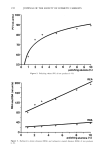
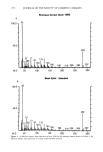
COLLAGEN SWELLING PREDICTS SURFACTANT IRRITATION 203 L• 12 10 I I I I I0 14 16 ALKYL CHAIN LENGTH Figure 2. Collagen swelling as a function of carbon chain length in alkyl sulfates. the test concentration was decreased from 8 mM to 2 mM. This behavior may reflect the fact that as the test concentrations are lowered, the shorter chain length homologs pass below their respective critical micelie concentrations. There have been no irritation studies reported addressing whether or not maximum activity of alkyl homologs is a function of surfactant concentration. This should be investigated further. EFFECT OF ETHYLENE OXIDE CONTENT The effect of varying the ethylene oxide content of alkyl sulfate surfactants on collagen swelling was determined by studying C 12 alkyl ether sulfates containing 0, 3, 6, and 9 moles of ethylene oxide. For the purpose of this study, ammonium lauryl sulfate (ALS) was considered the parent homolog of the alkyl ether sulfate series. The swelling re- sponse was found to be inversely related to EO content (Figure 4), i.e. swelling de- creased as the amount of ethoxylation increased and the least swelling was produced by the surfactant with the greatest ethylene oxide content (AEOS-9EO). Concentration dependence also decreased with increasing ethoxylation: it appeared as though apparent saturation had already occurred for the highly ethoxylated surfactants at these test con- ditions.
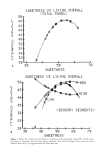
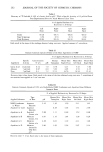
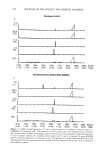
204 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS ].4 _• 0.6 - •: 0.4 - •' 0.2 - 8 I0 ALKYL CHAIN LENGTH alkyl $uloeat½$ (5). Putterman eta/. (3) compared skin swelling as a result of treatment with SLS, AEOS-1EO, and AEOS-3EO and showed that ethoxylation produced decreases in the swelling response. Rhein eta/. (10) compared the swelling induced in stratum corneum by AEOS containing 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, and 12 moles of EO, and found that swelling decreased with increased ethoxylation up to 6 ethylene oxide units, after which no further decreases in swelling could be detected. Table II compares in vivo human skin irritation scores and collagen swelling as a func- tion of EO content in AEOS surfactants. Human skin irritation was determined in vivo by the method of Frosch and Kligman (11). The treatments were applied to subjects with Duhring chambers for 5 days. The most severe irritation and highest collagen swelling was produced by the unethoxylated parent ALS (AEOS-0EO), and the severity of irritation and swelling decreased with ethoxylation of alkyl sulfate. No significant difference was found between the swelling produced by AEOS-9EO and water, and no irritation was found after 5 days of treatment. The effect of variation in the EO content of AEOS on irritation potential was also studied by Opdyke and Burnett (12). These workers used the Guinea Pig Immersion procedure to evaluate ammonium lauryl sulfates with 0, 1, 3, and 7 moles of ethylene oxide. AEOS-0EO (ALS) was toxic to all treatment animals, and AEOS-7EO was the mildest. The data clearly show that increasing the ethylene oxide content in AEOS surfactants produced corresponding decreases in human (Table III) and animal (12) skin irritation, in agreement with the results of the collagen swelling assay (Table III).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)