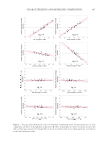
322 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE ANOVA for Quadratic model. The entrapment efficiency was in a range from 52.74% to 98.07%. The influence of the examined variables on 1.0/square root. Actual factors were described by a reduced square model. One-way ANOVA (p =0.05) indicated that the formulation parameters A-PLGA, B-span 80, C-PVA, AB, AC, BC, A2, B2, and C2 have a statistically significant effect on entrapment efficiency. Table V and Figure 4 represent the influence of studied variables on 1.0/Sqrt (35). In Table V, factor coding is coded. Sum of squares is type III–partial. The model F value of 4.40 implies the model is significant. There is only a 3.74% chance that an F value this large could occur due to noise. The p values 0.0500 indicate model terms are significant. In this case there are significant model terms. Values greater than 0.1000 indicate the Table III Experimental Design Points for the Studied Variables Values Factor 1 Factor 2 Factor 3 Response 1 Response 2 Std Run A:PLGA B:span 80 C:PVA In vitro drug release EE g ml g %%11 1 0 −1 0 50.42 98.07 12 2 0 1 0 54.63 94.67 7 3 −1 1 1 58.79 89.46 8 4 1 1 1 62.48 87.04 14 5 0 0 1 66.89 82.52 2 6 1 −1 −1 70.77 79.87 3 7 −1 1 −1 73.89 75.38 9 8 −1 0 0 76.07 72.49 6 9 1 −1 1 80.99 68.39 4 10 1 1 −1 83.58 64.97 10 11 1 0 0 87.99 60.57 13 12 0 0 −1 91.83 58.77 1 13 −1 −1 −1 94.77 55.99 5 14 −1 −1 1 98.74 52.74 EE: Entrapment efficiency PLGA: poly lactic-co-glycolic acid PVA: polyvinyl alcohol Std: standard. Table IV Response 1: In Vitro Drug Release Source Sum of squares df Mean square F value p value Model 2,552.12 9 283.57 4.32 0.0216 A-PLGA 27.06 1 27.06 4.22 0.0462 B-span 80 388.38 1 388.38 3.97 0.0149 C-PVA 220.43 1 220.43 4.81 0.0250 AB 379.91 1 379.91 4.11 0.0152 AC 0.0078 1 0.0078 4.01 0.0494 BC 317.39 1 317.39 2.60 0.0182 A2 487.51 1 487.51 3.95 0.0116 B2 586.20 1 586.20 4.80 0.0935 C2 320.08 1 320.08 4.62 0.0180 Residual 488.24 4 122.06 Cor Total 3,040.35 13 AB: PLGA &SPAN 80 AC: PLGA &PVA BC: SPAN 80 &PVA df: degrees of freedom PLGA: poly lactic-co-glycolic acid PVA: polyvinyl alcohol.
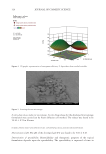
323 Microsponge Loaded Topical Gel model terms are not significant. If there are many insignificant model terms (not counting those required to support hierarchy), model reduction may improve your model. Scanning electron microscopy. Scanning electron microscopy of microsponge is shown in Figure 5. The shape of the microsponge was found to be spherical, and the size of the microsponge was in the micrometer range. Moreover, the micrograph also revealed the same agglomeration of microsponges, which might be due to the evaporation of water present in the formulation during sample preparation prior to SEM analysis (22). Figure 3. 3D graphic representation of in vitro drug release %dependence from studied variables. Table V Response 2: Entrapment Efficiency Source Sum of squares df Mean square F value p value Model 2,385.39 9 265.04 4.40 0.0206 A-PLGA 21.84 1 21.84 4.19 0.0794 B-span 80 318.77 1 318.77 4.89 0.0164 C-PVA 204.03 1 204.03 4.85 0.0245 AB 342.70 1 342.70 3.97 0.0152 AC 0.0072 1 0.0072 4.01 0.0497 BC 323.60 1 323.60 4.93 0.0162 A2 508.83 1 508.83 4.61 0.0983 B2 588.53 1 588.53 5.33 0.0821 C2 259.25 1 259.25 4.35 0.0200 Residual 441.46 4 110.36 Cor Total 2,826.84 13 AB: PLGA &SPAN 80 AC: PLGA &PVA BC: SPAN 80 &PVA df: degrees of freedom PLGA: poly lactic-co-glycolic acid PVA: polyvinyl alcohol.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)