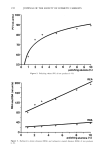
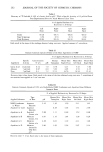
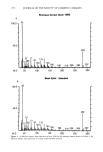
SANGUINARINE ANALYSIS BY HPLC 283 Table II Stability of Sanguinarine in Oral Rinse (ambient temperatures) Containing 300 •g/ml Sanguinaria Extract Equivalent to Theoretical Input Levels of 90 t-tg/ml Sanguinarine Time Elapsed (months) Sanguinarine (t.tg/ml) 0 88.2 7 89.1 10 92.7 13 86.6 16 87.1 19 85.6 22 85.3 25 87.3 28 79.8 31 86.2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Standard solutions containing pure sanguinarine provide a clean chromatogram devoid of other benzophenanthridine alkaloids (Figure 2). Sanguinarine analysis of the dried rhizomes enable a detailed study (9) of the best growing conditions for the Sanguinaria canadensis plant. Plants were collected from over 100 sites along a 1,000-mile transect essentially along the Appalachians from northern Georgia to Vermont. The rhizomes were weighed, dried, and the water content determined. Samples were ground and analyzed according to the method described. Plants were catalogued for soil type, pH, climate, drainage, litter depth, and other parameters. The sanguinarine content was found to range from 0.63% (of the dried rhizome weight) to 6.31%. The mean san- guinarine content was found to be 2.74% + 1.18% over 100 sites. Positive correla- tions were found between sanguinarine content and slope, litter depth, soil clay con- tent, soil structure, rhizome weight, and also the time of year the plant was collected. SaCI I I I I Figure 2. Chromatogram for pure sanguinarine chloride.
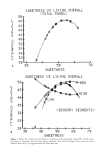
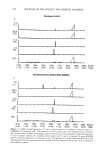
284 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS FLAVOR B D i I I 1 Figure 3. Typical chromatogram for sanguinaria extract isolated from oral rinse and toothpaste. Detailed studies on sanguinarine content as a function of geographic distribution and growing conditions will be the subject of a separate publication. Analysis of sanguinaria extract resulting from the chemical extraction process provided a quality control check for the extract produced. The sanguinarine content was typically around 50% of the total alkaloid content (Figure 1). A typical chromatogram for san- guinaria extract is identical to that found when it was extracted from toothpaste and oral rinse (Figure 3) except that the flavor peaks were not present. The retention times and relative peak areas for sanguinarine (B) and the five other benzophenanthridine Table III Toothpaste and Oral Rinse Formulas Analyzed by HPLC Method Toothpaste Oral Rinse Glycerin, 95% U.S.P. Sorbitol, 70% U.S.P. Carrageenan, F.C.C. Deionized Water Zinc Chloride, U.S.P. Dicalcium Phosphate, Dihydrate Hydrated Silica Sodium Saccharin Citric Acid, U.S.P. Sanguinaria Extract Titanium Dioxide, U.S.P. Sodium Lauryl Sulfare Flavor Deionized Water Zinc Chloride, U.S.P. Glycerin, 96% U.S.P. Sodium Saccharin, U.S.P. SDA 38B Alcohol Poloxamer 407 Polysorbate 80, N.F. Flavor Citric Acid, U.S.P. Sanguinaria Extract pH 5.0 pH 3.2
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)