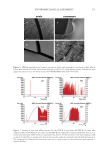
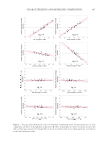
289 METHOD FOR SIMULTANEOUS QUANTITATION OF RESORCINOL system precision was verified by six replicate injections of standard solution. The method precision of the analytes was carried out six times using the proposed method. Repeatability was measured by multiple injections of homogenous samples prepared. Accuracy was carried out by percentage recovery studies at three different concentration levels. To the preanalyzed samples solution, a known amount of resorcinol, p-phenylenediamine, and m-aminophenol were added at 50%, 100%, and 150% levels. The robustness of the method was studied in the sample for flow rate, mobile phase ratio, wavelength, and pH. Ruggedness of the method was performed by two different analysts using the same experimental and environmental conditions as the sample concentration of 50 µg mL−1. The system suitability parameters, such as number of theoretical plates and tailing factor and resolution, were studied. The specificity of the method was demonstrated through forced degradation studies conducted on the sample using acidic, alkaline, oxidative, reductive, thermal, photolytic, humidity, heat, and hydrolytic conditions (30). The sample was exposed to these conditions, and the main peak was studied for the peak purity and percentage degradation. Absence of interfering peaks from blank and placebo with sample and standard peaks demonstrated specificity of the method. Stability of sample solutions was established by analyzing the concentrations of the samples that were stored at 25oC for 24 hours. Samples were reanalyzed after 24 hours and assay was determined. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The structures of the components in hair dyes are presented in Figure 1. RSM-generated 3D surface plots for the optimized chromatographic conditions are provided in Figure 2. The normal plot of residuals indicates whether the residuals follow a normal probability distribution or not. The 3D surface plots show the attainment of retention times for the simultaneous determination of resorcinol, m-aminophenol, and p-phenylenediamine under the optimized chromatographic conditions. The analysis of variance table for response surface combined cubic × mean model of resorcinol, m-aminophenol, and p-phenylenediamine has been provided in Table I. Considering RSM studies, it was found that the process order fits to combined cubic × mean model. From the solutions obtained using the desirability function it was found that a mobile phase composition ratio of 5:5:90 (ACN: methanol: hexane-1-sulfonic acid) with a flow rate of 1.5 mL min−1 and a run time of 15 minutes gave optimum retention times for simultaneous estimations of resorcinol, m-aminophenol, and p-phenylenediamine. To achieve shorter analysis time, the retention time was indicated as the response variable. We have also considered peak resolution, and the results obtained were within acceptance criteria of 1.5 of all the analytes. The design expert generated the desirability function data, and practical experimentations satisfy these chromatographic conditions. In addition to RSM-based desirability function, to find the optimum separation conditions for a model mixture of resorcinol, p-phenylenediamine, and m-aminophenol on a Luna C 8 column, the influence of separation parameters such as flow rate, ACN, methanol, and an ion-pairing reagent concentration on the retention of analytes were also studied. The proposed chromatographic system was found suitable for effective separation of resorcinol, p-phenylenediamine, and m-aminophenol with t R 7.232–7.273, 9.976–10.114, and 11.639–11.735 minutes, respectively, with sharp peak shapes and minimal tailing. The
290 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE chromatograms of standard and commercial products (GR and GG) are shown in Figure 3. The results of validation parameters are summarized in Table II. All the analytes gave a linear detector response in the concentration range of 10–150 µg mL−1 while regression equations obtained were y =8736x−27796, y =7045x, and y =555.9x +584.9, and r2 values of 0.9993, 0.999, and 0.9997, respectively for resorcinol, p-phenylenediamine, and m-aminophenol (Figure 4). The percentage recovery found for resorcinol, p-phenylenediamine, and m-aminophenol were 100.27 ± 2.19%, 99.60 ± 1.82%, and 99.73 ± 1.51%, respectively. The results of forced degradation studies, various parameters studied, and assays of commercial dye samples have been provided in Tables III–V. Yeh et al. reported an interlaboratory study on simultaneous determination of aminophenols and phenylenediamines in two commercial hair dyes (31). Figure 2. Normal plots of residuals and 3D surface graphs for resorcinol (a1 and a2), p-phenylenediamine (b1 and b2), and m-aminophenol (c1 and c2). Table I Analysis of Variance Table of Response Surface Combined Cubic Mean Model for Resorcinol, p-phenylenediamine, and m-aminophenol Items Sum of squares df Mean square F value p value Commenta Resorcinol 3,110.05 27 115.19 5.97 0.0001 a p-phenylenediamine 2,541.96 39 65.08 5.83 0.0026 b m-aminophenol 2,004.64 27 74.25 2.52 0.0152 c df: Degrees of freedom. a The model’s F values imply that the model is significant. There are only (a) 0.01%, (b) 0.02%, and (c) 1.52% chance that model F values this large could occur due to noise. Values of “prob F” less than 0.0500 indicate model terms are significant.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)