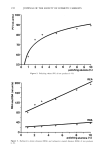
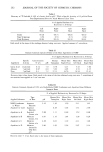
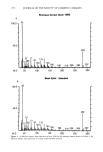
COLLAGEN SWELLING PREDICTS SURFACTANT IRRITATION 205 10 o• AEO o i o u AEO • o o AEOS-6 o • AEOS-9 o o o o o H2 0 0 I I I I I 0 2 4 6 8 I0 SURFACTANT CONCENTRATION (mMOLAR) Figure 4. Effect of ethoxylation of C12 alkyl sulfates on collagen swelling. EFFECT OF SURFACTANT CHARGE ON COLLAGEN SWELLING The effect of surfactant charge on collagen swelling was studied by treating collagen film with 10 mM solutions of anionic, nonionic, amphoteric, and cationic surfactants. Table III shows that the substrate responded by swelling to the treatment by anionic Table II Effect of Ethoxylation of C12 Alkyl Ether Sulfate on Skin Irritation and Collagen Swelling Skin Irritation Collagen Swelling (ml/g) Surfactant (In Vivo) (+) (In Vitro) (+ +) AEOS-0EO (ALS) Severe within 1 day 8.9 -+ 0.2 (a) AEOS-3EO Mild to moderate by 5th day 4.2 _+ 0.1 (b) AEOS-6EO Mild to moderate by 5th day 3.5 -+ 0.1 (c) AEOS-9EO None after 5 days 2.7 _+ 0.1 (d) Water -- 2.2 _+ 0. i (d) +, Irritation in vivo.' Human subjects, 10% concentration, pH 7, 2 to 3 subjects, Duhring chambers, 5 days. -F +, Collagen swelling test conditions: 2 replicates, concentration 10 mM, time 24 hours, pH 7.0. Values which are significantly different have different symbols (a, b, c, d) (p 0.05).
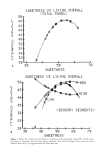
206 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table III Effect of Surfactant Charge and pH on Collagen Swelling Collagen Swelling (ml/g) Surfactant Type pH: 5 7 9 SLS Anionic 9.6 q- 0.5 ll.0 q- 0.3 11.7 q- 0.1 Tween 20 Nonionic N.D. 2.6 q- 0.1 N.D. CAPB Amphoteric 2.4 q- 0.1 2.4 q- 0.1 2.5 q- 0.1 DTAB Cationic 2.9 q- 0.1 2.8 q- 0.0 2.8 ___ 0.1 Water 2.6 q- 0.1 2.5 q- 0.0 2.2 q- 0.1 Test conditions: 2 replicates, concentration 10 mM, time 24 hours. N.D. = not determined. only, while both the uncharged and positively charged surfactants produced only slightly more swelling than water. EFFECT OF pH ON COLLAGEN SWELLING The swelling produced by anionic (SLS) and cationic surfactants (DTAB) in acidic, neutral, and alkaline pH solutions was also studied (Table III). Only the anionic surfac- tant responded to changes in pH. When the treatment solutions were pH 4 and lower, the collagen film began to swell until it formed a gel at about pH 2, and at lower pH the gel converts to a sol. The swelling induced by SLS was increased by raising the pH. Similar results were reported for skin and epidermal membranes (4,5). INFLUENCE OF AMPHOTERIC SURFACTANTS ON SLS-INDUCED COLLAGEN SWELLING Surface active betaines have been shown to inhibit the deleterious effects of anionic surfactants such as SLS (13-15), e.g. betaines and anionic surfactants result in shampoos which are mild in their effects on skin and eyes (16). Rhein eta/. (10) demon- strated that the extent of swelling in isolated human stratum corneum induced by SLS can be reduced by the addition of cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB) and lauryl dimethyl amine oxide. We investigated the interaction between CAPB and SLS by treating collagen film with solutions containing 2 to 10 mM amounts of either SLS, CAPB, or varying molar ratios of SLS:CAPB (total surfactant concentration was 10 mM). All treatments were at neu- tral pH. The results (Figure 5) show that the addition of CAPB to SLS produced sub- stantially lower swelling than SLS alone. Strong interactions were seen even at low betaine levels, e.g. the addition of 2 mM CAPB to 8 mM SLS produced a 20 percent reduction in swelling compared to 8 mM SLS alone. These results lend support to the hypothesis that surface active betaines interact beneficially with anionic surfactant in regard to irritation potential. DISCUSSION The process of swelling of collagen, and possibly skin and skin-like substrates, must begin with the adsorption of surfactants at the solution-substrate interface. Anionic surfactants, near neutral pH, adsorb primarily through hydrophobic interactions of the surfactant alkyl chains with the hydrophobic regions of the protein, and to a lesser degree through ionic interaction of the surfactant head group with charged sites on the
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)