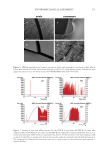
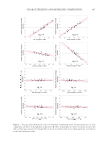
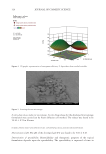
311 Characterizing and Modeling Complexion spots, and shine in determining people’s preferences for ideal complexion, and investigated their combined effects via a multivariate regression model, which provides a key tool for us to quantitatively describe ideal complexion. By analyzing facial images from a large female Chinese population (N =480), we show that this newly defined skin parameter of ideal complexion is normally distributed in the studied population with the vast majority exhibiting ICS values between 10% and 90% quantile (3.93–7.40) while the rest tailed off in the high and low ends (90% and 10% quantiles). The visual differences in high and low levels of ICS shown in Figure 10 agreed well with the general perception of Asians toward ideal complexion that is, skins with fair and even skin tone, fine texture, and free of pigmentary blemishes are preferred. This study helped provide data for adequate understanding of how ideal complexion is perceived by Chinese women as well as for objective quantification of the consumer-perceivable skin properties. The results of treatment efficacy evaluation provided data to demonstrate that a product claim of obtaining ideal complexion could be substantiated and the consumer preference likelihood could be quantitatively estimated based on the changes of the objectively measured skin properties. Regarding modeling complex skin properties, one general question that often arises is whether the multivariable model has added benefit in predicting a phenomenon when compared to each of the individual parameters. The added benefit was evident in this study. As shown in Figure 12, individually, the highest correlation coefficient was 0.5318, which was much less than that of the model, 0.9866, as shown in Figure 6. One thing worth noticing, however, is the behavior of dINT. While it correlated poorly with Bradley–Terry P individually (r =0.1268), significant contribution to Bradley–Terry P was shown in the multivariable model, owing to its interactions with other parameters to minimize residuals (Figure 7B). SVS showed a similar behavior but in an opposite direction—individually it correlated well with Bradley–Terry P (r =0.5008), but its contribution was not statistically significant in multiple regression analysis (Figure 7E). CONCLUSIONS From this study we concluded that skin complexion, a subjective and consumer-perceivable property of skin, could be characterized, quantified, and predicted with a linear model by using objectively measured basic visual attributes of facial skin. Use of paired comparison coupled with logit function, image analysis of basic skin parameters, and the Bradley–Terry Figure 12. Multivariate analysis showing correlations of individual skin attributes with the panel preference rank (Bradley–Terry P). Table on top: correlation coefficient of Bradley–Terry P and DRR, SVS, ITA°, etc. Charts on bottom: scatterplots with density ellipses and regression line showing each correlation.
312 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Model proved to be an effective way to study consumer-perceivable skin properties. The methods, models, and results reported in this study provide a way to link results of panel evaluation and objective measurement to enrich the derived ideal complexion score with consumer relevance. NOTE: Part of this study was presented at the 26th IFSCC Conference, October 18–27, 2021 (paper ID: SS_626). REFERENCES (1) L. Ang, B. J. Lee, H. Kim, and M. H. Yim, Prediction of hypertension based on facial complexion, Diagnostics, 11, 540 (2021). (2) Y. Umeda-Kameyama, M. Kameyama, T. Tanaka, B. Son, T. Kojima, M. Fukasawa, T. Iizuka, S. Ogawa, K. Iijima, and M. Akishita, Screening of Alzheimer’s disease by facial complexion using artificial intelligence, Aging, 13, 1765–1772 (2021). (3) C. Zhao, G. Li, F. Li, Z. Wang, and C. Liu, Qualitative and quantitative analysis for facial complexion in traditional Chinese medicine, BioMed Res. Int., 2014, 207589 (2014). (4) Q. Huixia, L. Xiaohui, Y. Chengda, Z. Yanlu, J. Senee, A. Laurent, R. Bazin, F. Flament, A. Adam, and B. Piot, Instrumental and clinical studies of the facial skin tone and pigmentation of Shanghaiese women. Changes induced by age and a cosmetic whitening product, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 34, 49–54 (2012). (5) A. Little, B. Jones, and L. DeBruine, Facial attractiveness: evolutionary based research. Philos. Trans. R Soc. B Biol. Sci., 366, 1638–1659 (2011). (6) B. Ghani, R. Jouhar, and N. Ahmed, Relationship of facial skin complexion with gingiva and tooth shade on smile attractiveness, J. Interdiscipl. Med. Dent. Sci., 4, 5 (2016). (7) A. S. Krishen, M. S. LaTour, and E. J. Alishah, Asian females in an advertising context: exploring skin tone tension, J. Curr. Issues Res. Advert., 35, 71–85 (2014). (8) Q. Xie and M. Zhang, White or tan? A cross-cultural analysis of skin beauty advertisements between China and the United States, Asian J. Commun., 23, 538–554 (2013). (9) A. Coondoo and R. Sarkar, The unhealthy obsession with fairness and the menace of fairness creams in India, Pigment Int., 8, 4–7 (2020). (10) C. A. D. Charles, Skin bleaching and the prestige complexion of sexual attraction, Sex. Cult., 15, 375–390 (2011). (11) Y. Kobayashi, S. Matsushita, and K. Morikawa, Effects of lip color on perceived lightness of human facial skin, i-Perception, 2017, July–August, 1–10 (2017). (12) A. Saeed, S. Maqsood, and A. Rafique, Color matters: field experiment to explore the impact of facial complexion in Pakistani labor market, Journal of the Asia Pacific Economy, 24, 347–363 (2019). (13) S. Ismail, S. Loya, and J. Hussain, Obsession for fair skin color in Pakistan, International Journal of Innovation and Research in Educational Sciences, 2, 2349–5219 (2015). (14) E. Li, H. Min, R. Belk, J. Kimura, and S. Bahl, Skin lightening and beauty in four Asian cultures, Adv. Consum. Res., 35, 444–449 (2008). (15) A. Saeed, S. Maqsood, and A. Rafique, The effects of sleep deprivation on the biophysical properties of facial skin, J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl., 7, 34–47 (2017). (16) S. I. Jang, M. Lee, J. Han, J. Kim, A. R. Kim, J. S. An, J. O. Park, B. J. Kim, and E. Kim, A study of skin characteristics with long-term sleep restriction in Korean women in their 40s, Skin Res. Technol., 26, 193–199 (2020). (17) L. M. Lu, X. Chen, and J. T. Xu, Determination methods for inspection of the complexion in traditional Chinese medicine: a review, Chin. J. Integr. Med., 7, 701–705 (2009). (18) T. Wu, B. Bai, F. Sun, C. Zhou, and P. Wang, Study on complexion recognition in TCM, 2010 International Conference on Computer and Communication Technologies in Agriculture Engineering, IEEE Xplore (2010).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)