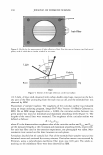
266 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE RADIATION STABILITY STUDY To evaluate the stability of vitamin A, the emulsions were irradiated under UVA and UVB lamps. RETI C emulsion irradiated under UV A showed high stability during the first hour, followed by a clear decrease in vitamin A concentration. Both after 30 and 60 minutes of irradiation in the same conditions, the percentage of retinal in the cream appeared unchanged. However, after 90 minutes, the retinal concentration began slightly to decrease (5.2% of degradation). Extending the period of irradiation, the photodegradation proceeded more quickly, and the retinal degraded percentage was 27.5% after 120 minutes, 45.7% after 150 minutes, and 53.2% after 180 minutes. Figures 1 and 2 show the percentage of retinal degradation versus time under UVA and UVB irradiation for RETI C and RETI C concentrate emulsions, respectively. The photodegradation of retinal in RETI C emulsion was more progressive under UVB radiation. In fact, the percentage of degradation had already begun to increase before 30 minutes of irradiation (7 .1 % of retinal degraded percentage), and it continued to in- 60 y = 0,4897x- 32,44 R2 = 0,9641 UVA "C 50 cu "C 40 ... • •• en cu "C 30 0 y = 0,207x + 1,7536 • C: R2 = 0,9777 UVB +i 20 •UVA f . ■ .. . � 10 ■UVB 0 ••• 0 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 time (min) Figure 1. Percentage of retinal degradation in RETI C emulsion under UV A and UVB irradiation. 60 "C 50 cu "C 40 en cu 30 0 20 cu � 0 10 ....• - 0 0 30 ■ 60 y = 0, 1523x + 14,327 R2 = 0,9458 UVA . . - ... - . . • 90 time (min) y = 0, 1677x + 0,8893 R 2 = 0,9585 UVB 120 150 180 •UVA ■UVB Figure 2. Percentage of retinal degradation in RETI C concentrate emulsion under UVA and UVB irradiation.
ANTI-AGING EFFECTIVENESS OF RETINOL EMULSIONS 267 crease over time: 15.2% after 60 minutes, 23.8% after 90 minutes, 26.3% after 120 minutes, 33.9% after 150 minutes and 36.4% after 180 minutes, respectively. At the beginning, the vitamin A was more stable under UV A than under UVB irradiation, but the photodegradation, as begun, appeared more drastic. In contrast, degradation was at once faster under UVB irradiation, but in this case, after three hours, the remaining concentration of retinal appeared higher. The presence of antioxidants can reduce the degradation of retinal contained in the emulsions: BHT, tocopherol, and EDTA are present at the same time in RETI C emulsion, while in RETI C concentrate emulsion, BHT is absent. Moreover, RETI C concentrate emulsion is characterized by the presence of PEG-40 stearate, PEG-10, and apricot kernel oil, three ingredients that could go towards the peroxidation processes. These differences could explain the different behavior of these two emulsions, especially under UV A irradiation. In fact, the curve of photodegradation of retinal, under UV A exposure, shows a lag time of 60 minutes in RETI C emulsion (see Figure 1), while in RETI C concentrate emulsion, retinal photodegradation starts after the first minutes of UV A exposure (see Figure 2). On the other hand, previously, in an article published by our research group (10), the presence of BHT was demonstrated to protect vitamin A from degradation induced by light and heat. The different behavior of the two formulations could also be explained by the presence in RETI C emulsion of butyl methoxy dibenzoylmethane, a sunscreen that can improve the photostability of retinal against UV A irradiation, as we have already demonstrated (10). After irradiation under UVA, RETI C concentrate emulsion showed a clear behavior. The percentage of retinal degraded was 18.0% after 30 minutes, 22.1 % after 60 min utes, 29.1% after 90 minutes, 35.3% after 120 minutes, 38.5% after 150 minutes, and 38.9% after 180 minutes. RETI C concentrate emulsion appeared more stable under UVB irradiation. The de graded retinal percentage was 4.6% after 30 minutes, 13.9% after 60 minutes, 17 .6% after 90 minutes, 20.5% after 120 minutes, 22.4% after 150 minutes, and 32.9% after 180 minutes. ST ABILITY OVER TIME AT 40 ° C Both emulsions were submitted to an accelerated aging test to check their physico chemical and organoleptic features over time. The stability of vitamin A in RETI C and RETI C concentrate emulsions after storage in an incubator at 40°C was studied. RETI C emulsion did not show any change of appearance either after one day or three days of storage at 40°C, but after one week it appeared dark yellow in color. Finally, after ten days, the emulsion was dark brown. RETI C concentrate emulsion changed from the original color after one day. After three days, the emulsion was dark yellow. After seven days, it was light brown, and at the end of the experiment (ten days) it was separated into three yellow layers. The percentage of retinal decrease was determined by HPLC analysis. The results are reported in Figure 3. Figure 4 shows the weight percentage of the creams remaining after
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)