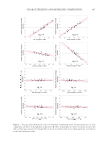
304 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE in greater values of Logit(A), and vice versa. The distribution of Logit(A) in this study population also appeared to be normal with a Shapiro–Wilk p value of 0.7129. Using Fit Model function in JMP, a statistically significant correlation was established between panel responses (Logit(A)) and the combined effects of objectively measured skin parameters (ΔPs). Equation 2 shows the expression of the generalized linear model, and the properties of the parameters in Equation 2 are listed in Table IV. Equation Logit(A C predicted i i i=1 2. 0 4 )=+∑C ∆P It was noticed that, of the eight parameters tested, only four showed strong correlation to the panel-preferred complexion (with statistical significance at 95% CL). While intuitively one might expect some other parameters to be important to complexion as well, the results of multiple regression did not suggest that, owing to the large residuals those parameters had produced. A correlation plot between Logit(A) and the model-predicted Logit(A) is shown in Figure 4. The correlation was statistically significant with a correlation coefficient of 0.841 (p 0.0001). Figure 4 shows that, between two images in each of the 54 pairs, the Table IV Description of Parameters in Equation 2 Index, i Ci ΔPi 0 0.5947 – 1 0.2416 ΔITA° 2 0.5624 ΔdINT 3 −0.6634 ΔdaStar 4 −3.4024 ΔdbStar Figure 4. Correlation plot between actual and predicted Logit(A). Actual: Logit(A) values obtained from panel responses. Predicted: Logit(A) values calculated from the basic skin parameters of image pairs using Equation 2.
305 Characterizing and Modeling Complexion panel-perceived differences in ideal complexion were positively correlated with the differences of the objectively measured skin parameters through a linear relationship. PANEL PREFERENCE RANKING BY BRADLEY–TERRY MODEL The correlation in Figure 4 was imperative for preference-ranking analysis when using the Bradley–Terry model to eventually determine relative ICSs among 36 subjects. By constructing a Bradley–Terry matrix for panel-preference scores, we incorporated the original Logit(A) results that were directly from the panel responses and filled in those required Logit(A) results through simulation of some virtually formed intra- and inter- group image pairs using Equation 2. Applying logistic function to all Logit(A) results and feeding the data to the Bradley–Terry model, a Bradley–Terry probability ranking order (Bradley–Terry P) in terms of panel preferences for ideal complexion was obtained for the 36 study subjects. A Shapiro–Wilk test on the logarithmically transformed Bradley–Terry p values showed that this quantity was also normally distributed, as shown in Figure 5. MODEL FOR PANEL PREFERENCE PREDICTION WITH BASIC SKIN ATTRIBUTES With the above established panel-preference rank toward ideal complexion, multiple regression analysis was performed once again to correlate the preference rank to the combined effects of basic skin attributes shown in Table III (excluding L*, a*, and b*) for the 36 subjects. A generalized linear model was established as the result. A correlation plot between the actual and the model-predicted Bradley–Terry ranks is shown in Figure 6, which displays a positive and strong correlation with a correlation coefficient of 0.9866 (p 0.0001). Leverage plots indicating individual effect of skin attributes on panel preference to ideal complexion are shown in Figure 7. A steep and upward slope indicates a strong and positive effect of a skin attribute on ideal complexion, while a flatter and downward slope indicates a mild and negative effect. Specifically, the charts in Figure 7 show that ITA° and dINT affected the panel preference positively, with a fair and shiny skin tone (higher ITA° and dINT) associated with a skin Figure 5. Distribution of log (Bradley–Terry P) values of the 36 study subjects.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)