3.73, 9.69, 2.32, 2.02, (10) 3.94, 1.01, 6.21, 7.07, 8.58, 5.45, 9.49, 14.59, 5.61, 6.56, 7.12, 6.56, 3.63, 9.44, 2.52, 2.22, (11) 2.19, 0.45, 4.19, 10.05, 6.27, 6.15, 15.00, 18.08, 8.44, 10.01, 6.37, 1.82, 3.09, 5.03, 1.49, 1.37, (12) 2.48, 0.63, 4.42, 10.31, 7.26, 6.77, 14.96, 13.04, 9.80, 11.11, 7.11, 1.83, 3.07, 4.48, 1.30,
28 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 1.41, (13) 2.43, 0.34, 4.66, 10.47, 6.48, 6.41, 15.87, 13.32, 8.29, 11.51, 6.84, 2.27, 2.89, 5.28, 1.33, 1.58, (14) 2.14, 0.22, 4.66, 11.56, 6.26, 5.81, 17.36, 13.42, 7.00, 11.58, 7.03, 2.06, 2.85, 5.05, 1.53, 1.46, (15) 2.72, 0.64, 5.93, 11.78, 6.05, 7.94, 11.61, 14.14, 7 (16) 3.12, 1.01, 6.45, 10.67, 7.05 2.72, 8.36, 3.22, 2.52, (17) 2.84, 6.93, 6.95, 5.68, 6.22, 3.65, 7.97, 6.09, 9.12, 12.65, 6.48, 6.91, 6.00 .91, 7.40, 5.25, 5.67, 2.99, 6.83, 1.32, 1.81, , 6.14, 11.38, 13.70, 5.94, 7.95, 5.54, 4.23, 0.74, 7.51, 10.06, 6.79, 6.34, 10.36, 12.73, 2.64, 2.58, (18) 3.21, 0.79, 7.20, 10.36, 7.15, , 6.18, 3.57, 8.55, 2.88, 2.85, (19)2.84, 0.85 6.79, 11.55, 5.96, 6.13, 11.05, 10.95, 6.43, 9.56, 5.12, 5.39, 2.87, 7.31, 4.48 2.70, (20) 3.07, 0.94, 6.85, 10.61, 6.40, 6.53, 10.30, 11.98, 5.96, 8.65, 5.36 5.55, 3.14, 7.72, 3.99, 2.93, (21) 2.72, 0.81, 7.06, 10.18, 6.55, 6.15, 10.48 12.90, 6.55, 8.27, 5.34, 5.65, 3.23, 7.56, 3.83, 2.72, (22) 2.33, 0.70, 7.28, 11.41 6.09, 6.62, 10.41, 12.34, 7.66, 8.32, 5.05, 5.12, 2.83, 7.05, 4.27, 2.52, (23) 2.84 0.80, 7.12, 10.70, 6.49, 6.31, 10.29, 12.26, 6.67, 8.11, 5.42, 5.68, 3.22, 7.69 3.68, 2.72, (24) 2.81, 0.70, 6.83, 10.34, 6.73, 6.12, 10.24, 12.15, 6.32, 8.63 5.62, 5.72, 3.21, 8.43, 3.41, 2.71, (25)2.31, 0.70, 6.53, 12.95, 6.32, 7.03, 10.54, 12.65, 7.03, 7.53, 5.42, 5.72, 3.31, 7.33, 2.41, 2.21, (26) 2.65, 0.88, 6.79, 12.49, 6.10 6.45, 10.80, 12.48, 7.11, 8.15, 5.29, 5.37, 2.98, 7.04, 2.98, 2.44, (27) 3.48 7.42 9.76 6.36 3.99 2.27 1.23, 5.90, 12.09, 7.08, 5.73, 9.41, 13.01, 6.67, 8.61, 5.85, 5.21, 3.06, 3.12, 2.15, (28) 2.88, 0.82, 5.85, 15.28, 5.52, 5.63, 9.35, 10.92, 8.71, 5.40, 5.62, 2.06, 6.45, 3.25, 2.49, (29).91, 2.12, 2.93, 13.22, 5.55, 3.53, 3.53, 10.29, 27.85, 5.25, 4.84, 2.52, 2.62, 5.65, 2.83, (30) 0.70, 0.39, 7.15, 5.53, 4.13, 14.92, 6.17, 9.90, 13.27, 8.30, 7.47, 3.11, 9.09, 3.61. (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (lO) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) REFERENCES D. R. Goddard and L. Michaelis, A study on keratin, J. Biol, Chem., 106, 605-614 (1934). D. R. Goddard and L. Michaelis, Derivatives of keratin, J. Biol. Chem., 112, 361-371 (1935). W. G. Crewther, Primary structure and chemical properties of wool, Proc. 5th Int. Wool Textile Res, Conf., Aachen, 1975, Vol. 1, pp 1-101. M. Feughelman, A two-phase structure for keratin fibers, Textile Res. J., 29, 223-228 (1959). M. Feughelman, The physical properties of alpha-keratin fibers, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 33, 385-406 (1982). E. Menefee, A mechanical model for wool, Textile Res. J., 38, 1149-1163 (1968). E. Menefee, Relation of keratin structure to its mechanical behavior, Appl. Polymer Symp., 18, 809- 821 (1971). M. Spei and H. Zahn, Low angle x-ray investigations of extended keratin fibers, Monatsh. Chem., 102, 1163-1181 (1971). M. Spei, Small angle x-ray studies of an ordered matrix in alpha-keratin, KolloidZ.-Z. Polymere. 250, 214-221 (1972). M. Spei, X-ray studies on the microfibril-matrix complex, Proc. 6th Int. Wool Textile Res. Conf, Pretoria, 1980, Vol. 2, pp 263-272. G. Heidemann and H. Halboth, Fibrillar swelling of alpha-keratin, Textile Res. J., 40, 861-862 (1970). M. Spei and H. Zahn, X-ray small-angle examination of swollen fiber keratins, Melhand Textilber., 60, 523-525 (1979). R. D. B. Fraser, T. P. MacRae, G. R. Millward, D. A. D. Parry, E. Suzuki, and P. A. Tulloch, The molecular structure of keratins, Appl. Polymer Symp., 18, 65-83 (1971). E. Menefee and S. J. Tillin, Determination of crosslink density by end group analysis after partial degradation: 2. Experimental application to keratin, Polymer, 22, 1219-1222 (1981). E. Menefee, "Physical and Chemical Consequences of Keratin Crosslinking, With Application to the
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)