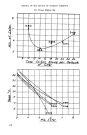
INFLUENCE OF ALIPHATIC type can generally be recommended for oils and fats of non-polar struc- ture and extreme insolubility in water, e.g. straight chain saturated petroleum oils. Animal and vege- table oils are more hydrophilic than these castor oil and coal tar hydro- carbons more so and fatty acids and simple esters such as methyl methacrylate monomer considerably more so. The best emulsifying prin- ciples among the polyglycol fatty esters generally follow in the same direction of increasing water solu- bility. As regards the fatty constituent, emulsifying quality is not greatly affected by substituting one fatty acid for another of approximately the same molecular weight and chain length but the physical qualities may be greatly altered. The oleates, •lino.'leates, ricino•eates and other unsaturated esters are usually brownish fluids coconut and palm kernel fatty esters, containing small proportions of unsaturated ingredi- ents, give yellowish oils with lower polyglycols and tan coloured soft fats with higher polyglycols purified laurates and myristates are paler, and esters irom the best grades of stearic acid and polyglycols are practically white. For this and various other reasons the stearates are generally the most popular for cosmetic formulations. The stearates, to a higher degree than the others, form viscous muci- lages with water. These are applied in hairdressing lotions and to sus- pend toilet powders or medicaments. especially when they are chemically CHF.•ISTRY DEVELOPMENTS active and disposed to react with electrolytes, as in the case of cala- mine or magnesia. The lower polyglycol esters, con- sisting, like the fatty alcohols, of a fatty chain compound with one hydroxyl group and a limited affin- ity for water, confer considerable emolliency and penetration. They are also easily removed and non- irritant, and so are popular ingredi- ents of cake make-up. They can be incorporated into almost any type of cream, either as the principal emulsifying agent, or as emollients. They are probably best in the heavier types of cream as used for cleansing or for winter use. They can incorporate weak acids or inorganic salts as used for astringents, depilatories, or in re- straint of perspiration. Most of these esters have the pro- perty, often characteristic of poly- alkylene derivatives, of being less soluble hot than cold, and so emul- sions should be made at as low a temperature as possible. For this reason they are not well suited for emulsifying waxes of high melting point. This peculiarity becomes less marked as the ester becomes more mater solluble, for instance, the monolaurates of polyglycols 400, 600 and 1000. In these cases wet- ting and detergent qualities become pr. onounced, and being free from injurious effect and compatible with most w a v i n g and bleaching materials they are effective wetting agents for the hairdresser. If added in subsidiary proportions to liquid soap shampoos, they sup- 139
JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS •lement detergency and exercise re- kaint of lime scumming in hard water rinsing at temperatures up to about 60øC., presumably by pepris- ing the calcium soap. Various mem- bers of the polyoxyethylene ether class have secured wide acceptance as soapless textile and industrial de- tergents. At this jz•ncture the lecturer passed around several samples [or examination, including' the liquid shampoos previously mentioned. He adde•d: I have here a few specimens for any who care to inspect them. They are not intended to rank as fine quality cosmetics but merely to illu- strate points that I have tried to in- dicate. Parrs are by weight. (1) Cleansing Cream Liquid paraffin ......... 50 Landin absorption base ... 5 Polyethylene glycol 300 mono- stearate ......... 5 Water ............ 40 This could be made a little thicker by putting some of the polyglycol ester with the water portion, or by adding a very little triethanolamine. (2) Cleansing Cream Polyethylene glycol 400 mono- stearate ......... Lanolin ........ Beeswax ........ Liquid paraffin ........ Water ........... Triethanolamine ..... "Carbitol", etc ...... Here there are more saponifiable fats present and so a slightly more hydrophilic polyglycol ester is used. (3) Vanishing Cream Stearic acid ......... 20 "Carbowax" 1000 mono- stearate ......... 5 Water ............ 70 Polyethylene glycol 300 roche- stearate ......... 5 Here a strongly hydrophilic ester is used to emulsify the stearic acid. The addition of the polyethylene glycol 300 stearate to the aqueous portion increases emolliency and consistency. (4) Astringent Cream, similar to (3) but containing c. 3 per cent A12(SO4).•. (5) Acid Cream, for protection against fumes from organic bases. (6) Polyethylene Glycol Stearate Mucilaginous Hair Cream Polyethylene glycol 400 mono- stearate ......... 6 Lanolin ......... 1 Water ......... 90 Polyethylene glycol+ perfume 3 Polyethylene glycol 400 laurate ......... q. ß 5 The last named constituent is pre- sent as a dispersant for the perfume oil. (7) 11 Oily Hair Cream 6 Polyethylene glycol 400 mono- 10 stearate ......... 15 Lanolin ......... 2 52 Liquid paraffin ...... 20 1 Polyethylene glycol 400 roeno- S stearate ......... Citric acid ......... 1 Water ............ 70 Polyethylene Glycol Stearate 140
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)