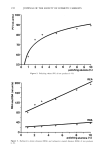
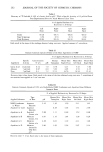
228 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table I Effect of Alcohol/Glycol on Gel Stability Formulation Constants % Dibenzylidene Sorbitol (1) 3.0 Steareth- 100 1.0 Aluminum Chlorohydrex (2) 10.0 Stearic Acid, Triple Pressed 0.5 Hydroxypropylcellulose 0.2 Cyclomethicone 5.0 Formulation Variables Formula Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 % % % % % % % % % % % % Butylene Glycol -- -- 10.0 10.0 10.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 30.0 30.0 30.0 HexyleneGlycol 30.0 30.0 30.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 10.0 10.0 10.0 -- -- -- Ethanol, Anhy. 50.3 33.5 16.8 50.3 33.5 16.8 50.3 33.5 16.8 50.3 33.5 16.8 Isopropanol -- 16.8 33.5 -- 16.8 33.5 -- 16.8 33.5 -- 16.8 33.5 Stability Data: Days Until Completely Liquid @ 60øC 2 3 3 2 3 4-6 3 4-6 4-6 3 4-6 4-6 @ 45øC 45 45 45 41 50 64 41 50 64 41 52 71 (1) Millithix 925 ©, Milliken Chemicals, Spartanburg, SC. (2) Rehydrol II ©, Reheis Chemical Company, Berkeley Heights, NJ. Methenamine is an amine. These additives were investigated utilizing the 16 formula- tions in Table II. Formula 7 from Table I is identical to formula 13 in Table II. The 45øC data for the two identical formulas evaluated at different times shows the variability inherent in this type of measurement. Since a statistical analysis of the data in Table II was anticipated, only one half of the 25 factorial design was necessary. However, a statistical analysis was not performed because of missing data points. A number of the formulations were so stable that an end point was not reached after 8 months at 60øC. The study was discontinued at this point because ethanol loss was becoming a concern at the high temperature. The inorganic salts, magnesium sulfate and zinc acetate, were evaluated at 0.3% be- cause of solubility constraints. The amides, cocamide MEA and acetamide MEA, be- cause of their lower buffering capacity were evaluated at 5 %. The amine, methenamine, because of its propensity to darken was evaluated at 0.1%. The comparison of the stability results for formula 14 to 15, 17, and 21 16 to 15, 19, and 23 18 to 17, 19, and 25 and 22 to 21, 23, and 25 shows that magnesium sulfate, at the levels studied, is the least effective stabilizing active of the five. The comparison of the stability results for formula 14 to 16, 18, and 22 15 to 16, 19, and 23 17 to 18, 19, and 25 and 21 to 22, 23, and 25 shows that at the levels studied, cocamide MEA is more effective than magnesium sulfate but less effective than the other three additives. Roehi disclosed cocamide MEA as a DBS stability aid. The comparison of the stability results for formula 15 to 14, 17, and 21 16 to 14, 18, and 22 19 to 17, 18, and 25 and 23 to 21, 22, and 25 shows that at the levels studied, zinc acetate is more effective than magnesium sulfate and cocamide MEA but less effective than methenamine and acetamide MEA.
CLEAR GEL ANTIPERSPIRANTS 229 The comparison of the stability results for formula 17 to 14, 15, and 21 18 to 14, 16, and 22 19 to 15, 16, and 23 and 25 to 21, 22, and 23 shows that at the levels studied, methenamine is more effective than all but acetamide MEA. The comparison of the stability results for formula 21 to 14, 15, and 17 22 to 14, 16, and 18 23 to 15, 16, and 19 and 25 to 17, 18, and 19 shows that acetamide MEA is the most effective of the five stability agents employed at the levels studied. Table III shows the result of formulating the five stability additives into one of Roehl's formulations (Formula 4/29). Formula 4/30 shows the increased stability achieved by using a less reactive solvent. Formula 4/31 shows the advantage of using acetamide MEA as both a stability aid and a solvent. Table IV shows the positive effect of incre- mental increases in the level of acetamide MEA on stability. Summarizing, the rank order of the effectiveness of the five stability additives at the practical concentrations studied is: acetamide MEA methenamine zinc acetate cocamide MEA magnesium sulfate. The concentration of additives was determined Table II Effect of Stability Additives on Gel Stability Formulation Constants % Dibenzylidene Sorbitol 3.0 Steareth- 100 1.0 Butylene Glycol 20.0 Hexylene Glycol 10.0 Aluminum Chlorohydrex 10.0 Stearic Acid, Triple Pressed 0.5 Hydroxypropylcellulose 0.2 Cyclomethicone 5.0 Formulation Variables Formula Number 13 14 15 16 17 lg 19 20 % % % % % % % % Ethanol, Anhy. 50.3 45.0 45.0 49.7 45.2 49.9 49.9 44.6 Magnesium Sulfate -- 0.3 -- 0.3 -- 0.3 -- 0.3 Cocamide MEA -- 5.0 5.0 -- 5.0 -- 5.0 Zinc Acetate -- -- 0.3 0.3 -- 0.3 0.3 Methenamine .... 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 Acetamide MEA ...... Stability Data: Days Until Completely Liquid @ 60øC 2 9 25 21 63 32 @ 45øC 35 263 445 445 445 445 Formula Number 21 22 23 24 25 26 % % % % % % Ethanol, Anhy. 40.3 45.0 45.0 39.7 45.2 39.9 Magnesium Sulfate 0.3 -- 0.3 -- 0.3 Cocamide MEA 5.0 -- -- 5.0 -- 5.0 Zinc Acetate -- 0.3 0.3 -- -- Methenamine -- -- 0.1 0.1 Acetamide MEA 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 Stability Data: Days Until Completely Liquid @ 60øC 102 60 123 247 247 247 @ 45øC 445 445 445 445 445 445 56 445 27 % 39.9 -- 5.0 0.3 0.1 5.0 247 445 98 445 28 % 44.6 0.3 __ 0.3 0.1 5.0 247 445
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)