329 J. Cosmet. Sci., 73, 329–344 (September/October 2022) Address all correspondence to Akil Ahmad, siti-h@utm.my aj.ahmad@psau.edu.sa Insights into the Application of Reverse Micelles in Cosmetic Formulations: A Review JOHN PETER VELLU, HASMIDA MOHD NASIR, SITI HAMIDAH MOHD SETAPAR, AKIL AHMAD, SING CHUONG CHUO AND MOHAMMED B. ALSHAMMARI Department of Chemical Process Engineering, Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia (J.P.V., S.H.M.S., S.C.C.) Centre of Lipid Engineering and Applied Research, Ibnu Sina Institute for Scientific and Industrial Research, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor, Malaysia (H.M.N., S.H.M.S., S.C.C.) SHE Empire Sdn. Bhd., Johor, Malaysia (H.M.N., S.H.M.S.) Department of Chemistry, College of Science and Humanities in Al-Kharj, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University, Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia (A.A., M.B.A.) Accepted for publication December 19, 2022. Synopsis Reverse micelles are aggregates of amphiphilic molecules in nonpolar solvents. They have polar cores surrounded by surfactant head groups that can solubilize various hydrophilic compounds such as dyes, proteins, and antibiotics. They are frequently studied for extraction of organic and inorganic compounds. Advantages of reverse micelles are ease of production, high encapsulation efficiency, and protection of encapsulated compounds. The cosmetic market has been continuously growing over the years as more innovative cosmetics products are released into the market. Reverse micelles can be used as nano-sized carriers to encapsulate various hydrophilic active ingredients in cosmetic formulations. They can be prepared using safe, biocompatible, nontoxic, and biodegradable materials, thus are suitable to be incorporated into cosmetic products. The viscoelastic property and the skin permeation property can be adjusted. Targeted delivery and sustained release of active ingredients can be achieved through proper formulation. In addition to being directly included in formulations, reverse micelle systems are also used for the preparation of active ingredients and the analysis of cosmetic products for quality control. Therefore, reverse micelles show great potential for application in the cosmetic sector. This paper reviews related works in past two decades and provides some insights for future studies to broaden the implementation of reverse micelle systems in cosmetic products. INTRODUCTION Beyond the beauty of the face or attractiveness of the skin is the health of the skin itself. Human beings tend to spend a lot of money on beauty products to improve their individual appearance. In recent decades, skin care has gained increasing attention of people of all ages. This leads to the rise of the cosmetic market around the world. The cosmetic market in Asian countries is one of the fastest growing markets (1). The sum value of global
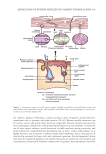
330 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE cosmetics and toiletry products sold in the year 2004 was $230 billion and continues to grow (2). Several online market researches anticipate the global cosmetic market to exceed $400 billion by the year 2027. In 2013, $407 million was spent on cosmetic and toiletry products imported into Malaysia, indicating that the demand for these products is mainly met by imports (3). This reflects both the undersupply and low consumer awareness of local cosmetic products. A study revealed that Malaysians are not aware of the cosmetic products made in Malaysia (4). Various active ingredients are included in cosmetic formulations for different functions, such as antioxidant activity, antimicrobial activity, antiaging properties, and UV filtering. However, not all active compounds are readily soluble in the solvents used in cosmetic formulations. Many techniques have been used to enhance solubilization of active ingredients in cosmetic formulations. These techniques include liposome, micelle, reverse micelle, solid lipid nanoparticle, noisome, nanocapsule, and others. Chemical stabilities, biocompatibility, and skin permeability of active ingredients can be increased with advance encapsulation technologies available for topical cosmetic application (5). The encapsulation technologies used in cosmetic formulations must also be non-irritating to the skin and nontoxic. Currently, in order to adhere to stricter regulations and consider an increasing public awareness of the environment, these techniques should also be sustainable and environmentally friendly. Amphiphilic molecules or surfactants can self-assemble into micelles (oil-in-water microemulsions) or reverse micelles (water-in-oil microemulsions) at appropriate compositions. They have unique structures that can be used to solubilize hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds. Aqueous solubility of hydrophobic compounds is greatly enhanced by encapsulation inside micelles, while oil solubility of hydrophilic compounds is greatly enhanced through encapsulation in reverse micelles. This characteristic is very useful for blending various active compounds in cosmetic formulations. Micelles are commonly used in cosmetic formulations due to many advantages, including ease of production, high encapsulation efficiency, protection of active ingredients, adjustable rheological properties, good skin-permeation properties, targeted delivery of active ingredients, and sustained release of active ingredients. However, there are fewer reports on the incorporation of reverse micelle in cosmetic products. This paper reviews the application of reverse micelles in cosmetics reported in the past two decades. The fundamentals of reverse micelle formation and the reports of reverse micelle for cosmetic applications are discussed in following sections. The authors’ intention is to gather as much knowledge as possible and provide insights on the topic. Reverse micelles have the advantages of normal micelles. However, due to the formulations of cosmetic products currently available, direct utilization of reverse micelles in the formulations is rare compared to normal micelles. Instead, most reports utilized reverse micelles for the extraction and purification of active compounds such as proteins and plant extracts for cosmetic formulations. More research on the use of reverse micelles for cosmetic applications is needed. ABBREVIATIONS: AOT Sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate CMC Critical micelle concentration CTAB Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)